Abstract
Pain is the hallmark of sickle cell disease (SCD) but burden of pain is underestimated when measured using health care visits for vaso-occlusive crisis. In the PiSCES study adult patients reported pain on > 50% of diary days but sought care on only 3.5 % of diary days. Accurate assessment of the burden of pain and related morbidity is crucial in clinical care and research studies in SCD.
Paper based pain diaries for assessing daily pain are limited by recall bias, errors, inflated retrospective reports and falsely high compliance due to backfilling of entries. Electronic pain diaries facilitate real-time data capture, are convenient, prevent backfilling, maximize compliance and facilitate data management. They have been used in children with arthritis, cancer, abdominal and musculoskeletal pain but no validated instrument is available for use in children with SCD.
To develop, establish the face and content validity, and usability of a novel web-based multidimensional electronic pain diary for children and adolescents with SCD.
Needs assessment: Pediatric subjects in a pilot SCD pain intensity diary study participated in qualitative interviews to assess their preferences regarding an electronic pain diary.
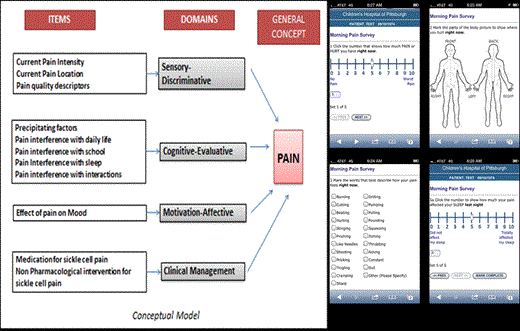
Instrument development: Items for the pain diary were adapted for SCD from “e-Ouch”(c), an electronic pain diary validated for use in children with arthritis. Items assess pain intensity, duration, interference with daily tasks, sleep, fatigue, precipitating factors, pain relieving treatments and response to treatments using the Numerical Rating Scale (0-10). We created a web-based pain diary that can be accessed via a secure website using a smartphone or computer.
Face validity: Experts in SCD, pain and psychometrics rated the items on a 5 point Likert scale for content, language, clinical relevance, comprehensiveness of answer choices and likely feasibility and acceptability in children with SCD. Two iterative cycles of expert review were conducted and were used for modification of items.
Content validity: Using items with established face validity, two iterative cycles of testing (n=5 each) with paper screenshots of questions using semi-structured cognitive interviewing techniques were done in pediatric patients age 15-22 with SCD.
Preliminary usability testing: Participants age 9-21(n=5) pilot tested the web-based electronic pain diary on a computer, smartphone and tablet. They were asked to recall their current pain and pain in the prior 12 hours while answering the diary questions. The usability testing was followed by semi-structured interviews.
Needs assessment: Patients indicated that electronic monitoring of pain could facilitate coordination of care, communication with providers and early intervention and that twice daily electronic documentation of pain would not pose an unacceptable burden.
Face validity: Items were reviewed by 15 experts in the first iterative cycle and 12 experts in the second iterative cycle and were modified for language, content and relevance; 2 items were deleted and 1 item was added.
Content Validity: During the first iterative cycle, participants identified items that were difficult to understand, ambiguous or irrelevant. Number of items was reduced from 18 to 13. During the second iterative cycle, one repetitive item was removed and others minimally modified. To minimize user burden items were redistributed so pain intensity, location, quality and precipitating factors were asked twice daily; effect of pain on sleep was asked in the morning and pain interference with daily activities, mood, school and interactions and clinical management items were asked in the evening.
Usability testing: Participants were easily able to navigate between questions, use the 0-10 NRS slider, select affected areas on the body image and select checkbox options and provided positive feedback on the question content and, layout of the diary, ease of its use and preference for accessing it from a smartphone.
This study established the face and content validity and usability of a web-based multidimensional electronic pain diary developed for use in children with SCD. This instrument can be used to assess pain as a patient reported outcome in clinical trials, to enhance communication in clinical care and as a comprehensive measure of pain phenotype in mechanistic studies.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal