Abstract
Abstract 143
Despite being exquisitely sensitive to insult, the thymus is remarkably resilient in young healthy animals. Endogenous regeneration of the thymus is a crucial function that allows for renewal of immune competence following infection or immunodepletion caused by cytoreductive chemotherapy or radiation. However, the mechanisms governing this regeneration remain poorly understood. Thymopoiesis is a highly complex process involving cross-talk between developing thymocytes and their supporting non-hematopoietic stromal microenvironment, which includes highly specialized thymic epithelial cells (TECs) that are crucial for T cell development.
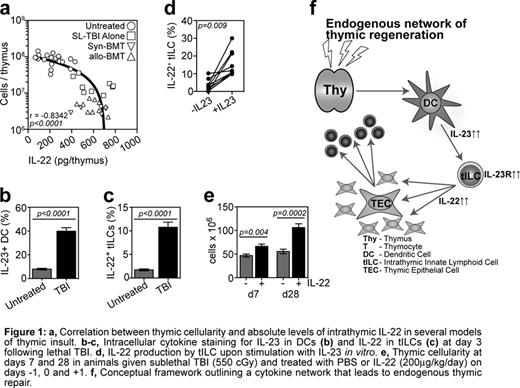
IL-22 is a recently identified cytokine predominantly associated with maintenance of barrier function at mucosal surfaces. Here we demonstrate for the first time a critical role for IL-22 in endogenous thymic repair. Comparing IL-22 KO and WT mice we observed that while IL-22 deficiency was redundant for steady-state thymopoiesis, it led to a pronounced and prolonged loss of thymus cellularity following sublethal total body irradiation (SL-TBI), which included depletion of both thymocytes (p=0.0001) and TECs (p=0.003). Strikingly, absolute levels of IL-22 were markedly increased following thymic insult (p<0.0001) despite the significant depletion of thymus cellularity. This resulted in a profound increase in the production of IL-22 on a per cell basis (p<0.0001). These enhanced levels of IL-22 peaked at days 5 to 7 after SL-TBI, immediately following the nadir of thymic cellularity. This was demonstrated by a strong negative correlation between thymic cellularity and absolute levels of IL-22 (Fig 1a).
In mucosal tissues the regulation of IL-22 production has been closely associated with IL-23 produced by dendritic cells (DCs) and ex vivo incubation of cells with IL-23 stimulates the production of IL-22. Following thymic insult there was a significant increase in the amount of IL-23 produced by DCs (Fig 1b) resulting in similar kinetics of intrathymic levels of IL-22 and IL-23. We identified a population of radio-resistant CD3−CD4+IL7Ra+RORg(t)+ thymic innate lymphoid cells (tILCs) that upregulate both their production of IL-22 (Fig 1c) and expression of the IL-23R (p=0.0006) upon exposure to TBI. This suggests that they are responsive to IL-23 produced by DCs in vivo following TBI and, in fact, in vitro stimulation of tILCs by IL-23 led to upregulation of Il-22 production by these cells (Fig 1d).
We found expression of the IL-22Ra on cortical and medullary TECs (cTECs and mTECs, respectively), and uniform expression across both mature MHCIIhi mTEC (mTEChi) and immature MHCIIlo mTECs (mTEClo). However, in vitro stimulation of TECs with recombinant IL-22 led to enhanced TEC proliferation primarily in cTEC and mTEClo subsets (p=0.002 and 0.004 respectively). It is currently unclear if IL-22 acts as a maturation signal for mTECs, however, the uniform expression of IL-22Ra between immature mTEClo and mature Aire-expressing mTEChi, together with the preferential promotion of proliferation amongst mTEClo and cTEC seem to argue against IL-22 as a maturational signal but rather as promoter of proliferation, which ultimately leads to terminal differentiation of TECs. Of major clinical importance, administration of exogenous IL-22 led to enhanced thymic recovery (Fig. 1e) following TBI, primarily by promoting the proliferation of TECs. Consistent with this, the administration of IL-22 also led to significantly enhanced thymopoiesis following syngeneic BMT.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal