Abstract
Abstract 726
ARC1779 is an aptamer that inhibits the prothrombotic function of VWF by binding the A1 domain of VWF and thereby blocking its interaction with the platelet GPIb receptor. It has been hypothesized that effective inhibition of the formation of microthrombi by ARC1779 during the acute treatment of TTP may result in short courses of plasma exchange (PE), but may also decrease end organ complications via the rapid inhibition of the development of microthrombotic disease.
Eligibility for the study included a platelet count of <100 ×109/L, microangiopathic findings, and the absence of an alternative explanation. Exclusion criteria included, malignancy or co-morbid condition with a life expectancy <3 months, or an additional diagnosis that accounts for the thrombocytopenia and microangiopathic findings. A total of 9 subjects (7 ARC1779, 2 placebo) were enrolled prior to the study being terminated by the sponsor (Table 1).
Patients were randomized (3:1) to either ARC1779 or placebo concurrently with therapy. ARC1779 was given as an intravenous loading dose (12.43 mg/kg) followed by a maintenance infusion (0.0006 mg/kg/min). The ARC1779 infusion continued during PE, but an additional re-loading dose (50% of the initial loading dose) was given at the completion of each PE. The infusion continued until achieving a response, defined by normalization of the platelet count (≥150 ×109) on each of 3 consecutive days, or to a maximum of 14 days. The dose was then tapered by 50% daily over two days and discontinued. Immune suppressive therapy (corticosteroids, rituximab) was permitted at investigator discretion. Treatment response, pharmacodynamic data (von Willebrand activity), and end organ injury (troponin-I, S100B) were studied prior to and throughout the treatment course.
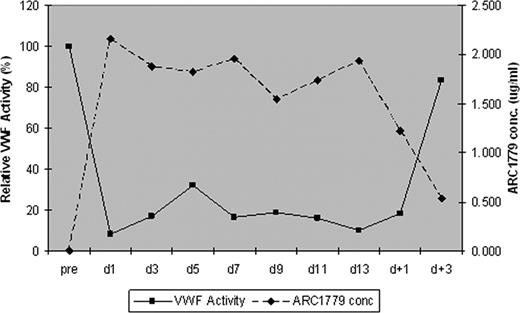
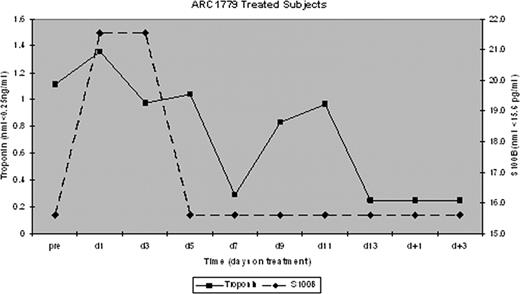
All 9 patients received daily PE. 6/7 patients receiving ARC1779 achieved a response after a median of 6 days (range, 5–15) compared to the 2 placebo patients who did not achieve a response within 14 days. Serial measurement of the VWF activity in the context of ARC1779 concentration (Figure 1) and the median troponin-I and S100B concentrations for ARC1779 treated subjects are shown in Figure 2. There were no bleeding complications despite documented, prolonged inhibition of VWF activity throughout therapy with ARC1779.
These data provide support for the concept of therapy directed at preventing the formation of microthombi in the treatment of acute TTP. The efficacy and safety of these novel therapeutic strategies will need to be assessed in the frame of large clinical trials, a challenge for clinical scientists who work on this rare disease.
Demographic details for all enrolled subjects.
| . | Age (range) . | Sex (M/F) . | Race . | Med. Platelet (× 106/uL) . | LDH (U/L) . | Hgb (g/dL) . | Serum Creat. (mg/dL) . | History TTP . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARC1779 (n=7) | 44 (33–51) | 4/3 | 3AA/4C | 12 (6–41) | 1063 (263–1804) | 7.0 (5.5–10.7) | 1.31 (0.8–2.46) | 3/7 |
| Placebo (n=2) | 32; 70 | 0/2 | 2C | 27; 6 | 647; 1258 | 8.5; 7.3 | 4.54, 0.99 | 0/2 |
| . | Age (range) . | Sex (M/F) . | Race . | Med. Platelet (× 106/uL) . | LDH (U/L) . | Hgb (g/dL) . | Serum Creat. (mg/dL) . | History TTP . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARC1779 (n=7) | 44 (33–51) | 4/3 | 3AA/4C | 12 (6–41) | 1063 (263–1804) | 7.0 (5.5–10.7) | 1.31 (0.8–2.46) | 3/7 |
| Placebo (n=2) | 32; 70 | 0/2 | 2C | 27; 6 | 647; 1258 | 8.5; 7.3 | 4.54, 0.99 | 0/2 |
Serial VWF activity measurements prior to and during therapy with ARC1779.
Serial VWF activity measurements prior to and during therapy with ARC1779.
Median troponin-I and S100B measurements for time points prior to, during, and after the discontinuation of ARC1779.
Median troponin-I and S100B measurements for time points prior to, during, and after the discontinuation of ARC1779.
Cataland:Archemix Corp.: Consultancy. Peyvandi:Archemix Corp.: Consultancy. Mannucci:Archemix Corp.: Consultancy. Lämmle:Archemix Corp.: Consultancy. Kremer Hovinga:Archemix Corp.: Consultancy. Machin:Archemix Corp.: Consultancy. Scully:Archemix Corp.: Consultancy. Rock:Archemix Corp.: Consultancy. Gilbert:Archemix Corp.: Consultancy. Knoebl:Archemix Corp.: Consultancy. Jilma:Archemix Corp.: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal