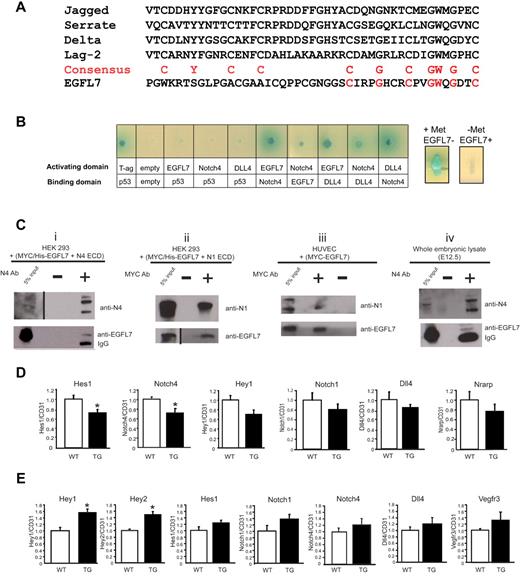
On page 6140 in the 23 December 2010 issue, there are errors in Figure 7A and 7C. In 7A, the DSL domain of Jagged, Serrate, Delta, and Lag-2 are not properly aligned with the putative DSL domain in EGFL7. In 7C, the Notch4 pull-down panels i and iv are the same; panel i was duplicated and used in both panels. In addition, the input and EGFL7 pull-down lanes in panel i are inverted. In the corrected figure, panels i and iv now also show the IgG bands for the EGFL7 pull-downs, and panels ii and iii show the lanes in the order they appear on the original blot. These changes do not in any way alter the results or the conclusion that EGFL7 directly interacts with endothelial Notch. The corrected Figure 7 and legend are shown.
EGFL7 interacts with Notch receptors and regulates Notch target gene expression in vivo. (A) Alignment of the DSL domain of Jagged, Serrate, Delta, and Lag-2 with the putative DSL domain in EGFL7. Red letters represent the consensus sequence. (B) Yeast-2-hybrid assay (left panel): EGFL7 interacts with NOTCH4 and DLL4. Full-length EGFL7, DLL4, or the extracellular domain of NOTCH4 were fused to either the DNA-binding domain or the transcriptional activation domain of GAL4, and protein-protein interactions were monitored by the ability of the transformed yeast to grow on defined medium, and expression of α-galactosidase. Yeast-3-hybrid assay (right panels): EGFL7 abolishes NOTCH4-DLL4 interaction. The Egfl7 ORF was cloned downstream of a methionine repressible promoter (Met25) and transformed into a yeast strain expressing Notch4-GAL activating domain and DLL4-GAL4 DNA-binding domain fusions. Expression of α-galactosidase was then assayed on X-gal selection plates with or without methionine. (Ci-ii) Coimmunoprecipitation assays with protein extracts prepared from HEK293 cells transfected with plasmids encoding MYC/His-tagged-Egfl7 and Notch4 ECD or Notch1 ECD. (i) A NOTCH4 antibody was used to immunoprecipitate NOTCH4 ECD, and protein complexes were probed for NOTCH4 and EGFL7 by Western blot. (ii) A MYC antibody was used to immunoprecipitate EGFL7, and protein complexes were probed for NOTCH1 and EGFL7 by Western blot. (iii) Coimmunoprecipitation assay with protein extracts prepared from HUVECs infected with an adenovirus encoding MYC-tagged-Egfl7. A MYC antibody was used to immunoprecipitate EGFL7, and protein complexes were probed for NOTCH1 and EGFL7 by Western blot. (iv) Coimmunoprecipitation assays using protein lysates prepared from E12.5 embryos. An antibody against NOTCH4 was used to immunoprecipitate NOTCH4, and protein complexes were probed for NOTCH4 and EGFL7 by Western blot. Vertical lines have been inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane. (D) Notch target gene expression in wild-type (□, n = 4) and Tie2-Egfl7 transgenic (■, n = 6) retinas. Gene expression was measured by quantitative RT-PCR and normalized to endothelial cell number using CD31 expression. (E) Notch target gene expression in wild-type (white bars, n = 6) and Tie2-Egfl7 transgenic embryos (black bars, n = 4). Data are represented as fold change compared with wild-type. *P < .05.
EGFL7 interacts with Notch receptors and regulates Notch target gene expression in vivo. (A) Alignment of the DSL domain of Jagged, Serrate, Delta, and Lag-2 with the putative DSL domain in EGFL7. Red letters represent the consensus sequence. (B) Yeast-2-hybrid assay (left panel): EGFL7 interacts with NOTCH4 and DLL4. Full-length EGFL7, DLL4, or the extracellular domain of NOTCH4 were fused to either the DNA-binding domain or the transcriptional activation domain of GAL4, and protein-protein interactions were monitored by the ability of the transformed yeast to grow on defined medium, and expression of α-galactosidase. Yeast-3-hybrid assay (right panels): EGFL7 abolishes NOTCH4-DLL4 interaction. The Egfl7 ORF was cloned downstream of a methionine repressible promoter (Met25) and transformed into a yeast strain expressing Notch4-GAL activating domain and DLL4-GAL4 DNA-binding domain fusions. Expression of α-galactosidase was then assayed on X-gal selection plates with or without methionine. (Ci-ii) Coimmunoprecipitation assays with protein extracts prepared from HEK293 cells transfected with plasmids encoding MYC/His-tagged-Egfl7 and Notch4 ECD or Notch1 ECD. (i) A NOTCH4 antibody was used to immunoprecipitate NOTCH4 ECD, and protein complexes were probed for NOTCH4 and EGFL7 by Western blot. (ii) A MYC antibody was used to immunoprecipitate EGFL7, and protein complexes were probed for NOTCH1 and EGFL7 by Western blot. (iii) Coimmunoprecipitation assay with protein extracts prepared from HUVECs infected with an adenovirus encoding MYC-tagged-Egfl7. A MYC antibody was used to immunoprecipitate EGFL7, and protein complexes were probed for NOTCH1 and EGFL7 by Western blot. (iv) Coimmunoprecipitation assays using protein lysates prepared from E12.5 embryos. An antibody against NOTCH4 was used to immunoprecipitate NOTCH4, and protein complexes were probed for NOTCH4 and EGFL7 by Western blot. Vertical lines have been inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane. (D) Notch target gene expression in wild-type (□, n = 4) and Tie2-Egfl7 transgenic (■, n = 6) retinas. Gene expression was measured by quantitative RT-PCR and normalized to endothelial cell number using CD31 expression. (E) Notch target gene expression in wild-type (white bars, n = 6) and Tie2-Egfl7 transgenic embryos (black bars, n = 4). Data are represented as fold change compared with wild-type. *P < .05.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal