Abstract
Syntaxin-11 (Stx11), an atypical member of the SNARE protein family, is part of the cytolytic machinery of T and NK cells and involved in the fusion of lytic granules with the plasmamembrane. Functional loss of syntaxin-11 in humans causes defective degranulation and impaired cytolytic activity of T and NK cells. Furthermore, patients with STX11 deficiency develop familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 4 (FHL4), a life-threatening disease of severe hyperinflammation. We established Stx11-deficient mice as an animal model for FHL4. Stx11-deficient mice exhibited severely reduced degranulation and cytolytic activity of CTL and NK cells and developed all clinical symptoms of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) after infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV). The HLH phenotype was further characterized by hyperactive CD8 T cells and continuous IFN-γ production. However, in contrast to perforin-deficient mice, which represent a model for FHL2, progression of HLH was not fatal. Survival of Stx11-deficient mice was determined by exhaustion of antigen-specific T cells, characterized by expression of inhibitory receptors, sequential loss of effector functions, and finally T-cell deletion. Blockade of inhibitory receptors on T cells in Stx11-deficient mice converted nonfatal disease course into fatal HLH, identifying T-cell exhaustion as an important factor for determination of disease severity in HLH.
Key Points
Syntaxin-11–deficient mice as the first animal model for human familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 4 (FHL4).
T-cell exhaustion limits HLH progression in syntaxin-11–deficient mice.
Introduction
Cytolytic activity is a key function of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK cells to eliminate infected and malignant cells. Thereby, cytotoxicity is mediated by polarized exocytosis of lytic granules at the immunological synapse. Lytic granules are secretory lysosomes containing effector molecules, such as perforin and granzymes. On interaction with target cells, CTLs undergo polarization, characterized by Ca2+ mobilization, reorientation of the microtubule organization center, and directed movement of lytic granules. The docking-priming-fusion steps of lytic granules are tightly controlled and result in the release of effector molecules at the immunological synapse. Synaptogamin-like proteins, members of the Rab and the Sec1/Munc18 protein families, as well as SNARE (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor) proteins are involved in this process. SNARE proteins are helical transmembrane molecules expressed on the vesicle and target membranes. On association, they build a trans-SNARE complex, which leads to the fusion of docked lipid bilayers.1
Syntaxin-11 (Stx11) is an atypical member of the Q-SNARE family and expressed in various cells of the immune system.2-8 Stx11 associates with Vti1b,7,9 SNAP23,10 and syntaxin binding protein 2 (STXBP2/Munc18-2),11,12 regulating the fusion of lytic granules with the plasma membrane at the immunological synapse. Consistent with this, CTLs and NK cells from patients with mutated STX11 gene or with experimentally reduced Stx11 expression levels displayed defects in degranulation and cytolytic activities.5,6 In addition, it was described recently that Stx11 plays a role in platelet exocytosis.13 Patients with mutations in the STX11 gene develop hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), a life-threatening disorder of severe hyperinflammation resulting from immune dysregulation.4,6,14 HLH is associated with defects in components of the cytolytic machinery of T and NK cells15-18 and characterized by inflammatory processes in various tissues as a result of infiltrating, hyperactive T cells, NK cells and macrophages, accompanied by massive cytokine production (IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-18).19 Because of this loss in immune homeostasis, patients present with prolonged fever, hepatosplenomegaly, neurologic manifestations, hypercytokinemia, and hemophagocytosis. The diagnostic criteria for HLH according to the Histiocyte Society are listed in Table 1.20
Diagnostic criteria for HLH
| Fever |
| Cytopenias in at least 2 cell lineages |
| Hypertriglyceridemia and/or hypofibrinogenemia |
| Hyperferritinemia |
| High sCD25 (sIL-2R) concentration |
| Splenomegaly |
| Hemophagocytosis in different organs |
| Low/absent NK cell cytotoxicity |
| Fever |
| Cytopenias in at least 2 cell lineages |
| Hypertriglyceridemia and/or hypofibrinogenemia |
| Hyperferritinemia |
| High sCD25 (sIL-2R) concentration |
| Splenomegaly |
| Hemophagocytosis in different organs |
| Low/absent NK cell cytotoxicity |
HLH is divided into primary (genetic) and secondary (acquired) forms. Typically, patients with primary HLH develop disease in early childhood with a poor prognosis in the absence of therapeutic intervention, which consists of immunochemotherapy to resolve the acute hyperinflammation followed by hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.21 HLH is a genetically heterogeneous disorder, and various mutations in the perforin gene and in genes involved in the intracellular transport and release of lytic granules have been demonstrated. Linkage analyses identified mutated perforin (PRF1) in FHL2 (familial HLH),22 and Munc13-4 (UNC13D) mutations in FHL3 patients.23 Furthermore, mutations in the STX11 and MUNC18-2/STXBP2 genes are associated with FHL4 and FHL5 in humans, respectively.4,11,12,24 Although the overall pattern of clinical features in HLH patients is quite characteristic, the onset and severity of disease are highly variable, depending on the mutated gene, the nature of the mutation, and probably environmental factors. These differences in disease progression are not understood and complicate phenotype/genotype correlations in patients, which would be helpful for more selective therapeutic interventions. In this context, animal models of HLH are useful to analyze the complex pathogenesis of the disease under more defined conditions, allowing a comparison between the different genetic defects in the lytic machinery of T and NK cells and disease progression.
This study describes a comprehensive analysis of HLH in Stx11-deficient mice after infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) and represents the first animal model for human FHL4. Stx11-deficient mice developed all clinical and laboratory features of HLH. However, in contrast to perforin-deficient mice, HLH progression was not fatal in Stx11-deficient mice. Animals displayed a more chronic disease and survived. Remarkably, the less severe clinical course of HLH was associated with exhaustive differentiation of CD8 T cells, characterized by expression of inhibitory receptors, a sequential loss of effector functions followed by final deletion of antigen-specific CTLs. Most importantly, blockade of inhibitory pathways in T cells of Stx11-deficient mice converted nonfatal disease course into fatal HLH progression, demonstrating a causal relationship between T-cell exhaustion and disease progression.
Methods
Mice and viruses
C57BL/6J mice were purchased from Janvier. Stx11−/− mice were generated by Udo zur Stadt on a C57BL/6 background by deletion of the only coding exon.25 Perforin-deficient C57BL/6-Prf1tm1Sdz (PKO) mice were obtained from Dr Hengartner (Zurich). Mice were kept under specific pathogen-free conditions. All mouse experiments were approved by the Regierungspraesidium Freiburg. LCMV-WE was grown on L929 cells and quantified using a standard focus-forming assay. Temperatures were obtained using a digital infrared ear thermometer (Braun, ThermoScan type 6022).
Clinical laboratory tests and ELISA
Blood counts were determined by a Sysmex KX-21 hematology analyzer. Glutamate dehydrogenase, glutamate pyruvate transaminase, triglycerides, and ferritin from sera were analyzed by the Department of Clinical Chemistry using the Roche Modular Analytics Evo. sCD25 in serum samples was quantified using the mouse IL-2Ralpha DuoSet kit (R&D Systems). Serum IFN-γ concentrations were determined by ELISA using purified rat antimouse IFN-γ (clone R4-6A2, BD Biosciences PharMingen) as capture antibody and biotin-labeled antimouse IFN-γ (clone XMG 1.2, BD Biosciences PharMingen) as detection antibody followed by streptavidin-HRP (BD Biosciences PharMingen) and Fast O-Phenylendiamine Dihydrochloride Tablet Sets (Sigma-Aldrich) for detection.
Histology
Organs were fixed in 4% formaldehyde. Immunhistochemistry was performed on paraffin-embedded sections using the biotinylated monoclonal rat IgG2b antimouse F4/80 antibody (clone Cl:A3-1, AbD Serotec) and biotinylated polyclonal antirat Immunoglobulin (Dako). Visualizing of F4/80+ cells was achieved using the Dako REAL Detection System, alkaline phosphatase/RED and hematoxylin counterstaining. Tissue processing/staining was performed at the Institute of Pathology. Hemophagocytosis was quantified by counting 10 high power fields (40×) of a defined area (97 656 μm2) per organ. Images were captured using a Carl Zeiss AxioImager M1 microscopy under a 10× or 40×/0.95 korr objective equipped with a 1/3” CMOS high definition full-HD camera MC-HD3 (Horn imaging GmbH). Images were acquired using AxioVision Version 4.8.2 software.
Antibodies, degranulation assay, and intracellular staining
Antibodies were purchased from eBioscience, BD Biosciences, BioLegend, or Bio X Cell. For NK-cell degranulation, 5 × 105 spleen cells from mice injected with 200 μg of polyinosinic acid/polycytidylic acid (poly I:C, Sigma-Aldrich) 24 hours before were incubated with 5 × 105 YAC-1 cells for 2 hours in the presence of anti-CD107a antibody. For intracellular cytokine staining, 106 lymphocytes were stimulated with 10−7M LCMV GP33-peptide (KAVYNFATM) for 4 hours in the presence of brefeldin A (20 μg/mL) and anti-CD107a antibody, then surface-stained with anti-CD8a antibody after fixation and permeabilization, using the Cytofix/Cytoperm kit (BD Biosciences) and anti–IFN-γ antibody staining. For detection of LCMV-specific CD8 T cells, fluorochrome-labeled H-2Db tetramers complexed with GP33-peptide were used. Sample analyses were performed using FACSCalibur (BD Biosciences) and FlowJo Version 7.2.2 software (TreeStar). For blockade of inhibitory pathways, 200 μg of anti–PD-L1 (10F.9G2) and 200 μg anti–LAG-3 (C9B7W) blocking antibodies or isotype control rat IgG1 (HRPN) and IgG2b (LTF-2) were administered intraperitoneally in 3-day intervals from day 10 to day 22 after infection.
Chromium-release assay
Cytolytic activity of CD8 T cells was determined by a 51Chromium-release assay using GP33-41 and NP396-404 (the 2 immunodominant T-cell epitopes of LCMV in B6 mice) and adeno peptide-loaded EL-4 cells as targets. Splenocytes from LCMV-infected mice and target cells were incubated for 5 hours at 37°C. For NK cell cytotoxcity, splenocytes from mice injected with 200 μg of poly I:C 24 hours before were used together with YAC-1 targets. Duplicate wells were assayed for each effector-target ratio and percentages of specific lysis were calculated.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SigmaPlot Version 9.0 software. Significant differences between data were evaluated using Student unpaired t test.
Results
Stx11−/− mice develop the full picture of HLH after LCMV infection
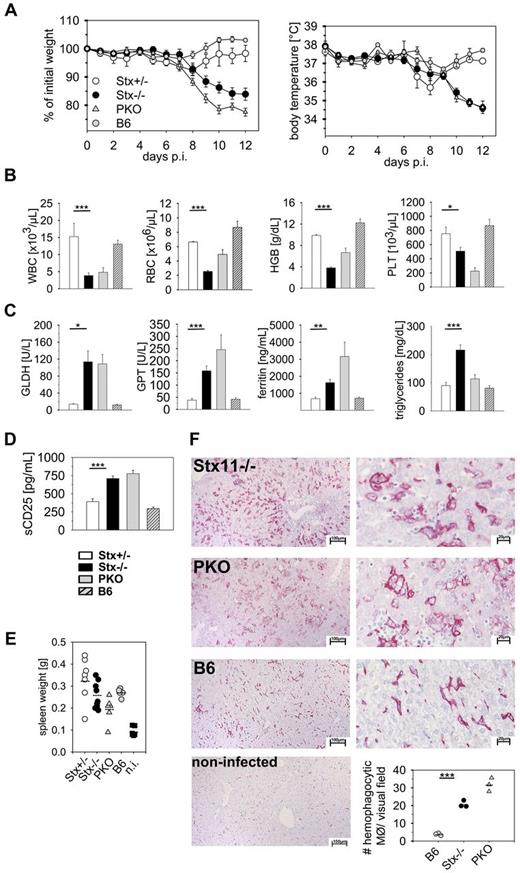
Stx11−/− mice are fertile and show normal development and cage activities. They exhibit no pigmentation defects, and their primary and secondary lymphoid organs appear normal in size and composition (supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article).25 Mice with deficiencies in genes of the cytolytic machinery do not develop HLH spontaneously.26-29 However, after LCMV infection, these mice exhibit clinical symptoms and laboratory abnormalities characteristic for HLH patients, with the exception that fever diagnosed in patients is mirrored by a drop in ear temperature in mice. We evaluated HLH in Stx11−/− mice after infection with LCMV compared with heterozygous (Stx11+/−) littermates, perforin-deficient (PKO) and C57BL/6 (B6) mice. HLH was assessed according to the diagnostic criteria defined by the HLH study group of the Histiocyte Society in their 2004 guidelines (HLH-2004; Table 1).20 After LCMV infection, Stx11−/− and PKO mice exhibited drastic weight loss and a drop in ear temperature within 12 days, which was not observed in Stx11+/− and B6 mice (Figure 1A). Interestingly, weight loss in Stx11−/− mice was less pronounced compared with PKO mice. Furthermore, Stx11−/− mice developed severe pancytopenia, as reflected by reduced counts for white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets and decreased levels of hemoglobin on day 12 after infection like PKO mice (Figure 1B). Laboratory biomarkers, such as liver enzymes (glutamate dehydrogenase, glutamate pyruvate transaminase), ferritin, and triglycerides, were significantly increased in the sera of Stx11−/− and PKO mice compared with Stx11+/− and B6 mice (Figure 1C). In addition, elevated levels of sCD25 were detectable in Stx11−/− and PKO mice (Figure 1D). Splenomegaly was observed in all mouse strains, irrespective of the genetic defect, which is a well-known feature of acute LCMV infection (Figure 1E). In humans, HLH is characterized by hemophagocytic activity of macrophages in various organs. Histologic examination of the liver revealed a massive infiltration of macrophages with pronounced hemophagocytosis in Stx11−/− and PKO mice, whereas in immunocompetent mice this picture was rarely seen (Figure 1F). Of note, although both Stx11−/− and PKO mice fulfilled all diagnostic criteria for HLH, distinct differences in the various clinical and laboratory parameters were detectable between the 2 mouse strains. In summary, using the diagnostic criteria for HLH, Stx11−/− mice displayed the full clinical picture of HLH, as observed in FHL4 patients.
LCMV-infected Stx11−/− mice display clinical and laboratory features of HLH.Stx11+/− (○), Stx11−/− (●), PKO ( ), and wild-type B6 (
), and wild-type B6 ( ) mice were infected with 200 PFU LCMV-WE intravenously. (A) Body weight and peripheral body temperature were monitored daily. (B-D) Peripheral blood cell counts (B), liver enzymes, ferritin levels, triglycerides (C), as well as serum sCD25 levels (D) were analyzed on day 12 after infection. (E) On day 12, these mice and noninfected (n.i.) B6 mice were assayed for splenomegaly. (F) Representative pictures of liver sections of day 12 LCMV-infected Stx11−/−, PKO, and B6 mice stained with anti-F4/80 (left 10×; right 40×). Bottom right graph: Semiquantitative analysis of hemophagocytosis by macrophages as assessed in 10 high power visual fields (40×) of a defined area (97 656 μm2) per mouse. Scale bars represent 100 μm and 20 μm, respectively. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data (mean ± SEM) represent 3 independent experiments with at least 3 mice per group. *P < .05 (Student unpaired t test). **P < .005 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test). n.s. indicates not significant.
) mice were infected with 200 PFU LCMV-WE intravenously. (A) Body weight and peripheral body temperature were monitored daily. (B-D) Peripheral blood cell counts (B), liver enzymes, ferritin levels, triglycerides (C), as well as serum sCD25 levels (D) were analyzed on day 12 after infection. (E) On day 12, these mice and noninfected (n.i.) B6 mice were assayed for splenomegaly. (F) Representative pictures of liver sections of day 12 LCMV-infected Stx11−/−, PKO, and B6 mice stained with anti-F4/80 (left 10×; right 40×). Bottom right graph: Semiquantitative analysis of hemophagocytosis by macrophages as assessed in 10 high power visual fields (40×) of a defined area (97 656 μm2) per mouse. Scale bars represent 100 μm and 20 μm, respectively. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data (mean ± SEM) represent 3 independent experiments with at least 3 mice per group. *P < .05 (Student unpaired t test). **P < .005 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test). n.s. indicates not significant.
LCMV-infected Stx11−/− mice display clinical and laboratory features of HLH.Stx11+/− (○), Stx11−/− (●), PKO ( ), and wild-type B6 (
), and wild-type B6 ( ) mice were infected with 200 PFU LCMV-WE intravenously. (A) Body weight and peripheral body temperature were monitored daily. (B-D) Peripheral blood cell counts (B), liver enzymes, ferritin levels, triglycerides (C), as well as serum sCD25 levels (D) were analyzed on day 12 after infection. (E) On day 12, these mice and noninfected (n.i.) B6 mice were assayed for splenomegaly. (F) Representative pictures of liver sections of day 12 LCMV-infected Stx11−/−, PKO, and B6 mice stained with anti-F4/80 (left 10×; right 40×). Bottom right graph: Semiquantitative analysis of hemophagocytosis by macrophages as assessed in 10 high power visual fields (40×) of a defined area (97 656 μm2) per mouse. Scale bars represent 100 μm and 20 μm, respectively. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data (mean ± SEM) represent 3 independent experiments with at least 3 mice per group. *P < .05 (Student unpaired t test). **P < .005 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test). n.s. indicates not significant.
) mice were infected with 200 PFU LCMV-WE intravenously. (A) Body weight and peripheral body temperature were monitored daily. (B-D) Peripheral blood cell counts (B), liver enzymes, ferritin levels, triglycerides (C), as well as serum sCD25 levels (D) were analyzed on day 12 after infection. (E) On day 12, these mice and noninfected (n.i.) B6 mice were assayed for splenomegaly. (F) Representative pictures of liver sections of day 12 LCMV-infected Stx11−/−, PKO, and B6 mice stained with anti-F4/80 (left 10×; right 40×). Bottom right graph: Semiquantitative analysis of hemophagocytosis by macrophages as assessed in 10 high power visual fields (40×) of a defined area (97 656 μm2) per mouse. Scale bars represent 100 μm and 20 μm, respectively. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data (mean ± SEM) represent 3 independent experiments with at least 3 mice per group. *P < .05 (Student unpaired t test). **P < .005 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test). n.s. indicates not significant.
NK cells and CTL of Stx11−/− mice are impaired in degranulation and cytolytic activity
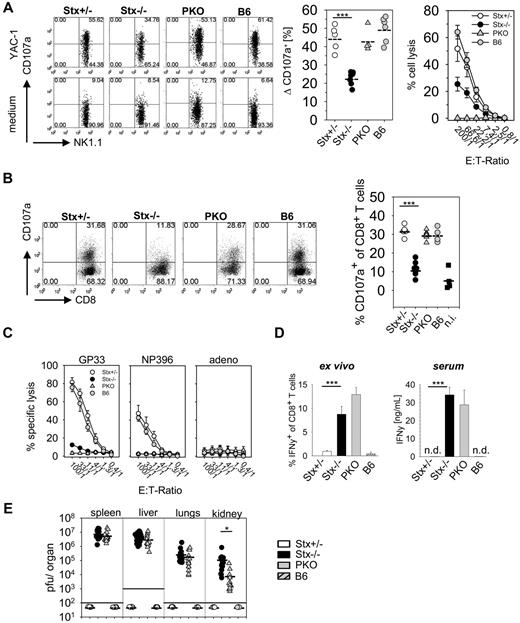
Because reduced cytolytic function of NK and T cells is characteristic for STX11-deficient patients,6 we analyzed degranulation and lytic activity of these cells in Stx11−/− mice. Degranulation of NK cells after poly I:C application was determined using a CD107a translocation assay. We detected impaired granule exocytosis of Stx11−/− NK cells compared with NK cells of PKO, Stx11+/− and B6 mice (Figure 2A left and middle panel). To analyze whether the degranulation defect of Stx11−/− NK cells translated in decreased cytolytic activity, an ex vivo 51Cr-release assay was performed. Stx11−/− NK cells showed strongly reduced lysis of YAC-1 cells, compared with heterozygous littermates or B6 mice (Figure 2A right panel). Moreover, degranulation and lytic function of Stx11−/− CTLs were reduced at day 12 after LCMV infection compared with CTLs from Stx11+/− and B6 mice (Figure 2B-C). Interestingly, compared with PKO T cells, a weak residual GP33-peptide specific T-cell cytotoxicity was still detectable in Stx11−/− mice (Figure 2C). Thus, similar to human patients, murine Stx11−/− NK cells and CTLs exhibited a profound defect in degranulation, which resulted in a drastic reduction of their cytolytic function.
NK cells and CD8 T cells of Stx11−/− mice display impaired effector functions. (A) Degranulation and cytotoxicity of NK cells from Stx11+/− (○), Stx11−/− (●), PKO ( ), and wild-type B6 (
), and wild-type B6 ( ) mice analyzed 24 hours after intraperitoneal injection of poly I:C on YAC-1 target cells. Degranulation is shown as increase of CD107a expression on NK1.1+CD3− cells after restimulation with YAC-1 cells or medium control. Statistical analysis shows delta CD107a, which is calculated as percentage of CD107a expression after YAC-1 stimulation minus percentage of CD107a after medium exposure (background). (B) Degranulation ability of CD8 T cells on day 12 after LCMV infection measured by surface expression of CD107a after 4 hours of in vitro restimulation with GP33 peptide. (C) Antiviral cytotoxic activity of Stx11+/− (○), Stx11−/− (●), PKO (
) mice analyzed 24 hours after intraperitoneal injection of poly I:C on YAC-1 target cells. Degranulation is shown as increase of CD107a expression on NK1.1+CD3− cells after restimulation with YAC-1 cells or medium control. Statistical analysis shows delta CD107a, which is calculated as percentage of CD107a expression after YAC-1 stimulation minus percentage of CD107a after medium exposure (background). (B) Degranulation ability of CD8 T cells on day 12 after LCMV infection measured by surface expression of CD107a after 4 hours of in vitro restimulation with GP33 peptide. (C) Antiviral cytotoxic activity of Stx11+/− (○), Stx11−/− (●), PKO ( ), and B6 (
), and B6 ( ) spleen cells toward target cells loaded with the immunodominant LCMV epitopes GP33-41 or NP396-404 or an irrelevant adeno peptide in a 5-hour 51Cr release assay. (D) Spontaneous (ex vivo, without restimulation) IFN-γ expression of CD8 T cells and serum levels of IFN-γ. (E) Viral titers were determined 12 days after LCMV infection in spleen, liver, lungs, and kidney. FACS illustrations are representative for the respective mouse groups; graphs beneath each FACS plot represent data for individual mice. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data are (mean ± SEM) representative for 3 independent experiments with at least 3 mice per group. *P < .05 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test). n.s. indicates not significant; and n.d., not detectable.
) spleen cells toward target cells loaded with the immunodominant LCMV epitopes GP33-41 or NP396-404 or an irrelevant adeno peptide in a 5-hour 51Cr release assay. (D) Spontaneous (ex vivo, without restimulation) IFN-γ expression of CD8 T cells and serum levels of IFN-γ. (E) Viral titers were determined 12 days after LCMV infection in spleen, liver, lungs, and kidney. FACS illustrations are representative for the respective mouse groups; graphs beneath each FACS plot represent data for individual mice. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data are (mean ± SEM) representative for 3 independent experiments with at least 3 mice per group. *P < .05 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test). n.s. indicates not significant; and n.d., not detectable.
NK cells and CD8 T cells of Stx11−/− mice display impaired effector functions. (A) Degranulation and cytotoxicity of NK cells from Stx11+/− (○), Stx11−/− (●), PKO ( ), and wild-type B6 (
), and wild-type B6 ( ) mice analyzed 24 hours after intraperitoneal injection of poly I:C on YAC-1 target cells. Degranulation is shown as increase of CD107a expression on NK1.1+CD3− cells after restimulation with YAC-1 cells or medium control. Statistical analysis shows delta CD107a, which is calculated as percentage of CD107a expression after YAC-1 stimulation minus percentage of CD107a after medium exposure (background). (B) Degranulation ability of CD8 T cells on day 12 after LCMV infection measured by surface expression of CD107a after 4 hours of in vitro restimulation with GP33 peptide. (C) Antiviral cytotoxic activity of Stx11+/− (○), Stx11−/− (●), PKO (
) mice analyzed 24 hours after intraperitoneal injection of poly I:C on YAC-1 target cells. Degranulation is shown as increase of CD107a expression on NK1.1+CD3− cells after restimulation with YAC-1 cells or medium control. Statistical analysis shows delta CD107a, which is calculated as percentage of CD107a expression after YAC-1 stimulation minus percentage of CD107a after medium exposure (background). (B) Degranulation ability of CD8 T cells on day 12 after LCMV infection measured by surface expression of CD107a after 4 hours of in vitro restimulation with GP33 peptide. (C) Antiviral cytotoxic activity of Stx11+/− (○), Stx11−/− (●), PKO ( ), and B6 (
), and B6 ( ) spleen cells toward target cells loaded with the immunodominant LCMV epitopes GP33-41 or NP396-404 or an irrelevant adeno peptide in a 5-hour 51Cr release assay. (D) Spontaneous (ex vivo, without restimulation) IFN-γ expression of CD8 T cells and serum levels of IFN-γ. (E) Viral titers were determined 12 days after LCMV infection in spleen, liver, lungs, and kidney. FACS illustrations are representative for the respective mouse groups; graphs beneath each FACS plot represent data for individual mice. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data are (mean ± SEM) representative for 3 independent experiments with at least 3 mice per group. *P < .05 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test). n.s. indicates not significant; and n.d., not detectable.
) spleen cells toward target cells loaded with the immunodominant LCMV epitopes GP33-41 or NP396-404 or an irrelevant adeno peptide in a 5-hour 51Cr release assay. (D) Spontaneous (ex vivo, without restimulation) IFN-γ expression of CD8 T cells and serum levels of IFN-γ. (E) Viral titers were determined 12 days after LCMV infection in spleen, liver, lungs, and kidney. FACS illustrations are representative for the respective mouse groups; graphs beneath each FACS plot represent data for individual mice. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data are (mean ± SEM) representative for 3 independent experiments with at least 3 mice per group. *P < .05 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test). n.s. indicates not significant; and n.d., not detectable.
Activated Stx11−/− CTL exhibit continuous IFN-γ expression and are mandatory for HLH development
Hyperactive T cells and elevated cytokine levels are important characteristics of HLH in patients.19 This is reflected in Stx11−/− mice by a high spontaneous IFN-γ expression of CTL analyzed ex vivo without further restimulation (Figure 2D left panel) and strongly elevated IFN-γ serum levels (Figure 2D right panel), whereas IFN-γ expression was already down-regulated in Stx11+/− and B6 mice. Despite this exaggerated CD8 T-cell response, Stx11−/− mice failed to clear LCMV infection (Figure 2E). Stx11+/− and B6 mice eliminated virus below detection limit by day 12 after infection, whereas high viral titers were detectable in spleen, liver, lungs, and kidney of Stx11−/− mice. Of note, Stx11−/− mice exhibited significantly elevated virus titers in kidney and slightly increased titers in liver and lungs compared with PKO mice. Taken together, Stx11−/− mice failed to eliminate LCMV and displayed CTL that continuously produced IFN-γ.
Depletion experiments confirmed that CD8 T cells are mandatory for HLH development. Stx11−/− mice showed neither weight loss nor a decrease in body temperature after anti-CD8 antibody treatment, compared with untreated littermates (supplemental Figure 1A). Furthermore, CD8 T cell–depleted Stx11−/− mice did not develop other criteria of HLH (data not shown). In contrast, depletion of NK cells did not prevent HLH as reflected by weight loss and decreased body temperature (supplemental Figure 1B). Thus, activated CD8 T cells, rather than NK cells, are the driving force for HLH in Stx11−/− mice after LCMV infection, consistent with findings in PKO mice.28
Nonfatal HLH progression in Stx11−/− mice is associated with early exhaustive differentiation of CTL
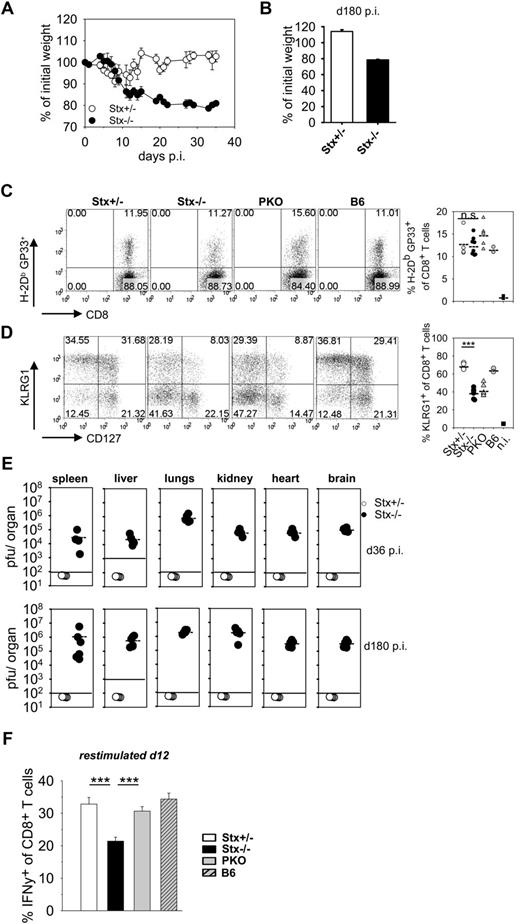
Although both Stx11−/− and PKO mice fulfilled all diagnostic criteria for HLH after LCMV infection, the further disease development was different. HLH progression in PKO mice was fatal and mice had to be eliminated due to animal care guidelines. Strikingly, Stx11−/− mice exhibited a less severe HLH progression and survived (supplemental Figure 2). This more chronic course of HLH was characterized by low body weight (Figure 3A), sustained splenomegaly, reduced white blood cell counts, and decreased hemoglobin levels (data not shown). Importantly, when followed for 180 days, at no point in time Stx11−/− mice regained their initial body weight (Figure 3B). To elucidate possible mechanisms for nonfatal disease progression in Stx11−/− mice, we analyzed differences in initial CD8 T-cell expansion and effector differentiation as well as final clearance of LCMV compared with PKO mice with fatal HLH. The frequencies of CD8 T cells specific for the GP33-epitope of LCMV were comparable in Stx11−/− and PKO mice at day 12 after LCMV infection (Figure 3C). Furthermore, differentiation into distinct CD8 T-cell effector subpopulations, as determined by KLRG1 and CD127 expression, was identical. Similar frequencies of short-lived effector cells (KLRG1hi/CD127lo phenotype) and memory effector precursor cells (KLRG1lo/CD127hi phenotype) were detectable in the 2 mouse strains. Interestingly, CTL of both Stx11−/− and PKO mice were impaired in expression of KLRG1 compared with Stx11+/− and B6 mice, which points to an abnormal differentiation status of CD8 T cells (Figure 3D). Late clearance of virus was not observed in Stx11−/− mice, and high LCMV titers were detectable in all organs examined at days 36 and 180 after infection (Figure 3E). Thus, neither T-cell expansion nor T-cell differentiation nor virus control can explain the differences in disease progression between Stx11−/− and PKO mice.
Nonfatal HLH progression in Stx11−/− mice. (A-B) Stx11+/− (○) and Stx11−/− (●) mice were infected intravenously with 200 PFU LCMV, and body weights were followed for 36 days after infection (A) and determined on day 180 after LCMV infection (B), respectively. (C) Frequency of LCMV-specific CD8 T cells was determined by GP33-tetramer staining. (D) CD8 T-cell differentiation into effector subpopulations was analyzed by staining for KLRG1 and CD127 expression to discriminate CTL with a short-lived effector cell or memory effector precursor cell phenotype. (E) Virus titers in the indicated organs were determined on days 36 and 180 after infection. (F) IFN-γ expression of CD8 T cells was measured after 4 hours of in vitro restimulation with GP33-peptide on day 12 after infection. IFN-γ expression of Stx11−/− CD8 T cells was statistically compared with Stx11+/− and PKO CD8 T cells, respectively. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data (mean ± SEM) represent at least 2 independent experiments with 3 mice per group. ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test). n.s. indicates not significant.
Nonfatal HLH progression in Stx11−/− mice. (A-B) Stx11+/− (○) and Stx11−/− (●) mice were infected intravenously with 200 PFU LCMV, and body weights were followed for 36 days after infection (A) and determined on day 180 after LCMV infection (B), respectively. (C) Frequency of LCMV-specific CD8 T cells was determined by GP33-tetramer staining. (D) CD8 T-cell differentiation into effector subpopulations was analyzed by staining for KLRG1 and CD127 expression to discriminate CTL with a short-lived effector cell or memory effector precursor cell phenotype. (E) Virus titers in the indicated organs were determined on days 36 and 180 after infection. (F) IFN-γ expression of CD8 T cells was measured after 4 hours of in vitro restimulation with GP33-peptide on day 12 after infection. IFN-γ expression of Stx11−/− CD8 T cells was statistically compared with Stx11+/− and PKO CD8 T cells, respectively. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data (mean ± SEM) represent at least 2 independent experiments with 3 mice per group. ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test). n.s. indicates not significant.
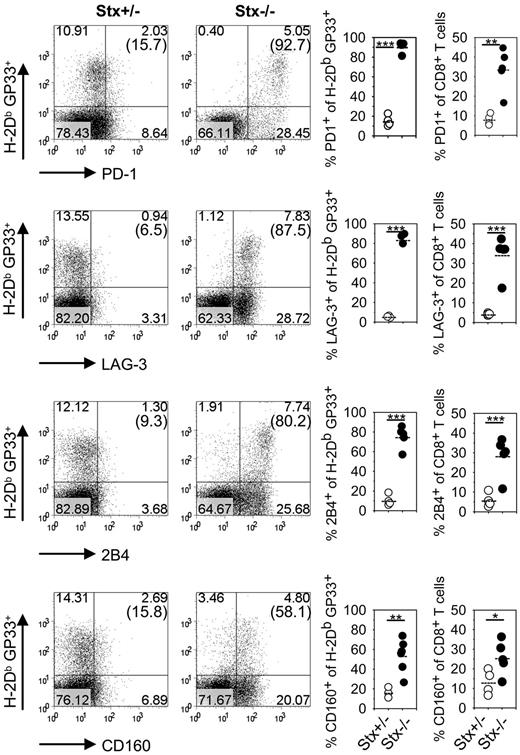
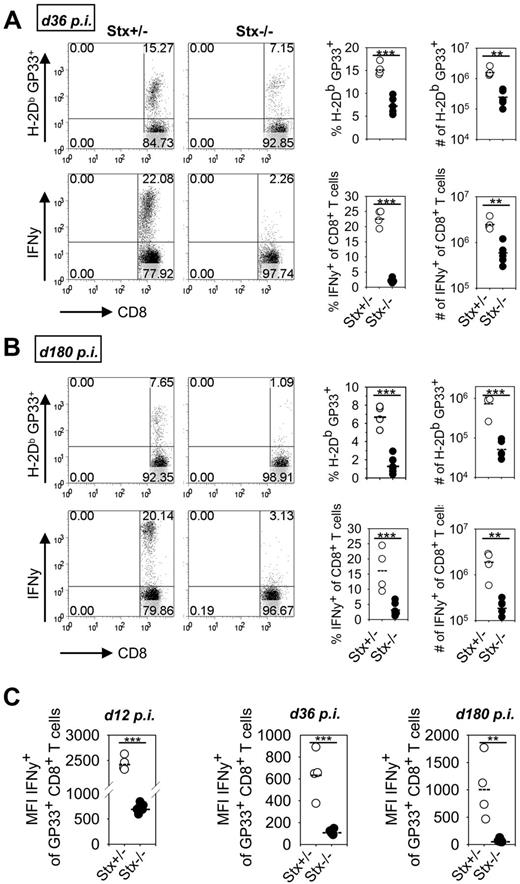
However, we noted a significant reduction in the percentage of IFN-γ–expressing CTLs after peptide restimulation in Stx11−/− versus PKO mice at day 12 (Figure 3F). Of note, impaired KLRG1 expression and reduced frequencies of IFN-γ–producing CTLs are seen under conditions of exhaustive differentiation during chronic infections.30-32 Thus, nonfatal HLH progression in Stx11−/− mice may be the result of an exhaustive differentiation of CTLs. We therefore analyzed expression of inhibitory receptors PD-1, LAG-3, 2B4, and CD160 on GP33-tetramer–positive CTLs of Stx11−/− mice on day 36 after LCMV infection (Figure 4). All of these receptors have been reported to negatively regulate the function of T cells.30,32,33 Interestingly, GP33-specific CTLs of Stx11−/− mice, but not those of heterozygous littermates, expressed these inhibitory receptors. The difference was also apparent when the overall CD8 compartment was analyzed (Figure 4 right panels). This implies that nonfatal HLH development in Stx11−/− mice is accompanied by exhaustive differentiation of CD8 T cells. Furthermore, the frequencies of GP33-specific CTLs in the CD8 compartment and their absolute numbers were significantly reduced in Stx11−/− mice by day 36 compared with heterozygous littermates (Figure 5A top panel). In addition, the frequencies and numbers of IFN-γ–positive T cells were strongly decreased in Stx11−/− mice (Figure 5A bottom panel). The exhausted phenotype of CTLs was even more pronounced at day 180. GP33-reactive CTLs were hardly detectable in Stx11−/− mice, and the percentages and numbers of IFN-γ–expressing T cells were drastically reduced (Figure 5B). Because hyperactive T cells and elevated cytokine levels are a hallmark of HLH pathogenesis, we analyzed IFN-γ expression levels of CTLs based on mean fluorescence intensities (MFI) after short-term restimulation (Figure 5C). By day 12, IFN-γ expression was already significantly lower in CTLs of Stx11−/− mice compared with heterozygous littermates. IFN-γ production was progressively reduced (day 36), and by day 180 hardly any IFN-γ expression could be induced in antigen-specific CTLs of Stx11−/− mice. Lack of IFN-γ production and the physical deletion of T cells are characteristic for a final stage of exhaustion, suggesting that T-cell exhaustion attenuates disease progression in Stx11−/− mice.
CD8 T cells of Stx11−/− mice express inhibitory receptors.Stx11+/− (○) and Stx11−/− (●) mice were infected intravenously with 200 PFU LCMV. After gating on CD8 T cells, GP33-specific cells were phenotyped for expression of inhibitory receptors PD-1, LAG-3, 2B4, and CD160. Inserted numbers indicate percentages of H-2Db GP33-tetramer-positive CD8 T cells, which express the respective exhaustion marker. FACS illustrations are representative for the mouse groups; graphs represent data for individual mice. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data (mean ± SEM) represent 2 independent experiments with 2 or 3 mice per group. *P < .05 (Student unpaired t test). **P < .005 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test).
CD8 T cells of Stx11−/− mice express inhibitory receptors.Stx11+/− (○) and Stx11−/− (●) mice were infected intravenously with 200 PFU LCMV. After gating on CD8 T cells, GP33-specific cells were phenotyped for expression of inhibitory receptors PD-1, LAG-3, 2B4, and CD160. Inserted numbers indicate percentages of H-2Db GP33-tetramer-positive CD8 T cells, which express the respective exhaustion marker. FACS illustrations are representative for the mouse groups; graphs represent data for individual mice. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data (mean ± SEM) represent 2 independent experiments with 2 or 3 mice per group. *P < .05 (Student unpaired t test). **P < .005 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test).
CD8 T cells of Stx11−/− mice display features of a final stage of exhaustion. (A-B) Stx11+/− (○) and Stx11−/− (●) mice were infected intravenously with 200 PFU LCMV. On day 36 (A) and day 180 (B), the frequencies of LCMV-specific CD8 T cells were determined by GP33-tetramer staining. IFN-γ production of CD8 T cells was analyzed after 4 hours of in vitro restimulation with GP33 peptide. FACS illustrations are representative for the respective mouse groups; graphs represent data for individual mice. (C) IFN-γ expression levels of GP33-tetramer-positive CD8 T cells from Stx11+/− (○) and Stx11−/− (●) mice were determined by mean fluorescence intensity after short-term restimulation on days 12, 36, and 180 after infection. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data (mean ± SEM) represent at least 2 independent experiments with 2 or 3 mice per group. **P < .005 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test).
CD8 T cells of Stx11−/− mice display features of a final stage of exhaustion. (A-B) Stx11+/− (○) and Stx11−/− (●) mice were infected intravenously with 200 PFU LCMV. On day 36 (A) and day 180 (B), the frequencies of LCMV-specific CD8 T cells were determined by GP33-tetramer staining. IFN-γ production of CD8 T cells was analyzed after 4 hours of in vitro restimulation with GP33 peptide. FACS illustrations are representative for the respective mouse groups; graphs represent data for individual mice. (C) IFN-γ expression levels of GP33-tetramer-positive CD8 T cells from Stx11+/− (○) and Stx11−/− (●) mice were determined by mean fluorescence intensity after short-term restimulation on days 12, 36, and 180 after infection. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data (mean ± SEM) represent at least 2 independent experiments with 2 or 3 mice per group. **P < .005 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test).
Blocking of PD-L1 and LAG-3 induces fatal HLH in Stx11−/− mice
If T-cell exhaustion was causally related to attenuated HLH progression in Stx11−/− mice, blocking of inhibitory receptor pathways on T cells, such as PD-1 and LAG-3, should induce fatal HLH. To address the impact of blocking inhibitory receptors on HLH-inducing CTLs, LCMV-infected Stx11−/− mice were treated with blocking antibodies specific for PD-L1 and LAG-3,32,34,35 starting from day 10 on, when clinical signs of HLH became apparent. Disease progression of individual mice was followed by analysis of body weight loss. Stx11−/− mice treated with isotype antibodies exhibited only a moderate weight loss until day 25 and showed nonfatal disease progression. In striking contrast, Stx11−/− mice treated with antibodies specific for LAG-3 and PD-L1 exhibited continued weight loss (Figure 6A), with the consequence that > 50% of the animals had to be eliminated according to animal care guidelines (Figure 6B). Thus, blocking of inhibitory receptor pathways in Stx11−/− mice converted nonfatal into fatal HLH, reflecting a disease phenotype observed in PKO mice. On day 25 Stx11−/− mice treated with blocking antibodies showed higher frequencies and absolute numbers of disease-mediating CD8 T cells (Figure 6C). Furthermore, higher frequencies and numbers of IFN-γ producing CTLs were detectable when blocking antibodies were administrated (Figure 6D). Thus, this experiment demonstrates a mechanistic link between early exhaustive differentiation of CTLs and attenuated disease in Stx11−/− mice, identifying T-cell exhaustion as a relevant factor in the determination of disease progression in HLH.
Blockade of inhibitory receptors on disease-mediating T cells induces fatal HLH in Stx11−/− mice. LCMV-infected Stx11−/− mice were treated with blocking antibodies directed against PD-L1 and LAG-3 (bAB) or isotype control antibodies (iso) every third day from day 10 to day 22 after infection. (A) Body weight of either isotype (●) or blocking antibody–treated (▴) Stx11−/− mice was followed (body weight by day 10 was adjusted to 100%). (B) Termination of the experiment due to animal guidelines is displayed as percentage of moribund mice in the 2 mouse groups. (C) Frequency and absolute numbers of GP33-tetramer–positive T cells in the 2 groups of antibody-treated Stx11−/− mice at day 25 after infection. (D) Frequency and absolute numbers of IFN-γ–expressing CD8 T cells in isotype or blocking antibody–treated Stx11−/− mice at day 25. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data (mean ± SEM) are representative for 2 independent experiments with 3-5 mice per group. *P < .05 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test).
Blockade of inhibitory receptors on disease-mediating T cells induces fatal HLH in Stx11−/− mice. LCMV-infected Stx11−/− mice were treated with blocking antibodies directed against PD-L1 and LAG-3 (bAB) or isotype control antibodies (iso) every third day from day 10 to day 22 after infection. (A) Body weight of either isotype (●) or blocking antibody–treated (▴) Stx11−/− mice was followed (body weight by day 10 was adjusted to 100%). (B) Termination of the experiment due to animal guidelines is displayed as percentage of moribund mice in the 2 mouse groups. (C) Frequency and absolute numbers of GP33-tetramer–positive T cells in the 2 groups of antibody-treated Stx11−/− mice at day 25 after infection. (D) Frequency and absolute numbers of IFN-γ–expressing CD8 T cells in isotype or blocking antibody–treated Stx11−/− mice at day 25. Horizontal lines in graphs represent mean values. Data (mean ± SEM) are representative for 2 independent experiments with 3-5 mice per group. *P < .05 (Student unpaired t test). ***P < .001 (Student unpaired t test).
Discussion
Using a new animal model for FHL4, this study identifies T-cell exhaustion as a disease-modifying parameter in HLH. After LCMV infection, Stx11−/− mice initially fulfilled all diagnostic criteria for HLH but showed long-term survival due to CTL exhaustion, whereas PKO mice developed lethal HLH. Degranulation and cytoloytic activity of NK cells and CTLs were drastically impaired in Stx11−/− mice, confirming the critical role of Stx11 in exocytosis of lytic granules. Although limited in cytolytic functions, CD8 T cells were hyperactive and expressed continuously high levels of IFN-γ associated with elevated cytokine levels in the serum. Within the first 12 days after infection, Stx11−/− and PKO mice displayed largely comparable diagnostic parameters with some subtle differences. However, after day 12, HLH was fatal in PKO mice, whereas Stx11−/− mice survived and exhibited a more chronic disease phenotype. Nonlethal HLH was characterized by a slow resolution of some, but not all, clinical symptoms, accompanied by exhaustive differentiation of CD8 T cells. This became manifested in the expression of inhibitory receptors, a sequential loss of effector functions, and final deletion of T cells. Importantly, blocking of inhibitory pathways converted nonfatal into fatal HLH in Stx11−/− mice, demonstrating a mechanistic link between T-cell exhaustion and disease progression.
HLH is a genetically heterogeneous disease with a relatively homogeneous clinical phenotype. However, depending on the genes affected and the particular mutation, distinct differences in the onset of disease, severity of clinical symptoms, and duration of disease-free remission periods have been reported.24 The majority of HLH patients with STX11 deficiency develop less severe disease (later onset, alleviated symptoms, longer periods of disease-free remission), compared with patients deficient in perforin.4,6,24 Later onset of HLH is also observed in Griscelli syndrome 2 and Chediak-Higashi syndrome 1 patients.36 Again, this is reflected in the corresponding animal models: whereas PKO mice die, Rab27a-deficient and Lyst-deficient souris mice survive HLH triggered by LCMV29 (B.J., unpublished results, 2011). Thus, HLH severity in the mouse models correlate with the different HLH onset observed in patients with the corresponding gene defects. Furthermore, phenotype/genotype correlations in FHL2 patients revealed that the time point of HLH onset critically influences HLH severity and is determined by the degree of cytolytic dysfunction.37,38
One explanation for the milder HLH phenotype in FHL4, FHL5, and Griscelli syndrome 2 patients could be the finding that the cytolytic function of NK cells is partially restored after in vitro culture with high IL-2 concentrations.6,11,12,39,40 It was suggested that residual cytotoxic activity of NK cells in these patients may be sufficient to better control infections or reconstitute effector cell homeostasis via killing of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and/or activated T cells. This would implicate a prominent rheostat function of NK cells41 in immune homeostasis during HLH development. Whether the high IL-2 concentrations restoring NK-cell functions in vitro are reached in vivo is unknown. Furthermore, when the same NK cells were analyzed directly ex vivo during an acute phase of HLH, degranulation and cytolytic activity were heavily impaired,6 which may argue against a restoration of NK-cell function in vivo. In FHL4 patients, it was speculated that the defect in NK-cell degranulation is responsible for HLH pathogenesis.6 Our results reveal that depletion of CD8 T cells, but not NK cells, prevented HLH development in Stx11−/− mice. This finding is consistent with results in PKO mice,28 indicating that CD8 T cells play a major role in LCMV-triggered HLH pathogenesis in both mouse models.
Based on the results obtained in experiments with Stx11−/− mice, we suggest T-cell exhaustion as an alternative explanation for the more attenuated phenotype in FHL4. T-cell exhaustion was originally described as a dysfunction of CD8 T cells followed by clonal deletion in the context of a chronic infection.42,43 Exhaustion is observed in CD4 and CD8 T cells during infections, such as LCMV, HIV, hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, adenovirus, and polyoma virus and was further documented during malignancies.31 Initial induction of functional T-cell responses, followed by a prolonged expression of inhibitory receptors, and a stepwise loss of effector functions that culminates in physical deletion are characteristics for T-cell exhaustion. Hereby, the sequential loss of different effector functions occurs in a hierarchical manner, first affecting IL-2 production and proliferative capacity, followed by loss of cytolytic function and TNF-α expression. Interestingly, reduced INFγ expression is correlated with an advanced state of exhaustion preceding the physical elimination of T cells.31,44,45 Most often T-cell exhaustion is induced under conditions of high and prolonged antigenic stimulation. Intrinsic factors, as inhibitory receptors and extrinsic factors such as inhibitory cytokines, T-cell help, and regulatory T cells determine exhaustive T-cell differentiation, tempering immune reactivity, and protecting the host against immunopathology.
We present first evidence that T-cell exhaustion is a pathophysiologic mechanism modifying HLH progression and determining survival in an animal model. At day 12 after LCMV infection, when both Stx11−/− and PKO mice had developed HLH and showed high virus titers, we observed lower expression levels and a reduced fraction of IFN-γ producing CTLs in Stx11−/− mice. Whereas PKO mice did not survive in the further course of disease, Stx11−/− mice survived and disease-mediating CD8 T cells expressed high levels of inhibitory receptors, such as PD-1, LAG-3, 2B4, and CD160 (day 36). Thereafter, a stepwise further loss of IFN-γ expression was observed and specific CTLs were deleted by time (day 180). Thus, T-cell exhaustion limited sustained IFN-γ production in Stx11−/− mice, which attenuated HLH progression. To examine, whether T-cell exhaustion was causally related to disease outcome in Stx11−/− mice, we blocked inhibitory signal pathways with the result that attenuated disease converted into fatal HLH.
The expression of inhibitory receptors per se is not indicative for exhaustive differentiation because these receptors are also transiently expressed on functional effector T cells during the acute phase of an immune response, thereby functioning as a fine-tuning/fail-safe mechanism to prevent immunopathology, autoimmunity, and possibly activation-induced cell death of effector T cells.34,46,47 This observation is reflected in our experiments by high expression of inhibitory receptors on virus-specific CTLs of B6 mice by day 6 after LCMV infection. After virus clearance (day 12), activated CTLs rapidly down-regulate the inhibitory receptors (supplemental Figure 3A). Because PKO and Stx11−/− mice are not able to control LCMV infection, activated CD8 T cells in both mouse strains still expressed inhibitory receptors by day 12 (supplemental Figure 3B). Although CD8 T cells in both PKO and Stx11−/− mice stained positive for inhibitory receptors, only Stx11−/− CD8 T cells progressively differentiated into an exhaustive phenotype, whereas PKO CD8 T cells remained highly activated with the consequence that PKO mice developed fatal HLH. Functionally, less severe HLH progression in Stx11−/− mice is reflected by a significant early down-regulation of IFN-γ expression in CTLs, which may be causative for the survival of the mice.
Sustained expression of inhibitory receptors is observed on exhausted T cells during chronic infections31,45 and is mandatory to maintain the dysfunctional status. In the chronic phase of infection, the number of coexpressed inhibitory receptors and their expression levels correlate with the severity of exhaustion.32,33 In vivo blockade of inhibitory receptor signaling pathways restored the effector functions of exhausted T cells during chronic infections in mice and primates, leading to rapid clearance of the pathogens.34,35,48 Interestingly, the combined blockade of inhibitory pathways acts synergistically on the recovery of T-cell effector functions.30,32 We found that coapplication of antibodies blocking the PD-1 and LAG-3 signaling pathways in Stx11−/− mice converted the nonfatal into fatal HLH, reflecting a disease phenotype as in PKO mice. Furthermore, an increase in the frequencies of disease-mediating and IFN-γ–expressing CD8 T cells was observed, which indicates restored T-cell effector functions. These experiments demonstrate a mechanistic link between early exhaustive differentiation of CTLs and attenuated HLH in Stx11−/− mice and identify T-cell exhaustion as a relevant factor in the determination of HLH severity. It will be of great interest to study whether this phenomenon can also be observed in HLH patients, in particular whether persistent expression of inhibitory receptors and exhaustive differentiation of T cells correlate with differences in HLH onset and the severity of clinical symptoms.
A so far unsolved question is why, under conditions of impaired virus control and chronic antigen-specific stimulation, CTLs in PKO mice induce fatal HLH, whereas CTLs in Stx11−/− mice exhibit early exhaustive differentiation leading to attenuated HLH progression. It is tempting to speculate that perforin and syntaxin-11 deficiencies affect different pathways of immune regulation. First, the 2 molecules may differentially influence intrinsic mechanisms of T-cell regulation and thereby directly determine the expansion, differentiation, and contraction of effector T cells. Second, deficiencies in perforin or synatxin-11 may have a different impact on early virus control, thereby influencing antigen load, antigen distribution, and antigen presentation by distinct cell types, which will then determine different fate decisions during T-cell stimulation. It is so far unclear whether the slightly increased virus titers in kidney, lung, and liver observed in Stx11−/− mice are the cause or the result of T-cell exhaustion. Third, because syntaxin-11 expression has been demonstrated in professional APCs, a deficiency may directly influence the quality of antigen presentation and, as a consequence, determine activation/differentiation of T cells. Fourth, CTLs from Stx11−/− and PKO mice may differ in their ability to eliminate antigen-presenting dendritic cells, which is an important rheostat function to limit T-cell responses.49-51 Therefore, differences in the control of the APC compartment by T cells may directly relate to variations in HLH progression.52,53 Most probably, dendritic cell elimination in this context is determined by differences in the residual cytolytic activity of syntaxin-11 versus perforin deficient CTLs and/or their different ability to kill APCs via death receptor-dependent pathways. Further experiments are needed to gain more insight into these complex mechanisms of immune regulation.
Our study with Stx11−/− mice, a new mouse model for FHL4, demonstrates that T-cell exhaustion can be an important disease-modifying parameter in HLH. Although Stx11−/− mice initially developed all clinical symptoms of HLH, they survived because of high expression of inhibitory receptors on disease-mediating CTLs and the stepwise loss of effector functions. Detailed analysis of patients will reveal whether T-cell exhaustion is a possible mechanism that accounts for the differences in the aggressiveness of HLH episodes in humans. This would have important implications for future therapeutic interventions in HLH as stimulation of inhibitory receptors could promote exhaustive differentiation of disease-mediating T cells.
There is an Inside Blood commentary on this article in this issue.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank H. Pircher for helpful discussion, S. Vucikuja for technical support, O. Schweier for tetramers, and K. Gräwe for histology.
This work was supported by the Thyssen Stiftung, the European Union (FP7 CURE-HLH grant agreement 201461), and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF 01 EO 0803).
Authorship
Contribution: T.K. and P.A. designed the study and prepared the manuscript; T.K. and B.J. performed experiments; J.M. and U.z.S. generated knockout mice; A.S.-G. performed histologic analysis; and G.J and S.E. gave conceptual advice.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Peter Aichele, Institute for Medical Microbiology and Hygiene, Department of Immunology, Hermann-Herder-Strasse 11, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany; e-mail peter.aichele@uniklinik-freiburg.de.