Abstract
Abstract 899
The classic definition of acute (aGVHD) and chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) was based on a cut-off day 100 after transplantation, but this did not reflect that aGVHD can occur later and that symptoms of aGVHD and cGVHD can occur simultaneously. In 2005 a NIH consensus classification was proposed which included 1) classic aGVHD, occurring before day 100, 2) persistent, recurrent or late aGVHD occurring thereafter, 3) classic cGVHD and 4) an overlap syndrome with simultaneous features of aGVHD and cGVHD. Only few studies have evaluated this classification and no studies have determined the differential impact of reduced intensity (RIC) and myeloablative conditioning (MAC).
We retrospectively analyzed 202 AML patients who were transplanted between 1999 and 2008. 102 patients received RIC (generally 6×30 mg/m2 FLU, 4×4 mg/kg BU, 4×10 mg/kg ATG) and immunosuppression with CSA/MMF and 100 patients received MAC (generally 6×2 Gy TBI and 2×60 mg/kg CY) and CSA/MTX. Donors were HLA-matched related (n=82), -matched unrelated (n=88) or -mismatched (n=32).
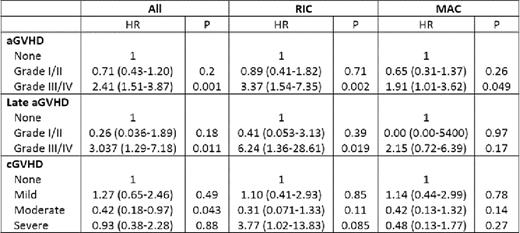
Leukocyte recovery was faster after RIC than after MAC (14 vs. 19 days, P<0.001) but time to reach full donor chimerism was similar (60 vs. 56 days, P=0.12). The cumulative incidence of classic aGVHD was lower after RIC than after MAC (40 vs. 67%, P<0.001) and it occurred later (31 vs. 23 days, P=0.041). No difference was seen in organ manifestations and in the overall aGVHD grade. The cumulative incidence of late aGVHD was low and did not differ between RIC and MAC (9 vs. 7%, P=NS). 13/16 patients with late aGVHD had persistent or recurrent classic aGVHD and 3/16 had de novo late aGVHD. Late aGVHD was less severe after RIC (grade III/IV 22 vs. 86%, P=0.041). The first signs of cGVHD were observed on days 86 after RIC and 97 after MAC with median onset on days 167 and 237, respectively (P=NS). The cumulative incidence of cGVHD tended to be lower after RIC (36 vs. 51%, P=0.088) and it tended to be less severe. Organ manifestations were similar except for cGVHD of the joints and fascia which affected 11% of MAC but no RIC patients (P=0.0021). More than half of cGVHD cases were subclassified as overlap cGVHD with no significant differences between RIC and MAC (51 vs. 65%, P=0.26). In multivariate Cox regression analysis of the whole cohort the only significant risk factor for aGVHD was MAC (HR 2.33, 95%CI 1.51–3.59, p<0.001). In RIC patients the administration of bone marrow lead to less aGVHD (HR 0.13, 95%CI 0.016–0.98, P=0.047). The only relevant risk factor for late aGVHD was prior aGVHD (HR 3.65, 95%CI 1.040–12.81, P=0.043). The most important risk factors for cGVHD were prior aGVHD (HR 2.77, 95%CI 1.64–5.67, P<0.001), female-to-male transplantation (HR 1.94, 95%CI 1.12–3.35, P=0.017) and advanced disease (HR 1.95, 95%CI 1.2–3.1, P=0.018). In multivariate Cox regression analysis with GVHD as time-dependant covariate aGVHD grade III/IV (HR 2.41, 95%CI: 1.51–3.87, P=0.001) and late aGVHD grade III/IV (HR 3.037, 95%CI 1.29–7.18, P=0.011) were associated with inferior overall survival (OS) while moderate cGVHD had a positive effect (HR 0.42, 95%CI 0.18–0.97, P=0.043). Classic and overlap cGVHD had no differential prognostic impact.
This study in AML patients shows that previously established GVHD risk factors remain valid for the new NIH classification. It also confirms the major impact of conditioning intensity on GVHD incidence, the negative prognostic impact of severe aGVHD and the benefit of moderate cGVHD. The new category late aGVHD may only include few patients but will allow more adequate allocation to therapies or clinical trials. Whether the subgroups classic and overlap cGVHD are clinically relevant remains to be determined.
Multivariate Cox regression analysis of OS.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal