Abstract
The combination of ATRA and ATO is very effective in treating APL, both in mouse models (Lallemand JEM 1999) and in patients (Lo Coco NEJM 2013). Having previously shown that the combination of ATRA and a specific DNA vaccine (pCDNA3PML-RARAFrC) rescues APL mice from relapse and enhances specific immune responses (Padua Nat Med 2003; Robin Blood 2006; Furugaki Blood 2010; Pokorna Mol Cell Probes 2013), we applied this approach using a novel non-specific DNA, pVAX14, as add-on therapy to ATRA +/- ATO.
APL transplanted mice (APL cells injected in syngeneic 6-week old mice, Brown PNAS 1997) were treated with various combinations of ATRA +/- ATO and DNA (pVAX1 (control DNA), pCDNA3PML-RARAFrC (specific DNA vaccine) or pVAX14. pVAX14 is a novel construct containing GC-rich sequences and coding for unique peptides, 3 of which we have shown to be immunogenic. Mice were monitored for survival, MRD (by RQ-PCR of PML-RARA) on days 19, 37, 57 and 67 in peripheral blood (PB), and as a measure of LICs by secondary transplantation of bone marrow (BM) or spleen cells from long term (more than 120 days) survivors (LTS) into syngeneic lethally irradiated mice. Immune responses were assessed on CD4 Memory T-cells (Tmem), IFNg production (ELISPOT) and anti-RARa (ELISA) antibody production. Functional studies including challenge experiments of LTS with leukemic cells assessed the protective effects of immunotherapy.
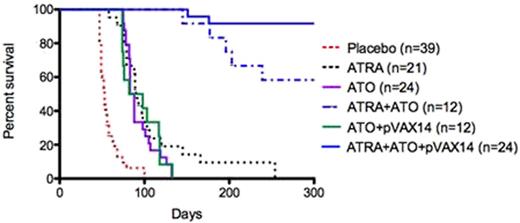
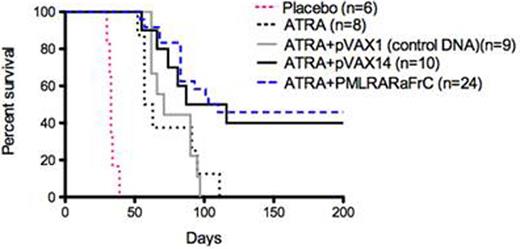
1) Survival. In a first set of experiments, ATRA+pVAX14 significantly increased survival compared to placebo, ATRA alone or ATRA+pVAX1 (control DNA) (p<0.001, p<0.03, p<0.05 respectively (Fig. 1); survival was similar with ATRA+pVAX14 and ATRA+pCDNA3PML-RARAFrC, with about 40% LTS. In a second set of experiments where ATO was introduced, ATO+pVAX14 was not superior to ATO alone, but ATRA+ATO+pVAX14 combination was significantly better than ATRA+ATO (p<0.05), providing 85% LTS (Fig. 2). MRD for PML-RARA in ATRA+ATO+pVAX14 mice was significantly lower than in ATRA mice (p<0.001) but the difference with ATRA+ATO mice was not significant up to day 67. Moreover, when we injected BM or spleen cells from both ATRA+ATO and ATRA+ATO+pVAX14 LTS none of the recipients develop APL (follow-up period of 140 days), indicating the clearance of LICs. 2) Immune response monitoring showed that effector Tmem were significantly higher in ATRA+ATO+pVAX14 > ATRA+ATO > ATRA (p<0.05 and p<0.001 respectively). LTS of ATRA+ATO+pVAX14 had increased IFNg producing lymph node cells when stimulated with APL cells or PML-RAR peptide compared to ATRA+ATO (p<0.02). Serum anti-RARa antibodies were significantly increased in all combinations compared to controls with ATRA+ATO+pVAX14 > ATRA+pVAX14 ≈ ATRA+ATO+pVAX1 (control DNA) ≈ ATRA+ATO > ATRA+pVAX1 (Control DNA) > ATRA (p<0.05, p<0.03, p<0.0006 respectively). When LTS mice of ATRA+ATO+pVAX14 and ATRA+ATO groups were challenged with APL spleen cells, survival was significantly higher in both groups (median survival 105 vs 80 days, p=NS) than in controls (syngeneic mice injected with APL cells) (p<0.001 and p<0.01 respectively)
Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showing that pVAX14 as well as the specific vaccine (pCDNA3PML-RARAFrC) (Padua Nat Med 2003) in combination with ATRA significantly prolongs survival in APL mice.
Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showing that pVAX14 as well as the specific vaccine (pCDNA3PML-RARAFrC) (Padua Nat Med 2003) in combination with ATRA significantly prolongs survival in APL mice.
Kaplan-Meier survival curves showing that the combination of ATRA+ATO+pVAX14 is the best in rescuing the APL mice.
Kaplan-Meier survival curves showing that the combination of ATRA+ATO+pVAX14 is the best in rescuing the APL mice.
The combination of the non-specific vaccine (pVAX14) with ATRA+ATO further improved survival over ATRA+ATO alone and elicited specific humoral and T-cell mediated responses targeting LICs. This vaccine is also effective in a mouse model of high risk MDS (Submitted to ASH 2103).
SP, LG and CLP contributed equally to this work.
Patel:CEFIPRA: Research Funding. Fenaux:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding. Chomienne:Vivavacs: Equity Ownership, I have patents pending through INSERM/Paris-Diderot related to technology employed in this present study. , I have patents pending through INSERM/Paris-Diderot related to technology employed in this present study. Patents & Royalties, Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees. Padua:Vivavacs: Equity Ownership, I have patents pending through INSERM/Paris-Diderot related to technology employed in this present study. I, I have patents pending through INSERM/Paris-Diderot related to technology employed in this present study. I Patents & Royalties, Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
SP, LG and CLP contributed equally to this work.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal