Abstract
Abstract 475 FN2
FN2
An IMiDs® immunomodulatory agent, Len has a dual mechanism of action: its tumoricidal effect directly leads to tumor cell death, and its immunomodulatory effect may keep the tumor in remission. A phase 3, randomized, placebo (Pbo)-controlled trial, MM-015 compares MPR-R with fixed-duration MPR and MP induction in transplant-ineligible NDMM pts. Interim results showed unprecedented reduction in disease progression risk with MPR-R (Palumbo et al, IMW 2011); this analysis focuses on pts aged 65–75 yrs in whom the greatest benefit was observed.
A total of 459 pts aged ≥ 65 yrs with NDMM were enrolled. Induction consisted of nine 28-day cycles of melphalan 0.18 mg/kg (D1-4), prednisone 2 mg/kg (D1-4), and Len 10 mg (D1-21) (MPR-R and MPR) or melphalan and prednisone with Pbo (MP). After induction, MPR-R pts received Len 10 mg (D1-21) maintenance until progression; MPR and MP pts received Pbo. Pts with progressive disease (PD) could enroll in an open-label extension phase to receive Len 25 mg (D1-21) ± dexamethasone 40 mg (D1-4, 9–12, and 17–20). This analysis includes data up to Feb 28, 2011 (median follow-up, 30 mos).
There were 116/152 (76%), 116/153 (76%), and 116/154 (75%) of MPR-R, MPR, and MP pts, respectively, aged 65–75 yrs. Nearly 50% had ISS stage III disease, > 40% had β2-microglobulin > 5.5 mg/L, and 40% had CrCL < 60 mL/min.
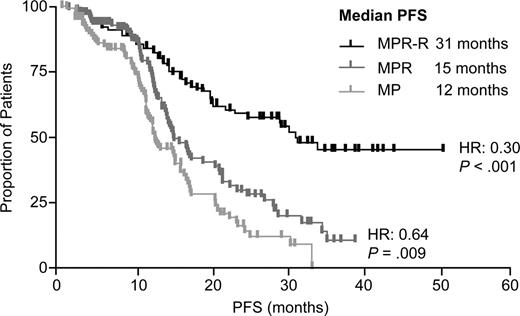
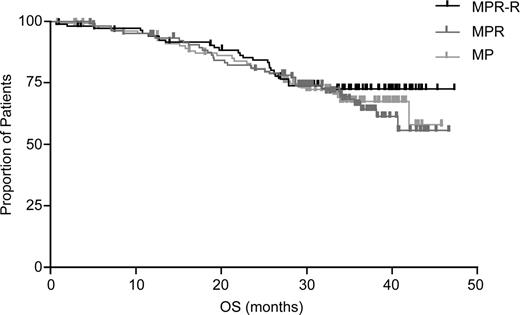
With a median follow-up of 30 mos, MPR-R reduced progression risk by 70% and significantly prolonged median PFS (31 mos) vs MP (12 mos; hazard ratio [HR]: 0.30 [95% CI, 0.20–0.45]; P <.001). PFS benefits were observed regardless of response quality or risk factors. Response rates were higher (79% vs 47%; P <.001) and of better quality (35% vs 10% ≥ very good partial response; P <.001) for MPR-R vs MP with shorter median time to response (2 vs 3 cycles; P =.002). There is a trend for extended OS with MPR-R vs MP (Kaplan-Meier estimated 3-yr OS rates: 73% vs 65%; P =.254).
MPR-R significantly extended median PFS vs MPR (31 vs 15 mos; HR: 0.44 [95% CI, 0.30–0.66]; P <.001). A preplanned landmark analysis calculating PFS from maintenance entry (MPR-R and MPR) demonstrated that Len maintenance reduced the risk of progression by 68% (HR: 0.32 [95% CI, 0.20–0.52]; P <.001). Similar results were observed in patients > 75 years old. Response rates and quality were similar.
MPR induction alone provided a significant PFS benefit vs MP (15 vs 12 mos; HR: 0.64 [95% CI, 0.45–0.90]; P =.009).
MPR induction had an acceptable safety profile, allowing the majority of pts to reach maintenance. During induction, discontinuation due to adverse events (AEs) occurred in 13% of MPR and 4% of MP pts. The most common induction grade (Gr) 4 hematologic AEs for MPR-R, MPR, and MP were neutropenia (39%, 29%, and 7%) and thrombocytopenia (33%, 12%, and 4%). Febrile neutropenia was low for all arms (1%, 1%, and 0%). The most frequent Gr 3/4 nonhematologic AE was bone pain (3%, 3%, and 4%).
Len maintenance was generally well tolerated, with no evidence of cumulative toxicities. Only 5% of Len maintenance pts discontinued due to AEs. The most frequent Gr 4 hematologic AEs were thrombocytopenia (5%), neutropenia (4%), and anemia (3%); and Gr 3/4 nonhematologic AEs included bone pain (5%) and diarrhea (5%).
Hematologic second primary malignancies (SPMs) during induction and maintenance were 3 (2 AML, 1 ALL), 1 (MDS), and 0 in the MPR-R, MPR, and MP arms, respectively. These corresponded to incidence rates (IRs) per 100 pt-yrs of 1.8, 0.7, and 0. Solid tumor SPMs occurred in 2 pts per arm, were heterogeneous and balanced across arms; IRs were 1.2, 1.4, and 1.6, respectively.
Continuous Len treatment with MPR-R significantly reduced disease progression risk compared with MP and MPR in pts aged 65–75 yrs. MPR induction significantly extended PFS vs MP. To date, MPR-R has provided one of the longest median PFS (31 mos) among other available regimens (bortezomib, melphalan, prednisone: 24–27 mos; melphalan, prednisone, thalidomide: 28 mos; bortezomib, melphalan, prednisone, thalidomide: 37 mos). The PFS benefit in the landmark analysis supports continuous treatment to suppress disease in all patient age groups. Management of toxicities is essential to allow pts to continue therapy and receive full benefits. Although hematologic SPMs were imbalanced, the risk of PD/death clearly outweighs the risk of SPMs. MPR-R should be considered a standard of care in transplant-ineligible NDMM pts aged 65–75 yrs.
Palumbo:Merck: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria. Off Label Use: Lenalidomide in newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma. Catalano:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Gisslinger:Celgene: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Speakers Bureau; AOP-Orphan: Speakers Bureau. Wiktor-Jedrzejczak:Celgene: Honoraria; Janssen-Cilag: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding. Delforge:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Weisel:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Van Droogenbroeck:Celgene: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy; Janssen Cilag: Consultancy. Cavo:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Millennium: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Blade:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding. Beksac:Celgene: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Janssen Cilag: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Spicka:Celgene: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Janssen-Cilag: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Honoraria. Yu:Celgene Corporation: Employment. Herbein:Celgene Corporation: Employment. Mei:Celgene Corporation: Employment. Jacques:Celgene Corporation: Employment. Dimopoulos:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal