Abstract
Drug-induced acute hemolytic anemia led to the discovery of G6PD deficiency. However, most clinical data are from isolated case reports. In 2 clinical trials of antimalarial preparations containing dapsone (4,4′-diaminodiphenylsulfone; 2.5 mg/kg once daily for 3 days), 95 G6PD-deficient hemizygous boys, 24 G6PD-deficient homozygous girls, and 200 girls heterozygous for G6PD deficiency received this agent. In the first 2 groups, there was a maximum decrease in hemoglobin averaging −2.64 g/dL (range −6.70 to +0.30 g/dL), which was significantly greater than for the comparator group receiving artemether-lumefantrine (adjusted difference −1.46 g/dL; 95% confidence interval −1.76, −1.15). Hemoglobin concentrations were decreased by ≥ 40% versus pretreatment in 24/119 (20.2%) of the G6PD-deficient children; 13/119 (10.9%) required blood transfusion. In the heterozygous girls, the mean maximum decrease in hemoglobin was −1.83 g/dL (range +0.90 to −5.20 g/dL); 1 in 200 (0.5%) required blood transfusion. All children eventually recovered. All the G6PD-deficient children had the G6PD A− variant, ie, mutations V68M and N126D. Drug-induced acute hemolytic anemia in G6PD A− subjects can be life-threatening, depending on the nature and dosage of the drug trigger. Therefore, contrary to current perception, in clinical terms the A− type of G6PD deficiency cannot be regarded as mild. This study is registered at http://www.clinicaltrials.gov as NCT00344006 and NCT00371735.
Introduction
Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency is common in populations that have been exposed to malaria, either in the present or in the past.1-4 This association appears to have arisen through natural selection,5 as G6PD-deficient individuals are relatively protected from severe malaria.6-8 This is particularly important in children because most fatalities from malaria (∼ 85%) occur in patients younger than 5 years of age. Malaria has been a powerful selective force in endemic areas for several thousands of years. Thus, it is perhaps not surprising that an estimated 330 million people worldwide are G6PD deficient.4
G6PD catalyzes the first step in the pentose phosphate pathway, oxidizing glucose 6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone, coupled to the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) to NADPH. In the erythrocyte, a cell with limited metabolic resources, this is the rate-limiting step in the production of NADPH, a key redox metabolite. In steady-state conditions, NADPH produced in G6PD-deficient erythrocytes by residual G6PD activity is adequate. However, G6PD-deficient erythrocytes are uniquely sensitive to any extra oxidative stress: this will cause cellular damage and premature destruction of erythrocytes through both intravascular and extravascular hemolysis.9 Clinically, this manifests as acute hemolytic anemia (AHA) with malaise, weakness, and abdominal or lumbar pain, which may be associated with passing dark urine (hemoglobinuria), followed by jaundice.9
The best characterized exogenous triggers of hemolysis in G6PD-deficient subjects are, apart from infection, fava beans and drugs.10 The clinical course of primaquine-induced hemolysis (which eventually led to the discovery of G6PD deficiency11 ) was charted in detail more than half a century ago in 6 adult volunteers.12 Since then, numerous drugs have been implicated as causes of G6PD-related hemolysis, most notably dapsone and other sulfones, methylthioninium chloride, niridazole, nitrofurantoin, pamaquin, quinolones, rasburicase, and sulfonamides,13 although most reports are of isolated cases.14
By the year 2000, the spread of chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum had made the malaria situation even worse than before in many African countries.15 The development of a combination of chlorproguanil-dapsone, initiated in the 1990s, was accelerated as a response to this situation.16 A randomized trial of chlorproguanil-dapsone against sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine led to the combination receiving a license in 2003 under the name Lapdap. A greater number of hematologic adverse events occurred in the dapsone-containing arm versus the comparator.17,18 However, the relative risk to G6PD-deficient versus G6PD-normal patients remained not exactly defined because G6PD genotyping was performed in some patients, but not prospectively.17-19 The safety risks of dapsone were outlined at a World Health Organization (WHO) Technical Consultation; G6PD testing was recommended before treatment and a hemoglobin level of < 7.0 g/dL was set as a contraindication for its use in any patient.18
The WHO technical consultation noted that data addressing specifically the risk of G6PD-related AHA in patients with malaria receiving dapsone were not available.18 Anemia had only been occasionally documented with a combination of pyrimethamine and dapsone that was introduced in 1953 (Maloprim) and used mostly for prophylaxis.20 Extensive use of dapsone in leprosy was generally at low doses and under conditions in which drug adverse event reporting would not be expected to occur. On the other hand, data from a study in adult healthy male volunteers had indicated that dapsone did decrease hemoglobin concentrations to a greater degree in primaquine-sensitive (ie, G6PD-deficient) individuals (n = 5) than in G6PD-normal control subjects (n = 10).21
In consideration of these issues, the protocol for 2 large phase 3 trials of the triple combination chlorproguanil-dapsone-artesunate (CDA) required G6PD genotyping of all patients and frequent blood monitoring.22,23 These studies, conducted at multiple sites in Africa, included 1806 malaria patients exposed to dapsone (2.5 mg/kg once daily for 3 days); the majority (95.0%) were children younger than 15 years of age.22,23 G6PD A− was the only mutation detected.24 The data obtained in these trials determined categorically that the use of CDA created an unacceptable risk of hemolysis in G6PD-deficient patients with malaria.22,23 CDA development was discontinued and Lapdap voluntarily withdrawn.19,22,23
In these CDA phase 3 trials, the risk of AHA was evaluated with the use of a composite “hemoglobin safety” end point, defined prospectively as a hemoglobin decrease of ≥ 4.0 g/dL or ≥ 40% versus pretreatment, or hemoglobin < 5.0 g/dL, or blood transfusion.22,23 When this composite end point was used, there was a significant difference between G6PD-normal and G6PD-deficient patients but not between G6PD-normal patients and female patients heterozygous for G6PD deficiency. This picture was clearly not the whole one because some heterozygous female patients had severe hemolysis.22,23
Here, we are reporting in full on the clinical course of acute hemolytic events in 119 children (< 15 years) treated with dapsone (either as chlorproguanil-dapsone or as CDA) in phase 3 trials who were hemizygous or homozygous for G6PD A−. This series is the largest ever reported of the hematologic impact of any drug on G6PD-deficient subjects. Most studies of drug-induced AHA are retrospective in the sense that investigations were initiated only after the patient had become ill. In contrast, this report is compiled from data collected prospectively in which a standard protocol was used. This allows us to examine the onset and time course and the full spectrum of hematologic effects of dapsone-induced AHA. The large dataset also allows statistical analyses that were not possible within the individual studies. The analysis of the 200 G6PD heterozygous females who received dapsone is unique in terms of pharmacogenetics because these individuals cannot be reliably identified by routine G6PD deficiency testing, only by appropriate genotyping. Overall, our findings indicate that contrary to a widespread perception, in many subjects with the African type of G6PD deficiency (G6PD A−), AHA is not mild and can be life-threatening.
Methods
Study design
Data were obtained from 2 multicenter, randomized, double-blind, clinical trials of CDA in acute P falciparum malaria. Details of the conduct of the 2 studies are included in 2 previous articles.22,23 To summarize, patients were randomized 2:1 CDA versus the comparator. In study 006,23 both treatment arms contained dapsone, administered as CDA or as chlorproguanil-dapsone to patients ages > 1 year enrolled from centers in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso; Kumasi, Ghana; Doneguebougou and Banambani, Mali; and Ile-Ife, Jos and Lagos, Nigeria, between April 2006 and May 2007. In study 005,22 CDA was compared with artemether-lumefantrine (AL) in patients ages > 1 to < 14 years enrolled from centers in Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso; Kintampo, Ghana; Eldoret, Kilifi, and Pingilikani, Kenya; Ibadan, Enugu, Jos, and Calabar, Nigeria; and Bagamoyo and Kiwangwa, Tanzania, between June 2006 and August 2007. Investigators were blind to drug treatment and G6PD genotype and phenotype.
Ethics statement
Both clinical trials were conducted according to Good Clinical Practices, applicable regulatory requirements, and the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical approval was obtained from the participating center's ethics committee or institutional review board and the WHO Special Program for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases. Parents or guardians of all patients provided written or oral witnessed informed consent; when patients were 12 years or older, their own assent was required as well.
Participants
Eligible subjects were of either sex presenting with microscopically verified acute uncomplicated P falciparum malaria (parasite count 2000-200 000 μL−1), fever within the previous 24 hours, hemoglobin ≥ 7.0 g/dL or hematocrit ≥ 25%, and weight ≥ 7.5 kg. Exclusion criteria are detailed in the previously published articles.22,23
Procedures
During screening, a full medical history was obtained and a clinical examination performed. Asexual parasite counts were determined via the use of WHO methods.22,23,25 Eligible patients received CDA 2/2.5/4 mg/kg or chlorproguanil-dapsone 2/2.5 mg/kg (both GlaxoSmithKline), both given once daily for 3 days (days 0, 1, 2), or 6-dose AL (Novartis Pharma AG), also given over the course of 3 days.22,23 Patients remained hospitalized between days 0 and 3 in study 005. In study 006, treatment was ambulatory from days 0 to 3; patients were subsequently visited at home from days 4 to 6 for early detection of clinical abnormalities. Follow-up was until day 42 in study 005 and day 28 in study 006. Venous blood samples (2 mL) for hematology evaluations were taken at pretreatment (day 0); days 1, 2, 3, 7, 14, and 28 in both studies; and at day 42 in study 005. Clinical chemistry assessments were made in study 005 at pretreatment (day 0); days 3, 7, and 42 plus days 14 and 28 if previous results were abnormal; and in study 006 at pretreatment, days 3, 7, and 28 plus day 14 if previous results were abnormal.
G6PD genotyping
G6PD genotyping was performed at the Kenya Medical Research Institute, Nairobi, Kenya, with quality control conducted at the Shoklo Malaria Research Unit, Mae Sot, Thailand. PCR amplification was used on a section of the G6PD gene, including G6PD B (wild type), G6PD A (A376G), and G6PD A− (G202A, A542T, G680T, and T968C). The analytical methods have been reported previously.24
Outcomes and statistical methods
The analysis included all enrolled patients ages < 15 years with the G6PD genotype available and hemoglobin data at pretreatment, day 3, and day 7. Data for patients who received dapsone within the CDA or chlorproguanil-dapsone combination were pooled (referred to henceforth as the dapsone group) and compared with results from the AL treatment arm. Patient pretreatment data were reported by the use of descriptive statistics. Changes from pretreatment for hemoglobin and hematocrit were defined as the difference between the pretreatment value and the lowest posttreatment value (maximum decrease or minimum increase), referred to as the “maximum decrease.” For other parameters, changes from pretreatment were defined as the difference between the pretreatment value and the highest posttreatment value (maximum increase or minimum decrease), referred to as the “maximum increase.”
All statistical analyses were performed posthoc. Differences between populations were compared with ANOVA, where adjustments were made for sex, center, age, weight, pretreatment hemoglobin, and G6PD status and in the case of the dapsone group also for study (005 or 006).
Results
Patients
Of 1830 patients with acute uncomplicated malaria, 928 were male and 902 female (Table 1). Of the males, 13.1% (122/928) were G6PD deficient. Among females, 26.2% (236/902) were heterozygous for G6PD deficiency (henceforth referred to as heterozygotes), and 3.3% (30/902) were homozygous for G6PD deficiency (henceforth referred to as homozygotes). On the basis of the frequency of the A− gene in male patients, these figures demonstrated no significant deviation from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Dapsone was received by 119 G6PD-deficient children (95 were hemizygotes and 24 homozygotes) as well as by 200 heterozygotes.
Pretreatment clinical and laboratory data
| Parameter . | G6PD-normal males (n = 806) . | Hemizygous G6PD-deficient males (n = 122) . | G6PD-normal females (n = 636) . | Heterozygous females (n = 236) . | Homozygous G6PD-deficient females (n = 30) . | All subjects (n = 1830) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y | 4.4 ± 3.1 | 4.3 ± 3.2 | 4.6 ± 3.2 | 4.2 ± 3.1 | 3.9 ± 3.1 | 4.4 ± 3.1 |
| Temperature, °C | 37.88 ± 0.99 | 37.75 ± 0.94 | 37.90 ± 0.96 | 37.81 ± 0.96 | 38.05 ± 0.91 | 37.87 ± 0.97 |
| Parasitemia, μL−1 | 52 516 (216-323 361) | 65 220 (1626-705 600) | 56 722 (185-389 415) | 53 429 (484-303 400) | 48 452 (1026-211 546) | 54 876 (185-705 600) |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 10.00 ± 1.57 | 9.94 ± 1.59 | 10.19 ± 1.56 | 9.94 ± 1.36 | 9.47 ± 1.64 | 10.05 ± 1.55 |
| Hematocrit, % | 30.5 ± 4.3 | 30.2 ± 4.6 | 31.0 ± 4.4 | 30.2 ± 3.8 | 29.0 ± 4.1 | 30.6 ± 4.3 |
| Reticulocytes, % | 1.4 ± 1.6 | 1.5 ± 1.4 | 1.5 ± 1.9 | 1.4 ± 1.2 | 1.7 ± 1.4 | 1.5 ± 1.7 |
| WBC ×109/L | 9.6 ± 4.0 | 9.8 ± 4.3 | 9.6 ± 4.0 | 9.7 ± 3.8 | 9.0 ± 4.3 | 9.6 ± 4.0 |
| Unconj bil, μmol/L | 10.1 ± 11.1 | 11.5 ± 13.1 | 10.8 ± 10.5 | 12.3 ± 19.1 | 11.3 ± 8.8 | 10.7 ± 12.4 |
| Platelets × 109/L | 197.0 ± 109.3 | 195.6 ± 88.9 | 199.3 ± 119.8 | 189.4 ± 98.6 | 216.4 ± 134.1 | 197.0 ± 111.0 |
| ALT, IU/L | 26.1 ± 20.7 | 33.8 ± 82.7 | 31.8 ± 42.1 | 29.0 ± 32.2 | 26.2 ± 18.1 | 29.0 ± 37.6 |
| AST, IU/L | 44.7 ± 32.3 | 52.4 ± 80.5 | 47.6 ± 44.6 | 43.8 ± 33.3 | 44.0 ± 23.8 | 46.1 ± 41.8 |
| Dapsone group, n | 631 | 95 | 514 | 200 | 24 | 1464 |
| AL group, n | 175 | 27 | 122 | 36 | 6 | 366 |
| Parameter . | G6PD-normal males (n = 806) . | Hemizygous G6PD-deficient males (n = 122) . | G6PD-normal females (n = 636) . | Heterozygous females (n = 236) . | Homozygous G6PD-deficient females (n = 30) . | All subjects (n = 1830) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y | 4.4 ± 3.1 | 4.3 ± 3.2 | 4.6 ± 3.2 | 4.2 ± 3.1 | 3.9 ± 3.1 | 4.4 ± 3.1 |
| Temperature, °C | 37.88 ± 0.99 | 37.75 ± 0.94 | 37.90 ± 0.96 | 37.81 ± 0.96 | 38.05 ± 0.91 | 37.87 ± 0.97 |
| Parasitemia, μL−1 | 52 516 (216-323 361) | 65 220 (1626-705 600) | 56 722 (185-389 415) | 53 429 (484-303 400) | 48 452 (1026-211 546) | 54 876 (185-705 600) |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 10.00 ± 1.57 | 9.94 ± 1.59 | 10.19 ± 1.56 | 9.94 ± 1.36 | 9.47 ± 1.64 | 10.05 ± 1.55 |
| Hematocrit, % | 30.5 ± 4.3 | 30.2 ± 4.6 | 31.0 ± 4.4 | 30.2 ± 3.8 | 29.0 ± 4.1 | 30.6 ± 4.3 |
| Reticulocytes, % | 1.4 ± 1.6 | 1.5 ± 1.4 | 1.5 ± 1.9 | 1.4 ± 1.2 | 1.7 ± 1.4 | 1.5 ± 1.7 |
| WBC ×109/L | 9.6 ± 4.0 | 9.8 ± 4.3 | 9.6 ± 4.0 | 9.7 ± 3.8 | 9.0 ± 4.3 | 9.6 ± 4.0 |
| Unconj bil, μmol/L | 10.1 ± 11.1 | 11.5 ± 13.1 | 10.8 ± 10.5 | 12.3 ± 19.1 | 11.3 ± 8.8 | 10.7 ± 12.4 |
| Platelets × 109/L | 197.0 ± 109.3 | 195.6 ± 88.9 | 199.3 ± 119.8 | 189.4 ± 98.6 | 216.4 ± 134.1 | 197.0 ± 111.0 |
| ALT, IU/L | 26.1 ± 20.7 | 33.8 ± 82.7 | 31.8 ± 42.1 | 29.0 ± 32.2 | 26.2 ± 18.1 | 29.0 ± 37.6 |
| AST, IU/L | 44.7 ± 32.3 | 52.4 ± 80.5 | 47.6 ± 44.6 | 43.8 ± 33.3 | 44.0 ± 23.8 | 46.1 ± 41.8 |
| Dapsone group, n | 631 | 95 | 514 | 200 | 24 | 1464 |
| AL group, n | 175 | 27 | 122 | 36 | 6 | 366 |
AL indicates artemether-lumefantrine; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; Unconj bil, unconjugated bilirubin; and WBC, white blood cell.
All baseline and laboratory values are mean ± SD except for parasitemia which is mean (range).
At the time they entered the study, most subjects were moderately anemic, probably resulting, at least in part, from their acute malaria (Table 1). Other pretreatment parameters were within normal limits, except for an elevated serum bilirubin, which commonly is observed in patients with acute malaria.26 There were no relevant differences in the mean values or the distributions of pretreatment parameters according to G6PD genotype (Table 1). There were no important differences in the pretreatment parameters of the dapsone group compared with the AL group (data not shown).
Clinical course in comparator group
Patients receiving AL had a small mean decrease in hemoglobin concentration of −0.65 g/dL on day 1 (see supplemental Figure 1, available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article). From day 2 onward, hemoglobin levels stabilized and then increased in the majority of patients (Figure 1). Statistical analyses showed that there was no effect of G6PD status on hematologic parameters that might suggest AHA in the AL group (Table 2). In principle, we can think of 2 not mutually exclusive explanations for this transient decrease in hemoglobin: (1) continuing hemolysis from malaria before parasitemia was cleared; (2) hemodilution as a result of adequate hydration being restored during clinical support of the patient. In corroboration of (1), we know it takes up to 48 hours to clear parasitemia22 ; in support of (2), other analytes, such as unconjugated bilirubin, also decreased from day 1 to day 2 (Figure 2D). None of the children required blood transfusion. Thus, we confirm that there is no evidence of AHA with AL and in this respect, the children who received AL can be regarded as a control group.
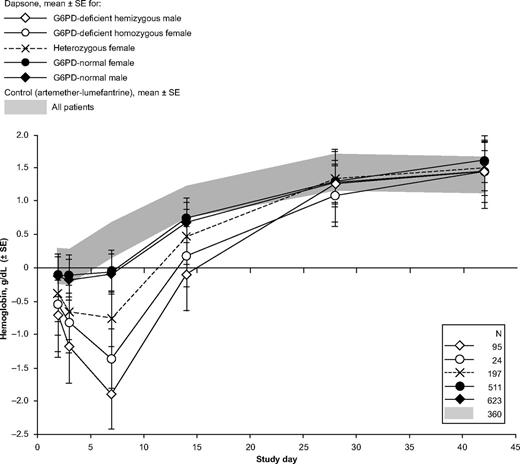
Change in hemoglobin concentrations relative to values obtained at day 1 in children receiving a dapsone-containing combination or AL for the treatment of falciparum malaria. For changes from pretreatment (day 0) values, see supplemental Figure 1.
Change in hemoglobin concentrations relative to values obtained at day 1 in children receiving a dapsone-containing combination or AL for the treatment of falciparum malaria. For changes from pretreatment (day 0) values, see supplemental Figure 1.
Adjusted mean difference between G6PD genotypes in the maximum change from pretreatment values for clinically important laboratory parameters in malaria patients receiving dapsone or AL
| Parameter . | Dapsone . | Artemether-lumefantrine . | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G6PD deficient vs G6PD normal . | G6PD deficient vs heterozygous . | Heterozygous vs G6PD normal . | Analysis of variance P* . | G6PD deficient vs G6PD normal . | G6PD deficient vs heterozygous . | Heterozygous vs G6PD normal . | Analysis of variance P* . | |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | −1.34 (−1.15, −1.52) | −0.91 (−0.68, −1.14) | −0.43 (−0.27, −0.58) | < .001 | 0.06 (0.41, −0.29) | −0.02 (0.47, −0.51) | 0.08 (0.44, −0.28) | .863 |
| Hematocrit, % | −3.8 (−3.2, −4.4) | −2.8 (−2.0, −3.5) | −1.0 (−0.5, −1.5) | < .001 | −0.2 (1.1, −1.5) | 0.7 (2.4, −1.1) | −0.9 (0.4, −2.1) | .400 |
| Reticulocytes, % | 2.4 (1.7-3.1) | 1.0 (0.1-2.0) | 1.4 (0.8-2.0) | < .001 | 0.1 (−0.8, 0.9) | 0.2 (−1.0, 1.3) | −0.1 (−0.9, 0.7) | .956 |
| WBC ×109/L | 1.4 (0.6-2.3) | 0.3 (−0.8, 1.4) | 1.1 (0.4-1.8) | < .001 | 1.0 (−0.4, 2.5) | −0.2 (−2.2, 1.9) | 1.2 (−0.3, 2.7) | .129 |
| Unconj bil, μmol/L | 6.8 (3.8-9.8) | 6.8 (2.8-10.7) | 0.0 (−2.7, 2.8) | < .001 | −2.3 (−6.3, 1.8) | 3.1 (−2.6, 8.7) | −5.3 (−9.5, −1.2) | .028 |
| Platelets ×109/L | −27.4 (−55.0, 0.1) | −43.3 (−78.5, −8.1) | 15.8 (−7.6, 39.2) | .053 | 18.0 (−35.1, 71.1) | −81.3 (−155.2, −7.4) | 99.4 (44.9-153.8) | .002 |
| ALT, IU/L | −4.3 (−18.0, 9.4) | −5.7 (−23.2, 11.8) | 1.4 (−10.3, 13.1) | .796 | −0.2 (−15.3, 15.0) | −2.2 (−23.3, 18.8) | 2.1 (−13.4, 17.6) | .966 |
| AST, IU/L | 6.3 (−14.2, 26.8) | −7.4 (−33.7, 18.9) | 13.7 (−3.9, 31.4) | .273 | 6.3 (−15.2, 27.9) | 1.5 (−28.6, 31.5) | 4.9 (−17.3, 27.0) | .782 |
| Parameter . | Dapsone . | Artemether-lumefantrine . | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G6PD deficient vs G6PD normal . | G6PD deficient vs heterozygous . | Heterozygous vs G6PD normal . | Analysis of variance P* . | G6PD deficient vs G6PD normal . | G6PD deficient vs heterozygous . | Heterozygous vs G6PD normal . | Analysis of variance P* . | |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | −1.34 (−1.15, −1.52) | −0.91 (−0.68, −1.14) | −0.43 (−0.27, −0.58) | < .001 | 0.06 (0.41, −0.29) | −0.02 (0.47, −0.51) | 0.08 (0.44, −0.28) | .863 |
| Hematocrit, % | −3.8 (−3.2, −4.4) | −2.8 (−2.0, −3.5) | −1.0 (−0.5, −1.5) | < .001 | −0.2 (1.1, −1.5) | 0.7 (2.4, −1.1) | −0.9 (0.4, −2.1) | .400 |
| Reticulocytes, % | 2.4 (1.7-3.1) | 1.0 (0.1-2.0) | 1.4 (0.8-2.0) | < .001 | 0.1 (−0.8, 0.9) | 0.2 (−1.0, 1.3) | −0.1 (−0.9, 0.7) | .956 |
| WBC ×109/L | 1.4 (0.6-2.3) | 0.3 (−0.8, 1.4) | 1.1 (0.4-1.8) | < .001 | 1.0 (−0.4, 2.5) | −0.2 (−2.2, 1.9) | 1.2 (−0.3, 2.7) | .129 |
| Unconj bil, μmol/L | 6.8 (3.8-9.8) | 6.8 (2.8-10.7) | 0.0 (−2.7, 2.8) | < .001 | −2.3 (−6.3, 1.8) | 3.1 (−2.6, 8.7) | −5.3 (−9.5, −1.2) | .028 |
| Platelets ×109/L | −27.4 (−55.0, 0.1) | −43.3 (−78.5, −8.1) | 15.8 (−7.6, 39.2) | .053 | 18.0 (−35.1, 71.1) | −81.3 (−155.2, −7.4) | 99.4 (44.9-153.8) | .002 |
| ALT, IU/L | −4.3 (−18.0, 9.4) | −5.7 (−23.2, 11.8) | 1.4 (−10.3, 13.1) | .796 | −0.2 (−15.3, 15.0) | −2.2 (−23.3, 18.8) | 2.1 (−13.4, 17.6) | .966 |
| AST, IU/L | 6.3 (−14.2, 26.8) | −7.4 (−33.7, 18.9) | 13.7 (−3.9, 31.4) | .273 | 6.3 (−15.2, 27.9) | 1.5 (−28.6, 31.5) | 4.9 (−17.3, 27.0) | .782 |
Values are the adjusted mean difference between G6PD genotypes in the maximum change from pre-treatment values (95% CI). In this analysis, each treatment group was compared separately. For hemoglobin and hematocrit, the adjusted mean change is for the maximum decrease (or minimum increase) vs pretreatment values. For all other parameters it is the maximum increase (or minimum decrease) vs pretreatment.
ALT indicates alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; Unconj bil, unconjugated bilirubin; and WBC, white blood cell.
Analysis of variance model included terms for sex, center, age, weight, pretreatment hemoglobin, and G6PD status. For dapsone subjects, a term was also fitted for study (trial 005 or 006).
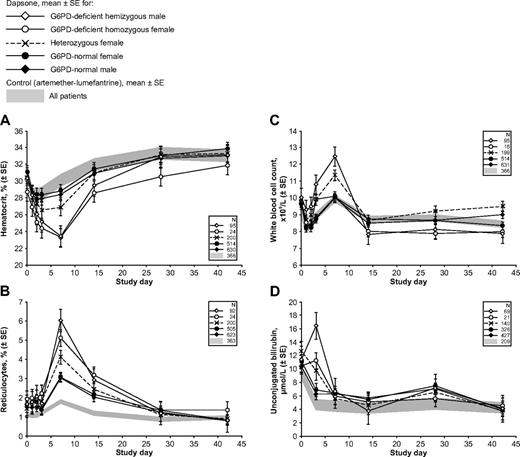
Hemolytic anemia in G6PD-deficient children with malaria receiving therapy with a dapsone-containing combination. The 4 panels report the following clinically important parameters: (A) hematocrit; (B) reticulocytes; (C) white blood cell count; and (D) unconjugated bilirubin. In each panel, the shaded area reflects data from the control group (children receiving AL), and the line plots represent mean values ± SE for children receiving a dapsone-containing combination for the 2 male and the 3 female G6PD genotypes. Similar panels for other laboratory parameters are in supplemental Figures 1 and 2.
Hemolytic anemia in G6PD-deficient children with malaria receiving therapy with a dapsone-containing combination. The 4 panels report the following clinically important parameters: (A) hematocrit; (B) reticulocytes; (C) white blood cell count; and (D) unconjugated bilirubin. In each panel, the shaded area reflects data from the control group (children receiving AL), and the line plots represent mean values ± SE for children receiving a dapsone-containing combination for the 2 male and the 3 female G6PD genotypes. Similar panels for other laboratory parameters are in supplemental Figures 1 and 2.
With respect to platelets, there was an unexplained greater increase in platelet counts in heterozygotes than in G6PD-normal or G6PD-deficient patients (Table 2). On the other hand, on treatment of malaria, there was no statistically significant difference in platelets between G6PD-deficient and G6PD-normal patients (18.0 × 109/L; 95% confidence interval [95% CI] −35.1, 71.1; Table 2).
Clinical course in G6PD-deficient children receiving dapsone
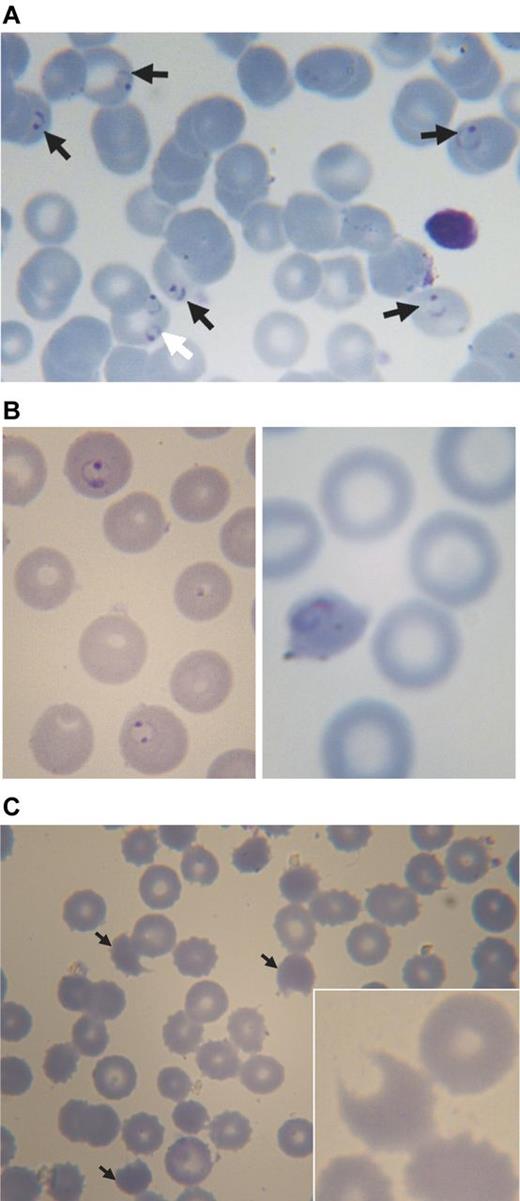
Almost all of the G6PD-deficient children who received dapsone showed evidence of hemolysis, with a marked decrease in hemoglobin (Figure 1, Figure 3). Whereas before treatment the erythrocyte morphology often was normal, except for the presence of P falciparum (Figure 4A), morphologic changes in the erythrocytes consistent with oxidative damage could be seen clearly in these G6PD-deficient children from day 1 (approximately 24 hours after the first dapsone dose), at a time when malaria parasites were still visible (Figure 4B). By day 3, the morphologic evidence of oxidative damage was prominent (Figure 4C).
Variability in hemoglobin levels in individual patients. (A) G6PD-deficient hemizygous male patients (n = 95); (B) G6PD-deficient homozygous female patients (n = 24).
Variability in hemoglobin levels in individual patients. (A) G6PD-deficient hemizygous male patients (n = 95); (B) G6PD-deficient homozygous female patients (n = 24).
Blood smears from a 3-year-old boy with acute malaria and G6PD deficiency treated with chlorproguanil-dapsone. (A) Pretreatment: black arrows point to erythrocytes parasitized by P falciparum (ring forms), the white arrow points to an erythrocyte containing 2 rings of P falciparum. (B) Approximately 24 hours after starting treatment (day 1): on the left abnormally shaped parasites are seen within spherocytes, on the right a parasite in a severely contracted erythrocyte. (C) On day 3: numerous contracted erythrocytes, spherocytes, and hemighosts (often referred to as “bite cells”; arrows). Inset: another hemighost at a greater magnification; the part of the erythrocyte that appears to be missing is the negative image of a Heinz body.51 Slides were prepared with Giemsa stain and Zeiss immersion oil. An Orthoplan light microscope was used (Leitz). Panel C (except the inset) was taken with an objective Plan-Apochromatic ×63 oil, aperture number 1.4 (Zeiss). The inset to panel C and all other photos were taken with objective ×100 oil, aperture number 1.3 (Leitz). Imaging was with a ProgRes C10plus (Jenoptik-Laser Optik Systeme) with acquisition software ProgRes Capture Basic (Jenoptik) running under Windows XP on a personal computer (assembled).
Blood smears from a 3-year-old boy with acute malaria and G6PD deficiency treated with chlorproguanil-dapsone. (A) Pretreatment: black arrows point to erythrocytes parasitized by P falciparum (ring forms), the white arrow points to an erythrocyte containing 2 rings of P falciparum. (B) Approximately 24 hours after starting treatment (day 1): on the left abnormally shaped parasites are seen within spherocytes, on the right a parasite in a severely contracted erythrocyte. (C) On day 3: numerous contracted erythrocytes, spherocytes, and hemighosts (often referred to as “bite cells”; arrows). Inset: another hemighost at a greater magnification; the part of the erythrocyte that appears to be missing is the negative image of a Heinz body.51 Slides were prepared with Giemsa stain and Zeiss immersion oil. An Orthoplan light microscope was used (Leitz). Panel C (except the inset) was taken with an objective Plan-Apochromatic ×63 oil, aperture number 1.4 (Zeiss). The inset to panel C and all other photos were taken with objective ×100 oil, aperture number 1.3 (Leitz). Imaging was with a ProgRes C10plus (Jenoptik-Laser Optik Systeme) with acquisition software ProgRes Capture Basic (Jenoptik) running under Windows XP on a personal computer (assembled).
In most G6PD-deficient children receiving dapsone, there was a gradual recovery of hemoglobin, which returned to the original level between days 28 and 42: this was heralded by a highly significant increase in reticulocytes, peaking at day 7 (Figure 2B). There was also a peak in WBC count at day 7 in hemizygous G6PD-deficient boys (although not for homozygous G6PD-deficient girls; Figure 2C). A substantial fraction of hemolysis in G6PD-deficient subjects exposed to an oxidative agent is extravascular27 and therefore reflected in hyperbilirubinemia (Figure 2D). Statistical analysis of all of these findings is presented in Table 2. Unfortunately, we do not have complete records of hemoglobinuria, a reliable index of intravascular hemolysis.
Given the large number (n = 119) of G6PD-deficient hemizygous boys and homozygous girls who received dapsone, we can chart rather precisely the course of the hemolytic attack (Table 3). The average lowest hemoglobin concentration across the observation period was 7.20 g/dL. The mean maximum decrease in hemoglobin versus pretreatment values was −2.64 g/dL. Considering that the majority of children were anemic before treatment, it is important also to consider the decrease in hemoglobin as the percentage of the pretreatment level; on average −26.0%. The mean maximum decrease versus the day 1 value was −2.08 g/dL. All of these parameters were significantly different from the AL group; statistical data are presented in Table 3.
Changes in clinically important hematologic and clinical chemistry parameters in G6PD-deficient malaria patients after receiving dapsone
| Laboratory parameter . | Dapsone G6PD deficient (n = 119)* . | Control group (n = 366) . | Adjusted difference (95% CI)† . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin | |||
| Lowest value, g/dL | 7.20 ± 1.50 | 8.64 ± 1.41 | −1.04 (−1.29, −0.79) |
| Maximum decrease from pretreatment, g/dL | −2.64 ± 1.58 | −1.37 ± 1.06 | −1.46 (−1.76, −1.15) |
| Maximum decrease from pretreatment, % | −26.0 ± 13.9 | −13.2 ± 9.9 | −13.9 (−16.8, −11.0) |
| Maximum decrease from day 1 value, g/dL | −2.08 ± 0.46 | −0.56 ± 1.47 | −1.61 (−1.91, −1.30) |
| Day 7 value, g/dL | 7.50 ± 1.57 | 9.76 ± 1.48 | −1.80 (−2.08, −1.51) |
| Reticulocytes, % | |||
| Highest value | 6.4 ± 6.6 | 2.3 ± 2.5 | 1.4 (0.5-2.3) |
| Maximum increase from pretreatment | 4.9 ± 6.3 | 1.2 ± 2.3 | 1.4 (0.5-2.3) |
| White blood count, ×109/L | |||
| Highest value | 13.9 ± 5.9 | 11.8 ± 4.5 | 2.3 (1.1-3.5) |
| Maximum increase from pretreatment | 4.0 ± 5.8 | 2.9 ± 4.1 | 1.7 (0.5-2.9) |
| Unconjugated bilirubin, μmol/L | |||
| Highest value | 12.9 ± 14.3 | 4.1 ± 5.5 | 5.0 (2.3-7.8) |
| Maximum increase from pretreatment | 4.4 ± 13.7 | −1.1 ± 7.3 | 4.4 (1.0-7.9) |
| Laboratory parameter . | Dapsone G6PD deficient (n = 119)* . | Control group (n = 366) . | Adjusted difference (95% CI)† . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin | |||
| Lowest value, g/dL | 7.20 ± 1.50 | 8.64 ± 1.41 | −1.04 (−1.29, −0.79) |
| Maximum decrease from pretreatment, g/dL | −2.64 ± 1.58 | −1.37 ± 1.06 | −1.46 (−1.76, −1.15) |
| Maximum decrease from pretreatment, % | −26.0 ± 13.9 | −13.2 ± 9.9 | −13.9 (−16.8, −11.0) |
| Maximum decrease from day 1 value, g/dL | −2.08 ± 0.46 | −0.56 ± 1.47 | −1.61 (−1.91, −1.30) |
| Day 7 value, g/dL | 7.50 ± 1.57 | 9.76 ± 1.48 | −1.80 (−2.08, −1.51) |
| Reticulocytes, % | |||
| Highest value | 6.4 ± 6.6 | 2.3 ± 2.5 | 1.4 (0.5-2.3) |
| Maximum increase from pretreatment | 4.9 ± 6.3 | 1.2 ± 2.3 | 1.4 (0.5-2.3) |
| White blood count, ×109/L | |||
| Highest value | 13.9 ± 5.9 | 11.8 ± 4.5 | 2.3 (1.1-3.5) |
| Maximum increase from pretreatment | 4.0 ± 5.8 | 2.9 ± 4.1 | 1.7 (0.5-2.9) |
| Unconjugated bilirubin, μmol/L | |||
| Highest value | 12.9 ± 14.3 | 4.1 ± 5.5 | 5.0 (2.3-7.8) |
| Maximum increase from pretreatment | 4.4 ± 13.7 | −1.1 ± 7.3 | 4.4 (1.0-7.9) |
Values are mean ± SD except where indicated otherwise. The control group received artemether-lumefantrine. Changes from pretreatment were defined as maximum decrease (or minimum increase) for hemoglobin and hematocrit and as maximum increase (or minimum decrease) for other parameters.
Total of 95 G6PD-deficient hemizygous male plus 24 G6PD-deficient homozygous female patients.
Difference between treatment groups adjusted for sex, center, age, weight, pretreatment hemoglobin, and G6PD status. For dapsone subjects, a term was also fitted for study (trial 005 or 006).
In 13 of 119 (10.9%) G6PD-deficient children treated with dapsone, the hemolytic attack was severe enough to require blood transfusion, which was administered on days 4-7 (supplemental Table 1 and illustrative clinical summaries). One heterozygous female and 2 G6PD-normal male patients also required a blood transfusion.
In 2 of the 95 G6PD-deficient hemizygous boys who received dapsone, there was no decrease in hemoglobin. One was a 4-year-old boy who had received a recent blood transfusion for “malarial anemia” and had a pretreatment hemoglobin level of 11.4 g/dL. It seems probable that the transfused (presumably G6PD-normal) erythrocytes “masked” hemolysis of the boy's endogenous erythrocytes. The other was a 3-year-old hemizygous boy who had a pretreatment hemoglobin level of 7.9 g/dL; in this case, we can only speculate that the child, perhaps in response to preexisting anemia, might have had a young erythrocyte population that would be less sensitive to oxidative hemolysis.
In the girls heterozygous for G6PD deficiency treated with dapsone (n = 200), the mean maximum decrease in hemoglobin concentration was −1.83 ± 1.09 g/dL. The maximum decrease in hemoglobin for heterozygotes was intermediate between that of G6PD-normal and G6PD-deficient patients (Figure 5). Statistical analysis showed that the mean maximum decrease in hemoglobin for heterozygotes was significantly less then that observed for G6PD-deficient patients (adjusted difference −0.91 g/dL; 95% CI −0.68, −1.14) but significantly greater than for G6PD-normal patients (adjusted difference −4.3 95% CI −2.7, −5.8; Table 2). However, in some of the heterozygotes, the hemolytic attack was as severe as in some of the homozygous females (Figure 6).
The G6PD genotype was a major determinant of the severity of anemia in children given dapsone. The cumulative frequency of the maximum decrease in hemoglobin concentration versus pretreatment levels in G6PD-normal children given dapsone was similar to that of the control group; in G6PD-deficient children it is much greater, and in girls heterozygous for G6PD deficiency it is intermediate.
The G6PD genotype was a major determinant of the severity of anemia in children given dapsone. The cumulative frequency of the maximum decrease in hemoglobin concentration versus pretreatment levels in G6PD-normal children given dapsone was similar to that of the control group; in G6PD-deficient children it is much greater, and in girls heterozygous for G6PD deficiency it is intermediate.
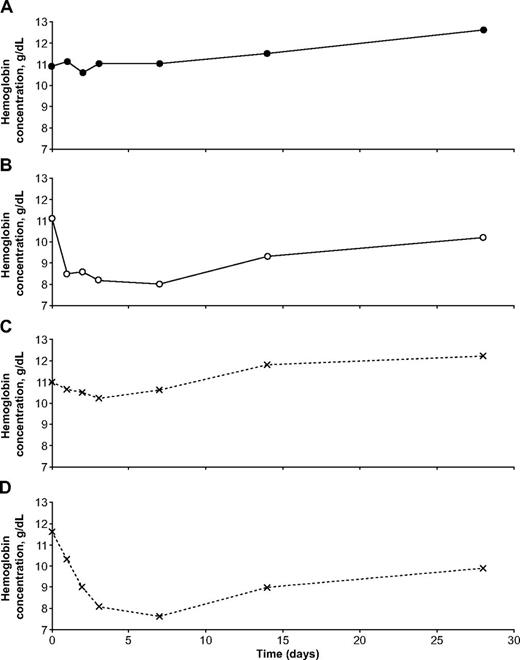
Illustrative examples of the hematologic impact of dapsone in individual patients with falciparum malaria. These 4 girls were all from the same site (Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso). (A) was G6PD normal, (B) was homozygous for G6PD deficiency, and (C) and (D) were heterozygous for G6PD deficiency. It is seen that one of the heterozygotes behaved almost exactly like a G6PD-normal child, whereas the other behaved almost exactly like a homozygous G6PD-deficient child.
Illustrative examples of the hematologic impact of dapsone in individual patients with falciparum malaria. These 4 girls were all from the same site (Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso). (A) was G6PD normal, (B) was homozygous for G6PD deficiency, and (C) and (D) were heterozygous for G6PD deficiency. It is seen that one of the heterozygotes behaved almost exactly like a G6PD-normal child, whereas the other behaved almost exactly like a homozygous G6PD-deficient child.
Methemoglobinemia is known to occur with dapsone; indeed, we found that in the children who received dapsone, the mean highest posttreatment level was 5.2%, (n = 30) whereas in those that received AL it was 1.9% (n = 10). Within the dapsone group, the mean highest posttreatment methemoglobin level in G6PD-deficient children (n = 5) was 8.0% (range 3.2%-15.1%), compared with 4.5% (range 1.5%-15.3%) in G6PD-normal children (n = 21; see supplemental Table 2 for individual patient data and supplemental Figure 2B for data summary).
Discussion
Dapsone regularly causes hemolysis in G6PD-deficient children with malaria. Morphologic changes in the erythrocytes of these children were visible as early as 24 hours after the start of therapy, and the consequent hemolysis resulted in a hemoglobin nadir recorded at day 7, with eventual recovery in most children by day 28.
Although from different parts of Africa, the 119 G6PD-deficient boys and girls included in this analysis constitute a rather homogenous group because they all presented with acute P falciparum malaria and received the same dose of dapsone (2.5 mg/kg/d given for 3 days) within the CDA or the chlorproguanil-dapsone combination. In addition, they all had the same G6PD variant, A−. The hemolysis was associated with hyperbilirubinemia, and it was regularly followed by a significant reticulocyte response (Figure 2). To the best of our knowledge, the time course of these hematologic changes has never been previously reported for such a large series of G6PD-deficient patients with drug-induced AHA. Leukocytosis—with a predominance of granulocytes—may occur in favism,28 and here we confirm that it also occurs in drug-induced AHA. Although urinalysis was not performed routinely, dark urine was noted, particularly in the children who required blood transfusion.
Dapsone-induced hemolysis had previously been studied experimentally in G6PD-deficient healthy adult male volunteers.21 Dapsone was given for 21 days to 5 G6PD-deficient subjects in doses ranging from 25 to 200 mg/d (0.4-2.5 mg/kg/d) and to 10 G6PD-normal controls at doses of 50-300 mg/d (0.7-4.1 mg/kg/d).21 The one G6PD-deficient subject who received a dose similar to that in this series (200 mg/d, equivalent to about 2.5 mg/kg/d) had a decrease in hemoglobin of approximately −3.6 g/dL (it was expressed in the original article in terms of hematocrit). The other drug causing AHA in G6PD-deficient subjects that has been studied experimentally is primaquine: in 6 primaquine-sensitive (subsequently proven to be G6PD-deficient) adult volunteers, 30 mg/d for 6 days (approximately 0.4 mg/kg/d) caused a decrease in hemoglobin of approximately −4.0 g/dL.12 This was evident on day 2 to day 3 (often associated with passing dark urine), reached a nadir about day 8, followed by recovery to pretreatment hemoglobin levels by about day 28, without blood transfusion.12,29,30 The authors remarked that in the only subject who took part in both studies, the hemolysis caused by dapsone 100 mg/d was somewhat less than that caused by primaquine 30 mg/d.21
Several factors can influence the severity of a drug-induced hemolytic attack in a G6PD-deficient subject, including the pharmacology of the drug, the dose, the G6PD mutation, the age, and coexisting disease conditions. If we take into account the differences between the current report and the volunteer studies, particularly with respect to age, the findings are remarkably similar. This is possibly because the volunteer subjects were all African-American, and it became known subsequently that the most common G6PD mutation in African-Americans is G202A, A376G (V68M, N126D),31 the same mutation found in the children in this study.24 On the other hand, there were 2 differences. First, in the volunteer studies, drug sensitivity decreased with continued drug challenge because of a gradual increase in the proportion of young erythrocytes, which have greater G6PD activity than aging cells.30 This did not take place in the current study because dapsone was given for only 3 days. The other, more important difference is that the serious hemolytic effect of dapsone was made more dangerous and sometimes life-threatening in these children because they had malaria, and particularly malarial anemia; at study start 93 of 119 (78.2%) of the hemizygous G6PD-deficient children were anemic, and 7 of 119 (5.9%) were severely anemic (according to WHO definitions).32 In addition, the same absolute decrease in hemoglobin in a child must be regarded as more “severe” than a similar decrease in an adult male because normal hemoglobin levels are lower in children younger 12 years of age (11.5 g/dL) than in adult men (13.0 g/dL).32
Variable severity of hemolysis
Of 119 G6PD-deficient children, 26 (21.8%) had a decrease in hemoglobin of only 13% or less (the mean change in the AL group) versus pretreatment. At the other end of the scale, 24 of 119 (20.2%) G6PD-deficient children had a hemoglobin decrease ≥ 40% versus pretreatment. Such a great variation may appear at first surprising. We did not measure G6PD enzyme activity in this study, but it is possible that in some patients, previous anemia associated with either malnutrition or malaria or both could generate a young erythrocyte population relatively resistant to the oxidative effect of dapsone. The intensity, duration, and variable combination of such factors could account for variability in the hemolytic response to dapsone. In addition, we know very little about the interactions of G6PD with other genetic traits that may affect the vulnerability of erythrocytes with respect to oxidative challenge.
Mechanism of action of dapsone
The most extensive use of dapsone has been in the long-term therapy of leprosy. In several studies, a decrease in the mean hemoglobin level of the order of between −1.0 g/dL and −2.0 g/dL has been documented; and in different studies from 5% to 25% of patients, not all of them G6PD deficient, have developed overt hemolytic anemia.33-35 Apparently, the oxidative action of dapsone is so potent that it can cause damage even to G6PD-normal erythrocytes, but it stands to reason that the damage will be far more severe when the erythrocytes are G6PD deficient. In the current study, there was no evidence of dapsone-related hemolysis in G6PD-normal children, possibly because of the short duration of dapsone therapy used to treat malaria.
Although the precise mechanisms whereby dapsone (4,4′-diaminodiphenylsulfone, or DDS) causes methemoglobinemia and hemolysis are not fully elucidated, several points about its metabolism have been established (see supplemental Figure 3). First, the active molecule, DDS, can be inactivated by acetylation to monoacetyl dapsone; and the steady-state balance between DDS and monoacetyl dapsone can be influenced by genetic polymorphism of N-acetyltransferase-2. DDS is also converted to a hydroxylamine derivative (DDS-NHOH) by enzymes of the P450 cytochrome family; DDS-NHOH is the main metabolite thought to be responsible for the hematologic toxicity of dapsone.36,37 This toxicity depends in part on a reaction between DDS-NHOH and hemoglobin that, in the presence of oxygen, produces methemoglobin and nitroso-dapsone.36 Reactive oxygen radicals (ROS) are known to be generated whenever hemoglobin is converted to methemoglobin, perhaps in greater amounts in the presence of DDS-NHOH and nitroso-dapsone.36 ROS are normally detoxified by GSH, the supply of which ultimately depends on G6PD (see supplemental Figure 3). Consistent with this, in liver microsomes GSH and NADPH are protective against dapsone-induced cellular damage, precisely the molecules that are in limited supply in G6PD-deficient erythrocytes.37 Thus, we can visualize how methemoglobinemia follows dapsone administration independent of G6PD status (as we have indeed observed), whereas the threat posed by ROS to erythrocytes is much greater if these are deficient in G6PD.
Recent work has shown that DDS-NHOH can produce changes in erythrocyte membrane proteins,38 specifically affecting the phosphorylation of band 3. This can cause hemolysis even in G6PD-normal individuals.33-35 However, in G6PD-deficient erythrocytes, membrane remodeling appears to be increased.38 Presumably membrane damage combined with the pressure from ROS ultimately causes the demise of G6PD-deficient cells. Coming back to our patients, serial blood smears have enabled us to visualize dapsone in action: on one hand, the malaria parasites are being dramatically affected—as expected—in number and in shape (Figure 4A-B), and at the same time the erythrocytes are experiencing severe oxidative damage (Figure 4B-C). It is probably the first time that this has been documented.
Hemolysis in G6PD heterozygotes
Data on drug-induced AHA in females heterozygous for G6PD deficiency are limited to case reports. This series included 200 girls who were heterozygous for G6PD A−. From the individual trials, it appeared that female heterozygotes were at no greater risk of clinically significant hemolysis than G6PD normal patients.22,23 However, the greater power of the current pooled analysis has allowed us to outline the spectrum of severity of hemolysis in heterozygotes. As expected, overall this is significantly less than in G6PD-deficient children and is highly variable (Table 2, Figure 5) as can be expected from erythrocyte mosaicism. Indeed, as a result of random X-chromosome inactivation in G6PD heterozygotes, on average 50% of erythrocytes will be G6PD deficient, but the scatter around this mean is wide.39,40 One would expect, therefore, that the severity of hemolysis in heterozygotes will be, on average, approximately half that observed for hemizygous G6PD-deficient males. This is indeed the case with respect to favism41 ; and it has been assumed, but had been never previously proven, for drug-induced AHA. Here for the first time it has become possible to test this theoretical prediction. We found that indeed the decrease in hemoglobin in this group was approximately half way between that of G6PD-normal and that of G6PD-deficient children (Figure 5). At the same time, not surprisingly, within the heterozygote group there were individual cases with severe hemolysis or hardly any hemolysis (Figure 6).
Hemolysis and AL
We found no evidence of G6PD-related hemolysis with AL. A mild decrease in hemoglobin from day 0 to day 1 was reversed in the first few days of therapy across all G6PD genotypes. The mechanism of action of artemisinins is thought to involve the alkylation of heme digested by P falciparum,42 although artemisinin activation also can be triggered by undigested hemoglobin.43 There are a few cases in the literature of hemolytic anemia during or after treatment with intravenous artesunate alone or in combination with mefloquine, and one report after oral treatment with AL in a (G6PD normal) patient with HIV and severe falciparum malaria.44 However, these are rare adverse events. It appears that clinically, in the majority of patients administered artemisinins, the presence of malaria and dehydration rather than the drug exert the most important effects on hematologic parameters.
Testing for G6PD deficiency
It is fortunate that there are today effective antimalarials that can be used safely for the treatment of P falciparum infection in G6PD-deficient children. However, if one had to use a potentially hemolytic agent, as is the case for primaquine with respect to Plasmodium vivax eradication, then testing for G6PD deficiency would be imperative. Although in the past this has been regarded as an unrealistic proposition for many malaria-endemic areas, testing is now possible with minimal facilities (rapid diagnosis test) at low cost and results can be available within an hour.45 A reservation raised commonly with respect to G6PD tests is that they would fail to detect a fraction of heterozygotes. This is certainly true, but those heterozygotes that risk being misclassified as G6PD normal are those that have a majority of G6PD-normal erythrocytes, and therefore they are unlikely to develop a serious hemolytic attack.
Severe hemolytic anemia in G6PD A−
Since the 1960s, a widespread notion about the risk of AHA in G6PD deficiency has been that its severity depends on the specific G6PD variant involved.46 This was based largely on the observation that when primaquine was administered experimentally to G6PD-deficient subjects from Sardinia (who presumably had the G6PD Mediterranean mutation),47 it caused a more severe hemolytic attack than previously reported in African-Americans with G6PD A−.30 In addition, the mean value of G6PD activity in erythrocytes with G6PD Med is lower than in erythrocytes with G6PD A−. A statement in the report of a WHO meeting held in 1966 led to the term “mild” being used for G6PD A−.46 This document also stated that favism, a severe clinical manifestation of G6PD deficiency, did not occur in G6PD A− individuals.46 However, it became clear subsequently that this statement was incorrect: subjects with G6PD A− can develop severe favism.48-50 Despite numerous case reports of severe hemolysis occurring after oxidative challenge in patients with G6PD A−, the notion that the clinical implications of G6PD A− are generally mild has persisted. It is evident from this analysis that patients with G6PD A− are at risk of a serious hemolytic attack whenever the trigger is powerful enough. It remains of course possible that with the same dose of dapsone that was used in these children, hemolytic attacks might be even more severe with other G6PD variants. In the meantime, we submit that the term “mild” for the G6PD A− type of G6PD deficiency can be misleading and should best be abandoned.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the participating patients and their parents and all the other investigators who have been professionally involved in the CDA trials. They are grateful to Ann Miller at GSK for information on dapsone and thank Noelle Henry, Leon Kiswendssida, and Michel Kambire for their help in reviewing slides and Professor Paolo Romagnoli for help with the photomicrographs.
The dataset used in this report was derived from two phase 3 studies included in the CDA clinical trial program that were conducted within a development agreement between the Medicines for Malaria Venture, the World Health Organization Special Program for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases, and GlaxoSmithKline PLC. Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, Liverpool University, and the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine were involved as academic partners. This work, however, was not funded as part of the CDA clinical trial program.
Authorship
Contribution: A.P., N.C., S.D., Z.P., and A.B.T. contributed to the design of the clinical trials. L.L. was not involved in the clinical trial design. A.P., N.D.R., N.C., and L.L. contributed to the analysis plan for the manuscript; Z.P. and A.B.T. were involved in data acquisition; N.C. performed the statistical analysis, and N.D.R and L.L. provided additional analysis; N.D.R. and L.L. wrote the first draft of the article and developed the article through to the final version; A.P. and S.D. documented the clinical cases reported in real time during the trials and provided medical guidance to the overall data analysis plan for the CDA trials; and all authors took part in the preparation of the manuscript and interpretation of data and approved the final version.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: N.C. and A.P. are employees of GlaxoSmithKline PLC and hold share options in GlaxoSmithKline PLC. N.D.R. was funded by GlaxoSmithKline PLC. S.D. is a former employee of GlaxoSmithKline PLC and a current employee of the Medicines for Malaria Venture. L.L. was a member of the Expert Panel summoned by the World Health Organization in Geneva in June 2004 regarding the use of Lapdap. A.B.T.'s institution is in receipt of a grant from GlaxoSmithKline PLC. Since 2010, L.L. has had a consultancy agreement with GlaxoSmithKline PLC for a clinical trial unrelated to dapsone. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Allan Pamba, Director, Public Engagement & Access Initiatives, GlaxoSmithKline Developing Countries and Market Access, GSK House CN6 08, 980 Great Western Road, Brentford, TW8 9GS, London, United Kingdom; e-mail: allan.pamba@GSK.com; and Lucio Luzzatto, Direttore Scientifico, Instituto Toscano Tumori (ITT), Honorary Professor of Haematology, University of Firenza, Via Taddeo Alderotti 26N, 50139 Firenze, Italy; e-mail: lucio.luzzatto@ittumori.it.
References
Author notes
A.P. and N.D.R. contributed equally to this work and should be considered first authors.