Abstract
Abstract 3689
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is characterized by the presence of CD30-positive Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells. The standard of care for patients (pts) with relapsed or refractory HL is salvage chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant (auto-SCT). However, approximately 50% of pts experience relapse of HL after auto-SCT and this population represents a pronounced unmet need. In a 756-pt retrospective analysis, the median overall survival (OS) in HL pts who relapsed after auto-SCT was 2.4 years, as measured from the time of auto-SCT, with shorter time to relapse after auto-SCT being the most predictive factor for shortened survival (Horning et al, 2008). Brentuximab vedotin (ADCETRIS®) comprises an anti-CD30 antibody conjugated by a protease-cleavable linker to monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), a microtubule-disrupting agent. Brentuximab vedotin selectively induces apoptotic death of CD30-positive cells by binding, internalizing, and releasing MMAE. A pivotal phase 2 study was conducted to determine the efficacy and safety of brentuximab vedotin in 102 pts with relapsed or refractory HL after auto-SCT (ClinicalTrials.gov #NCT00848926). Long-term survival data from this ongoing trial are described.
Pts received 1.8 mg/kg brentuximab vedotin every 3 weeks as a 30-minute outpatient IV infusion for up to 16 cycles. The primary endpoint was the objective response rate (ORR) per independent review according to the Revised Response Criteria for Malignant Lymphoma (Cheson 2007). Long-term follow-up assessments to determine survival and disease status occurred every 3 months (mos) for 2 years, every 6 mos during Years 3 to 5, and annually thereafter.
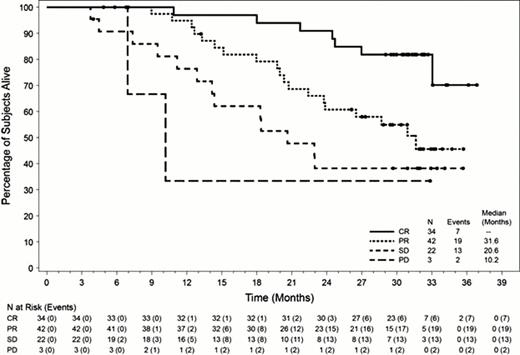
In these heavily pretreated pts with poor prognosis, the median time to relapse after auto-SCT was 6.7 mos (range, 0–131 mos). Pts received a median of 9 cycles of brentuximab vedotin and the ORR was 75% (76 of 102 pts), with complete remissions (CRs) obtained by 33% of pts (n=34). At the time of this analysis (July 2012), the median observation time from first dose was 29.5 mos (range, 1.8 to 36.9 mos). 60 of 102 pts (59%) were alive at the time of last follow up and the median OS has not yet been reached. The estimated 24-mo survival rate was 65% (95% CI: 55%, 74%). Median OS by best clinical response was 31.6 mos for pts with partial remission (PR, n=42), 20.6 mos for pts with stable disease (SD, n=22), and 10.2 mos for pts with progressive disease (PD, n=3); median OS for pts who obtained a CR (n=34) has not yet been reached. Evaluation of numerous demographic and baseline characteristics including age, gender, bone marrow involvement, presence of B symptoms, tumor size, and ECOG performance status showed that the only subgroup of pts who had a significantly more favorable survival rate following brentuximab vedotin treatment were those with a baseline ECOG score of 0 (24-mo survival rate of 81% vs. 47% for pts with ECOG scores of 0 vs. 1, respectively). Notably, no significant difference in OS was evident in the subgroup of pts who had relapsed within a year of auto-SCT compared with those who had relapsed >1 year after auto-SCT. As previously reported, the most common (≥15%) brentuximab vedotin-related adverse events of any grade were peripheral sensory neuropathy, nausea, fatigue, neutropenia, and diarrhea. Adverse events of Grade 3 or higher that occurred in ≥5% of pts were neutropenia, peripheral sensory neuropathy, thrombocytopenia, and anemia.
After a median observation time of approximately 2.5 years from first dose of brentuximab vedotin, 60 of 102 pts (59%) with relapsed or refractory HL were alive at the time of last follow up and the median OS has not yet been reached. The estimated 24-mo survival rate was 65%. The only pretreatment factor evaluated that was associated with a higher 24-mo survival rate was a baseline ECOG score of 0. Prolonged OS was observed in pts with both long and short progression-free intervals after auto-SCT. Pts who achieved a CR with brentuximab vedotin experienced longer OS than pts who did not achieve a CR. Based upon these findings, combination regimens that incorporate brentuximab vedotin are presently being evaluated in clinical trials to determine whether the proportion of pts who achieve durable CRs might be further increased.
Chen:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau, Travel Expenses Other. Gopal:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Smith:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding; Spectrum: Consultancy; Cephalon: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; GlaxoSmith Kline: Speakers Bureau. Ansell:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding. Rosenblatt:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding. Savage:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Connors:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding. Engert:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Millennium: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria. Larsen:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Sievers:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Honoraria, Research Funding. Younes:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Millennium: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria; Affimed: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Johnson & Johnson: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal