Abstract
Abstract 3867
Despite their mature appearance, the B cells from chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) possess immature characteristics both functionally and biochemically. CLL B cells display known biochemical markers characteristic of cells early in the blood lineage, including ROR1, Wnt16, and LEF1. In addition, CLL B cells have higher levels of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and of the oxidant-induced transcription factor Nrf2 [NFE2L2], compared to normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). Intracellular ROS status has been suggested to be a marker of cancer stem/progenitor cells possibly due to their high expression of oncogenes. Downstream targets of Nrf2 include the Aldehyde dehydrogenase [ALDH] enzymes, which are believed to play a crucial role in stem cell biology because they protect the cells against oxidative stress caused by accumulation of aldehydes. Here, we use ALDH activity to visualize populations of CLL B cells that may have stem/progenitor properties.
Materials and Methods: Isolated PBMC from normal donors and CLL patients with aggressive and indolent disease were stained for ALDH activity with an Aldefluor assay kit (StemCell Technologies). The ALDH inhibitor, diethylaminobenzaldehyde (DEAB), was used to confirm that the fluorescent activity was due to ALDH activity. At the end of the Aldefluor assay, the cells were stained for cell surface markers, CD19, CD5, CD38 and CD34. 50,000 total events were collected for FACS analysis. Normalized Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) values were calculated by dividing each MFI value to average MFI value of normal CD19+ cells for each experiment. Data analyses were performed by FlowJo software and Prizm. P-values were calculated by One-Way ANOVA analysis with Post-Bonferroni's multiple comparison test.
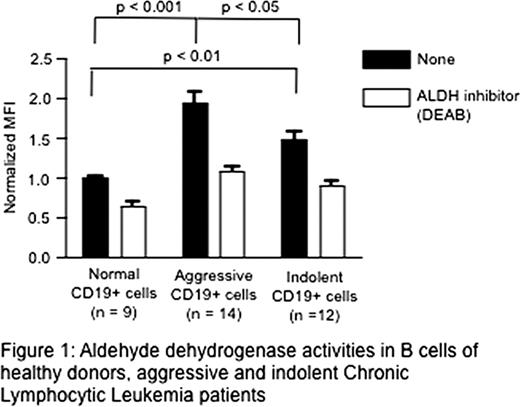
We examine the level of ALDH expression and activity in CD19+ cells of healthy donors (n = 9), CLL samples that expressed unmutated IgVH and that were ZAP-70 positive (defined as “aggressive”, n = 14) or samples that expressed mutated IgVH and were ZAP-70 negative (defined as “indolent”, n=12). CLL B cells from patients with aggressive disease had significantly higher ALDH activities compared to normal B cells (p < 0.001) and indolent CLL B cells (p < 0.05) (Figure1). Indolent CLL B cells also have higher level of ALDH activities compared to normal B cells (p < 0.01) (Figure1). Treatment with the ALDH inhibitor, DEAB, suppressed the increased fluorescence observed in CLL B cells. In addition, ALDH high CLL B cells are CD34 negative. These data show that CLL B cells express a marker known to be associated with stem/progenitor cells, but these populations are different from CD34 positive hematopoietic stem cells. In addition, our data show that a stem/progenitor cell marker is associated with the pathogenesis of CLL.
Kipps:Igenica: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Abbot Industries: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Research Funding; GSK: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal