Abstract
High dose melphalan (MEL) preceding autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) for MM continues to be the standard of care. No regimen has been clearly proven superior to MEL 200 mg/m2 (MEL 200). The combination of Busulfan (Bu) and MEL was shown to improve progression free survival (PFS) (Lahuerta, et al; Haematologica. 2010 Nov; 95 (11):1913-20). The combination of bortezomib (Vel) with MEL also demonstrated superior PFS vs. MEL alone using historical controls (Roussel et al; Blood. 2010; 115:32-7). We studied a conditioning regimen combining Bu, MEL and Vel (BuMelVel) in an open label phase II study aimed at improving PFS after HCT for MM. To assess the potential value of this novel regimen, we performed a comparative analysis between BuMelVel and a cohort of patients conditioned with MEL 200 from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) database.
Between July 2009 and May 2012, 43 eligible patients received BuMelVel conditioning followed by HCT. Bu was administered daily intravenous (IV) for a total of 4 days with the first 2 days (day -6, -5) at fixed dose of 130 mg/m2 over 3 hours and the subsequent 2 doses (day -4, -3) adjusted to achieve a target area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) total of 20,000 mM* min by performing pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis after the first dose of IV Bu. Mel 140 mg/m2 and Vel 1.6 mg/m2 were administered IV on Day-2 and Day -1 respectively. Outcomes were compared with a contemporaneous North American cohort (n=162) receiving single agent MEL 200 conditioning from the CIBMTR database. Controls were matched on age, sex, Karnofsky performance status (KPS), stage and interval from diagnosis to HCT. Multivariate analysis of Relapse, PFS, and overall survival (OS) was performed. Median follow up of survivors was 25 months. Planned maintenance therapy was not used.
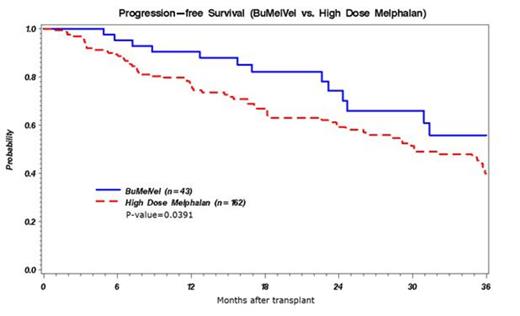
Age, gender, KPS, isotype, and stage were similar between groups (Table 1.). The MEL 200 cohort had more standard risk patients per Mayo Stratification of Myeloma and Risk-Adapted Therapy (mSMART) (78% vs. 40% in BuMelVel, p <0.0001) and more patients with only 1 prior line of therapy pre-HCT (67% vs. 47%, p = 0.02). Platelet and neutrophil engraftment kinetics were similar. Veno-occlusive disease (VOD) was not observed in the BuMelVel group and there was no non-relapse mortality (NRM). The incidence of relapse and PFS at 1 year were superior in the BuMelVel cohort (Table 1.). OS was similar between the cohorts. In multivariate analysis, PFS was superior in the BuMelVel cohort (HR for relapse/death in MEL 200 =1.87, p=0.04). Lack of a very good partial response or higher (≥VGPR) prior to HCT was associated with inferior PFS whereas lower KPS (<80) and higher international stage were associated with mortality.
| Patient Characteristics: . | BuMelVel . | Melphalan 200 . | P-value . |
|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | ||
| International Stage II/III | 20 (47) | 79 (53) | 0.74 |
| mSmart risk stratification | |||
| Standard risk | 17 (40) | 127 (78) | <0.0001 |
| High risk | 4 ( 9) | 18 (11) | |
| Unknown | 22 (51) | 17 (10) | |
| Disease Status prior to HCT | |||
| CR/VGPR | 3/15 (7/35) | 33/43 (20/27) | |
| PR | 23 (53) | 72 (44) | 0.19 |
| Line of therapy pre-HCT >1 | 23 (53) | 54 (33) | 0.02 |
| Outcomes: | % (95% CI) | ||
| NRM @12 months | 0 | 3 (1-6) | 0.04 |
| Incidence of Relapse @12 months | 10 (3-20) | 21 (15-28) | 0.04 |
| PFS @ 12 months | 90(76-96) | 60(69-83) | 0.02 |
| OS @ 24 months | 90(76-96) | 88(81-92) | 0.67 |
| Patient Characteristics: . | BuMelVel . | Melphalan 200 . | P-value . |
|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | ||
| International Stage II/III | 20 (47) | 79 (53) | 0.74 |
| mSmart risk stratification | |||
| Standard risk | 17 (40) | 127 (78) | <0.0001 |
| High risk | 4 ( 9) | 18 (11) | |
| Unknown | 22 (51) | 17 (10) | |
| Disease Status prior to HCT | |||
| CR/VGPR | 3/15 (7/35) | 33/43 (20/27) | |
| PR | 23 (53) | 72 (44) | 0.19 |
| Line of therapy pre-HCT >1 | 23 (53) | 54 (33) | 0.02 |
| Outcomes: | % (95% CI) | ||
| NRM @12 months | 0 | 3 (1-6) | 0.04 |
| Incidence of Relapse @12 months | 10 (3-20) | 21 (15-28) | 0.04 |
| PFS @ 12 months | 90(76-96) | 60(69-83) | 0.02 |
| OS @ 24 months | 90(76-96) | 88(81-92) | 0.67 |
PK directed dosing of Bu can be safely combined with Mel 140 followed by bortezomib without higher risk of VOD or NRM and in the absence of maintenance therapy. Within the constraints of a short follow up and uncontrolled post-transplant salvage therapies on both groups, no difference in OS has yet been observed. This novel conditioning regimen is safe and was associated with superior PFS compared with similarly matched controls and warrants further testing.
Rodriguez:Otsuka: Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Vesole:Millennium: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal