Abstract
Abstract 5189
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a severe and life-threatening disease. It is characterized by excessive growth of pulmonary artery endothelial and smooth muscle cells leading to a profound pulmonary artery remodeling and consequently increased pulmonary artery pressure and vascular resistance. Most patients with the heritable form of PAH harbor a mutation in the bone morphogenic protein (BMP) receptor 2 (BMPR2) resulting in dysregulated BMP signaling. In addition, aberrant BMP signaling was also observed in the idiopathic form of PAH although the underlying molecular mechanisms have not been elucidated. Recently, it was shown that BMP antagonist Gremlin-1 was elevated in pulmonary vessels of mice during development of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension (Cahill et al, Circulation. 2012;125(7):920–30).
The aim of this prospective study was to investigate the plasma levels of Gremlin-1 in PAH patients (Dana point classification group I) and to correlate Gremlin-1 levels to clinical and hemodynamic parameters. Thirty subjects were included in the study (19 patients with PAH treated at the PH clinics of the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Germany and 11 healthy volunteers) after giving informed consent.
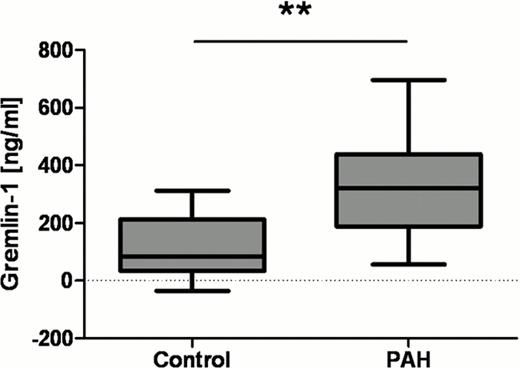
The mean Gremlin-1 plasma level was 2. 6-fold increased with 333 ± 160 ng/ml, in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension compared to those of healthy control subjects with a mean Gremlin-1 plasma level of 118 ± 115 ng/ml (p=0. 001 in t-test).
Gremlin-1 plasma levels of PAH patients were correlated to demographic, clinical and hemodynamic parameters including age, sex, 6-minute walk distance, systemic and pulmonary blood pressure & vascular resistance, lung function testing, NT-proBNP (N terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide) and NYHA/WHO functional classification.
A positive correlation between Gremlin-1 plasma levels and NT-proBNP plasma levels was observed (Spearman Rho 0. 809 with p<0. 001). Furthermore, a negative correlation was observed between the Gremlin-1 levels and the 6-minute walk distance (Spearman Rho −0. 522 with p=0. 032).
The plasma levels of BMP antagonist Gremlin-1 are significantly elevated in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension and may serve as new serological marker. Gremlin-1 might mirror the state of BMP dysregulation and represent a potential follow up marker under a future targeted therapy. Furthermore, since Gremlin-1 was shown to induce proliferative effects on both endothelial as well as smooth muscle cells, it might also contribute directly to the aberrant vessel growth observed in PAH.
Increased Gremlin-1 plasma levels in pulmonary arterial hypertension patients.
Increased Gremlin-1 plasma levels in pulmonary arterial hypertension patients.
Gremlin-1 plasma levels of patients with pulmonary hypertension (n=19) were analyzed in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Compared to healthy subjects (n=11), mean plasma levels of Gremlin-1 were 2. 6-fold increased in PH patients (t-test p=0. 001). Box plots show the median (center horizontal line), the 25th to the 75th percentile (box) and the range (whiskers).** indicates p<0. 01.
Hennigs:Bayer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Actelion: Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Fiedler:Pfizer Inc. : Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal