Abstract
Enhanced progenitor proliferation, bone marrow (BM) hypervascularization and disturbed immune regulation contribute to the pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Inhibition of mammalian-target of rapamycin (mTor) by temsirolimus (TEM) might be a promising strategy to target these disease-specific cellular alterations. We report on the effects of single agent TEM on the clinical course as well as on immune composition and BM vascularization of MDS patients treated within the prospective, multicenter “TEMDS”-trial (NCT01111448).
Twenty patients being either IPSS low/int-1 MDS (n = 9) or IPSS int-2/high after azacitidine failure were treated with TEM at a dose of 25 mg/week in the absence of toxicity or disease progression. BM was reevaluated after 4 months of treatment with the option of TEM continuation for a maximum of 12 months in responding patients. Translational research within this study included flowcytometry-based measurement of changes in T-cell composition as well as determination of cytokine levels and BM-vascularization prior to and after TEM.
Of 20 patients treated, 15 discontinued TEM treatment prematurely due to intolerable side effects (n = 11), infectious complications (n = 3), or progression to AML (n = 1). Fatigue, stomatitis and profound leukopenia were the most frequent adverse events. A total of 13 severe adverse events were encountered in 10 patients and 1 patient died of infectious complications during TEM treatment. Of the 5 patients who were treated for at least 4 months and underwent regular BM reevaluation, none showed signs of response according to IWG criteria.
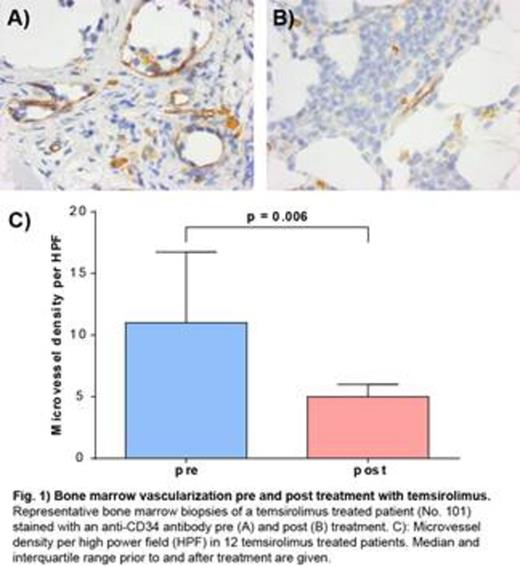
TEM treatment resulted in a remarkable, although non-significant, decrease in total number of lymphocytes in the pB (pre: 74.6%, post: 48.4%, p = 0,083) and BM (pre: 23.5% post: 20.1%, p = 0.123). Within the T-helper cell compartment a trend towards an increase in regulatory T-cell (Treg) frequency was observed (pB: pre: 6.0 %, post: 6.4 %, p = 0.083). Moreover, the balance between naive (CD45RA+/CD45RO-) and activated/memory (CD45RA-/CD45RO+) Treg shifted significantly in favor of the latter (p = 0.004). Plasma analysis in BM and pB revealed, that these changes were obviously not mediated by alterations in TGFβ plasma levels. In a total of 12 assessable patients, a significant (p = 0.006) decrease of BM vascularization was observed after treatment with TEM for a median of 5 weeks (Fig. 1). There were, however, no changes in the medullary or peripheral blood VEGF concentration (data not shown).
Selective inhibition of the mTOR signaling cascade in MDS patients results in specific alterations of the composition of T-cell subsets as well as BM vascularization. Given the absence of any hematological response we suggest that these drug-induced modifications cannot alter the natural course of the disease.
Wermke:Pfizer: Research Funding. Off Label Use: Temsirolimus is licensend for the treatment of MCL and RCC but not MDS. Platzbecker:Pfizer: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal