Abstract
Abstract 4035
NK cells are cytotoxic lymphocytes that have drawn considerable attention in recent years as a promising tool for immunotherapy in patients with various refractory hematological malignancies and metastatic solid tumors. Clinical results of experimental protocols have shown only a partial response attributed mainly to the relatively low number of NK cells infused and their short in vivo persistence.
An important challenge, therefore, in advancing the clinical applicability of NK cells is to expand ex vivo NK cells that display increased functionality upon in vivo infusion. In efforts to induce NK cell expansion, different combinations of cytokines have been studied. However, most reports show a modest expansion and demonstrate a need for additional stimuli.
Nicotinamide (NAM) is a form of Vitamin B3 and a potent inhibitor of enzymes that use NAD for their activity. Hence, NAM is directly involved in the control of redox sensitive enzymes, mitochondrial functions, cell metabolism, the production of energy, and cell motility.
Here we show that NAM (2.5–5 mM) enhances expansion (60-80 fold) of functional NK cells in feeder-free cultures stimulated with IL-2 and IL-15 for two weeks. This effect was observed in cultures initiated with purified CD56+ (CD56 enriched/CD3 depleted) or with CD3 depleted, peripheral blood and cord blood cells.
Immunophenotyping of the cultured NK cells has so far revealed that NAM substantially modulates three cell surface receptors. CD200R and programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) expressed on NK cells interact with their ligands on tumor cells which leads to a suppression in NK cell anti-tumor activity and tumor immunoevasion. These two receptors are down-regulated by NAM. CD62L (L-selectin) defines an NK subset with increased self-renewal capacity and its expression was reported to be pivotal for NK cells trafficking to lymphoid organs and their homeostatic proliferation. Following expansion in culture with IL-2, CD62L is down-regulated, whilst NAM increased its expression with a dose-dependent effect.
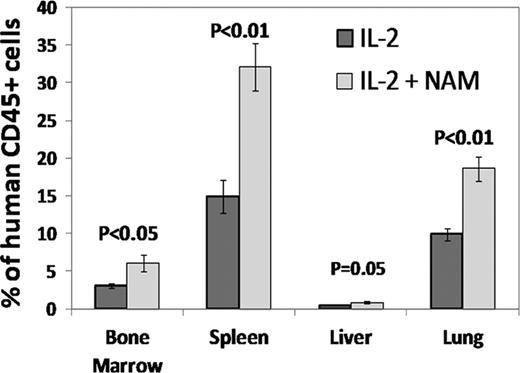
In conclusion, expansion of NK cells with NAM was found to increase in vivo homing and survival and to augment tumor cytotoxic effect of NK cells. This suggests a potential for enhancing the clinical efficacy of adoptively transferred NK cells. Based on these intriguing findings we are developing a cell product for adoptive cell-mediated immune therapy.
Frei:Gamida Cell: Employment. Persi:Gamida Cell: Employment. Lador:Gamida Cell: Employment, Equity Ownership. Peled:Gamida Cell: Consultancy. Nagler:Gamida Cell: Consultancy. Peled:Gamida Cell: Employment, Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal