Abstract
Dasatinib is a highly potent BCR-ABL inhibitor, with a 325-fold higher potency than imatinib and a 16-fold higher potency than nilotinib in vitro. Across a series of phase II and III trials with more than 2 years of follow-up, dasatinib has demonstrated durable efficacy in patients with CML following resistance or intolerance to imatinib. We conducted a phase II study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of dasatinib in Japanese patients with imatinib resistance or intolerance CML.
Fifty- five CML-CP patients from 2009 to 2011 with resistance (n=40) or intolerance (n=26) to imatinib were registered to dasatinib administration (100mg once daily). Eleven among 26 patients with intolerance also showed resistance to imatinib at the registration. Imatinib resistance was defined as a lack of partial cytogenetical response at 3 months, a lack of complete cytogenetic response at 6 months or a lack of a major molecular response at 12 months of imatinib treatment. This criteria was identical to the criteria in ELN 2013 recommendation for first line. In another words, the resistance in this study means non-optimal criteria (warning and failure) of definition of the response to TKIs, first line, in ELN 2013 recommendation. Efficacy and safety were assessed using rates of major molecular response (MMR)/ MR4.5 (either (i) detectable disease with<0.0032% BCR-ABL1 IS or (ii) undetectable disease in cDNA with >32,000 ABL1 transcripts in the same volume of cDNA used to test for BCR-ABL1) at 12 months and drug-related adverse events (AEs) respectively. All analyses were based on the modified to intension-to treat.
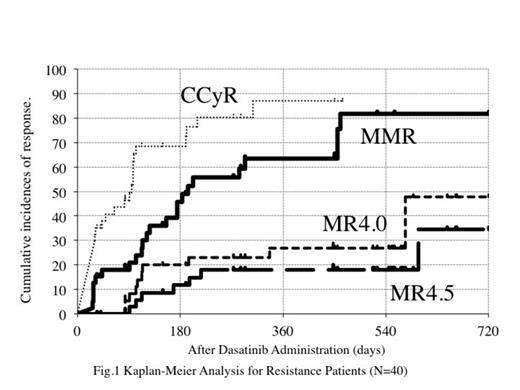
One patient was withdrawal before dasatinib administration. The median duration of imatinib therapy was 545 days. The overall incidence of MMR (primary endopoint) and MR4.5 at 12 months was 67.2% (95% confidence interval, 53.3-81.1%), and 20.2 % (95% CI, 8.4–32.0 %), respectively. Forty patients with resistance to imatinib, who were warning and failure patients judged by ELN 2013 criteria, were reassessed. Cumulative MMR and MR4.5 rate were 63.4% (95% CI: 46.3-80.6) and 18.0% (95% CI: 4.9-31.1) respectively at 12 months. Eleven patients, who showed more than 1% IS at 3 months of dasatinib treatment, did not reach to MMR at 12 months or discontinued dasatinib due to insufficient efficacy in this resistance cohort. However, progression to the accelerated or blastic phase had not been observed. When imatinib were changed to dasatinib, 5 patients showed the mutations, which were effective in dasatinib therapy. New mutations have not been observed during the treatment of dasatinib.
Among 54 patients, most non-hematological AEs were in grade 1/2. including diarrhea (12.7%), rash (7.3%), myalgia (5.5%) and vomiting (3.6%). Grade 3/4 non-hematological AEs were infrequent, including decreased potassium (3.6%), and increased creatinine (3.6%). Grade 1/2 fluid retention AEs were shown in 9.1% of patients, including edema (3.6%). Pleural effusion, which was only in Grade 1/2, was shown in 32.7% of patients. Grade 3/4 hematological toxicities included anemia (7.3%) and thrombocytopenia (3.6 %). Only 3 patients have permanently discontinued dasatinib treatment due to AEs.
The patients with non-optimal responses (warning and failure) judged by ELN 2013 criteria should have early intervention to dasatinib, which is less toxicity in CML-CP patients. This intervention might induce good prognosis. The BCR-ABL1 IS less than 1% at 3 months of dasatinib administration will be the valuable landmark for outcome.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal