Abstract
Abstract 4107
A somatic point mutation of Janus Kinase 2 (JAK2) tyrosine kinase (JAK2 V617F) has been shown to occur at a high frequency in myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) patients. JAK2 V617F is a constitutively activated kinase that activates the JAK/STAT signaling pathway and dysregulates cell growth and function. These findings suggest that the inhibition of aberrant JAK2 activation has a therapeutic benefit.
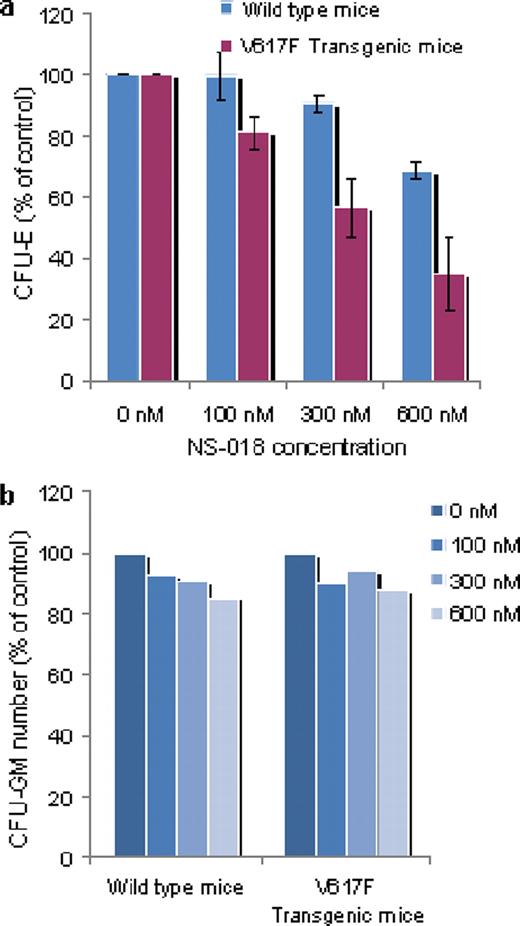
Our novel JAK2 inhibitor, NS-018, is highly active against JAK2 with an IC50 value of less than 1 nM, and it has 30–50-fold selectivities for JAK2 over other JAK-family kinases such as JAK1, JAK3 and Tyk2. We determined the X-ray structure of JAK2 in complex with NS-018. An Asp-Phe-Gly (DFG) motif is located at the N-terminus of the activation loop and regulates ATP binding. The resolved X-ray structure showed that NS-018 bound to JAK2 in the “DFG-in” active conformation. A molecular modeling study indicated that NS-018 would hardly bind to JAK2 in the “DFG-out” inactive conformation. In accordance with the structural analysis, NS-018 preferentially suppressed the growth of bone-marrow cells expressing activated JAK2. Thus, NS-018 reduced in a dose-dependent manner the number of erythroid colony-forming units (CFU-E) derived from bone-marrow cells taken from JAK2 V617F transgenic mice, but had only a limited effect on the number of colonies from wild-type mice (Figure A). NS-018 had no effect on the number of granulocyte-macrophage colony-forming units (CFU-GM) from either mouse strain. Furthermore, NS-018 showed potent antiproliferative activity against Ba/F3 cells expressing JAK2 V617F with an IC50 value of <100 nM but showed only minimal cytotoxicity against most other hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cell lines (IC50 >3 μ M). In a mouse Ba/F3-JAK2 V617F leukemia model, NS-018 significantly prolonged survival during repeated oral administrations at 6.25 mg/kg bid and reduced splenomegaly at doses as low as 1.5 mg/kg bid. NS-018 was well tolerated at dosages of more than 100 mg/kg bid.
In conclusion, NS-018 is a potent JAK2 inhibitor which preferentially inhibits an activated form of JAK2 and has potent in vitro and in vivo efficiency in preclinical studies. NS-018 is expected to be suitable for the treatment of MPN caused by aberrant JAK2 activation and its effectiveness will be verified by early-phase clinical investigations in the near future.
JAK2 V617F preferential inhibition of erythrocyte colony growth
Bone-marrow cells were collected from femurs of JAK2 V617F transgenic mice and same-strain BDF1 wild-type mice. (a) To detect CFU-E colonies, cells were treated with NS-018 in semisolid methylcellulose containing erythropoietin (EPO) and cell clusters were counted after incubation for two days. (b) To detect CFU-GM colonies, cells were treated with NS-018 in semisolid methylcellulose containing EPO, interleukin-3 (IL-3), IL-6 and stem cell factor and colonies were counted on day 7.
Nakaya:Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd: Employment. Naito:Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd: Employment. Homan:Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd: Employment. Sugahara:Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd: Employment. Horio:Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd: Employment. Niwa:Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd: Employment. Shimoda:Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal