Abstract
Abstract 818
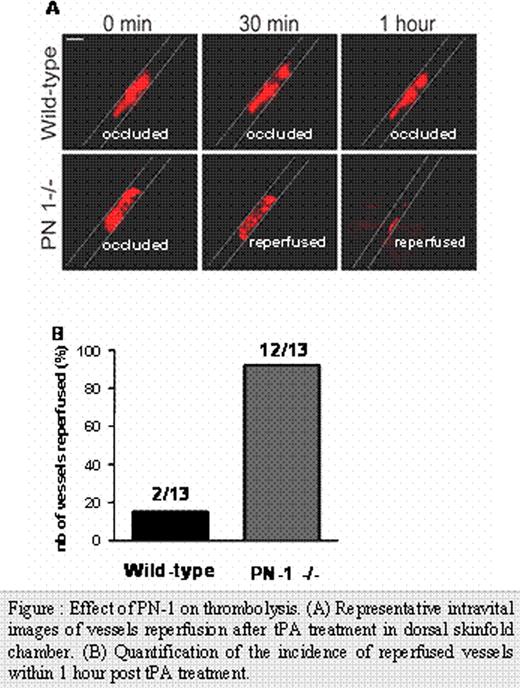
Fibrinolysis, a physiological process leading to clot resorbtion, is strictly controlled by fibrin-localized plasminogen activators (tPA and uPA) and by inhibitors like plasminogen activator type-1 (PAI-1). The serpin PAI-1 is a plasmatic serine protease inhibitor, that is also stored in platelets α-granules. PAI-1 inhibits both the action of urokinase- and tissue-type plasminogen activators (uPA and tPA respectively), and is up to now considered as the principal inhibitor of fibrinolysis in vivo. Interestingly, platelets are also known to inhibit fibrinolysis by both PAI-1-dependent and PAI-1-independent mechanisms. The individual role of other serpins, specifically protease nexin-1 (PN-1) in the thrombolytic process has not been investigated so far. Indeed, we recently demonstrated that a significant amount of PN-1 is stored within the α-granules of platelets and plays an antithrombotic function in vivo. PN-1, also known as SERPINE2, deserves a special interest since it also significantly inhibits in vitro uPA, tPA and plasmin. In this study, we explored the effect of PN-1 on fibrinolysis in vitro and in vivo. We evidenced the antifibrinolytic activity of platelet PN-1 in vitro using a specific PN-1-blocking antibody and PN-1 deficient platelets and, in vivo in PN-1−/− mice. Our data directly indicate that platelet PN-1 inhibits both tPA and plasmin activities in fibrin zymography. Remarkably, whereas fibrin-bound tPA or plasmin activity is not affected by PAI-1, we showed that PN-1 inhibits both plasmin generation induced by tPA-bound to fibrin and fibrin-bound plasmin. Moreover, PN-1 blockade or PN-1 deficiency result in an increased lysis of fibrin clots generated from platelet-rich plasma indicating that PN-1 regulates endogenous tPA-mediated lysis. Rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM®) analysis shows that platelet PN-1 significantly decreases the rate of fibrinolysis ex vivo. Futhermore, blockade or deficiency of PN-1 provides direct evidence for an acceleration of the lysis-front velocity in platelet-rich clots. To challenge the role of PN-1 on fibrinolysis in vivo, we have developed an original murine model of thrombolysis. Using a dorsal skinfold chamber, thrombus formation induced by ferric chloride injury of venules and subsequent thrombolysis were visualized by microscopy on alive animals. This new approach allows a reproducible quantification of thrombus formation and of tPA- induced thrombus lysis. We observed that thrombi are more readily lysed in PN-1-deficient mice than in wild-type mice. Moreover, in PN-1 deficient mice, the rate and the extent of reperfusion were both increased (Figure A and B). These data demonstrate that platelet PN-1 is a new negative regulator of thrombolysis activity of plasmin, both in solution and within the clot. For the first time, this study shows that PN-1 protects towards thrombolysis and therefore could give rise to new approaches for therapeutic application. Indeed, PN-1 might be a promising target for optimizing thrombolytic therapy by tPA.
Effect of PN-1 on thrombolysis. (A) Representative intravital images of vessels reperfusion after tPA treatment in dorsal skinfold chamber. (B) Quantification of the incidence of reperfused vessels within 1 hour post tPA treatment
Effect of PN-1 on thrombolysis. (A) Representative intravital images of vessels reperfusion after tPA treatment in dorsal skinfold chamber. (B) Quantification of the incidence of reperfused vessels within 1 hour post tPA treatment
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal