Abstract
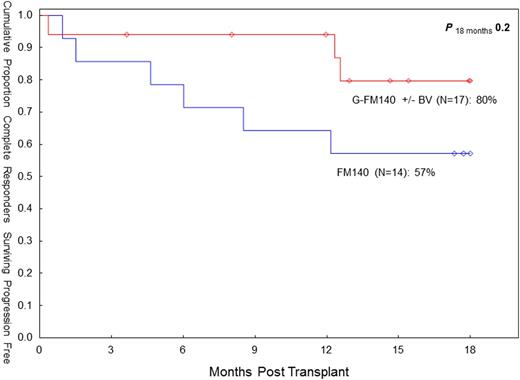
Progressive disease (PD) remains the main cause of treatment failure following RIC allo-SCT in HL. In 08/2007 we elected to add gemcitabine (G), a highly active agent in relapsed/refractory HL, to our standard fludarabine (F) - melphalan (M) RIC (Anderlini et al, Haematol 93:257, 2008) in patients with relapsed/refractory HL undergoing allo-SCT. Subsequently, brentuximab vedotin (BV) was introduced as salvage therapy prior to allo-SCT in order to maximize response. The ultimate goal of this strategy is to augment cytoreduction pretransplant and improve OS/PFS while reducing PD. Main G-associated non-hematologic toxicities include pulmonary, skin toxicities and mucositis. Between 8/07 and 04/13, twenty-seven HL patients underwent an allo-SCT with the G-FM regimen. They had failed multiple conventional treatments (median prior chemotherapy regimens: 4), radiation therapy (44%) and a prior auto-SCT (70%). The median age was 31 years (range 20-46). Disease status at SCT was complete remission (CR) or undetermined (CRu) (n=17; 63%), partial remission (PR; n=9; 33%), and other (n=1; 4%). The median time to PD after auto-SCT was 5 months (range 1-68). Fourteen patients (52%) received BV prior to allo-SCT, and in seven (50%) it was the last therapy prior to allo-SCT. In these seven patients the CR rate after BV was 100%. The donor was an HLA-identical sibling (n=16) or matched unrelated donor (MUD; n=11). The conditioning regimen was G (800 mg/m sq IV x1), F (33 mg/m sq IV daily x4) and M (70 mg/m sq IV daily x2). Thymoglobulin (4 mg/kg IV) was added in MUD allografts. Twenty patients received peripheral blood progenitor cells, and seven bone marrow. Myeloid recovery was prompt, with an absolute neutrophil count >500/mcL at day +11 (median). Median platelet recovery at 20K/mcL was at day +13. Chimerism studies indicate 100% donor-derived engraftment in 23/23 evaluable patients (100%). There were three early (ie before day 30) deaths and one case of graft failure. Cumulative incidence of day 100 and overall transplant-related mortality (TRM) was 15% (both). Cumulative incidence of acute (grade II-IV) and chronic graft-vs-host disease (extensive) was 19% (95% CI: 9-42) and 39% (95% CI: 24-65), respectively. Pulmonary toxicity (NCI CTC v3) was seen in nine patients (33%). Grade 4-5 pulmonary toxicity was seen in three patients (13%). Otherwise it was grade 1-3 (n=6). Cutaneous toxicity (skin rash, responsive to steroid therapy) was seen in five patients (19%: grade 3 n=1; grade 1-2 n=4). Mucositis was seen in thirteen patients (48%). It was grade 3 (n=1) and grade 1-2 (n=12). The overall response rate (CR/CRU) prior to allo-SCT was 79% (11/14) in BV-treated patients vs. 46% (6/13) in BV-naïve patients (p=0.12, Fisher's exact). The overall response rate (CR/CRU) after allo-SCT was 85%, both in BV-treated and in BV-naïve patients. Six patients expired (graft rejection n=1, pneumonia n=2; respiratory failure n=1, PD n=2). Twenty-one patients are alive with a median follow-up of 18 months (range 4-55). At the last f/up, actuarial estimates for OS and PFS are 69% (95% CI: 41-86) and 55% (95% CI: 31-74), respectively. Cumulative overall PD incidence is 30% (95% CI 15-61). The seven patients who received BV as last line of therapy prior to allo-SCT are all alive and in CR/CRu. The G-FM140 regimen continues to show promise in this high-risk patient group. The inclusion of G may affect pulmonary toxicity, but TRM remained low. With the current BV-supported approach, the CR rate pretransplant may be improved. PFS (18-mo) in CR/CRu patients pretransplant seems to compare favorably to our FM140 experience in complete responders (80% vs 57%, p=0.20). While this BV-based transplant strategy needs further evaluation, the role of RIC allo-SCT in HL may need reassessment in the BV era.
| Variable . | FM140 . | G-FM140 . |
|---|---|---|
| Patient number | 58 | 27 |
| Age (yrs) | 32 (19-59) | 31 (20-46) |
| Brentuximab vedotin pre-alloSCT (Y/N) | 0 / 58 | 14 / 13 |
| CR/CRu pretransplant | 24% * | 63% |
| TRM (day 100/overall) | 7% / 15% | 15% /15% |
| OS (2-year) | 64% (95% CI 49-76) | 78% (95% CI 53-91) |
| PFS (2-year) | 32% (95% CI 20-45) | 55% (95% CI 31-74) |
| PD (2-year) | 55% (95% CI 43-70) | 30% (95% CI 15-61) |
| Time to PD after allo-SCT (months) | 4.5 (1-35) | 13 (2-22) |
| Variable . | FM140 . | G-FM140 . |
|---|---|---|
| Patient number | 58 | 27 |
| Age (yrs) | 32 (19-59) | 31 (20-46) |
| Brentuximab vedotin pre-alloSCT (Y/N) | 0 / 58 | 14 / 13 |
| CR/CRu pretransplant | 24% * | 63% |
| TRM (day 100/overall) | 7% / 15% | 15% /15% |
| OS (2-year) | 64% (95% CI 49-76) | 78% (95% CI 53-91) |
| PFS (2-year) | 32% (95% CI 20-45) | 55% (95% CI 31-74) |
| PD (2-year) | 55% (95% CI 43-70) | 30% (95% CI 15-61) |
| Time to PD after allo-SCT (months) | 4.5 (1-35) | 13 (2-22) |
Study group included patients (n=28) with < PR pretransplant.
Off Label Use: Gemcitabine, fludarabine, melphalan, thymoglobulin (transplant conditioning).
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal