Abstract
Abstract 3737
Umbilical Cord Blood (UUCB) Regulatory T cells (Tregs) co-expressing CD4/CD25 have been shown to inhibit alloreactive T cell function. We hypothesized that prophylactic infusion of 3rd party UCB Tregs can abrogate Graft versus Host Disease (GvHD).
(a) Treg generation: Naturally occurring CD25+ Tregs, purified from thawed UCB units by magnetic activated cell sorting (MACS) using Miltenyi CD25 reagents (as per manufacturer's instructions), were cultured at 1×106 cells/ml in ExVivo medium (Gibco) containing interleukin (IL)-2 (100 IU/ml) with irradiated K562 cells engineered to express CD86, CD69, CD187c, IL-15, CD64 and OKT3 (provided by Dr. Laurence Cooper, MDACC) or with microbeads bearing CD3 and CD28 antibodies on their surface (T-Cell Expander, Invitrogen). Cultures were initiated at a ratio of 1 Treg: 4 engineered K562 cells or Invitogen beads and maintained at 1×106 cells/ml over a 14 day period by the addition of fresh medium. Fresh IL-2 was added to maintain 100 IU/ml on an every-other-day basis. Flow cytometry, Western blot analysis and demonstration of ability to reduce in vitro MLR reactions confirmed the Treg phenotype of the expanded cells. (b) Xenogeneic graft vs. host model: On day -1, NOD-SCID IL2Rgnull (NSG) mice were sublethally-irradiated (320 cGy) and received 107 Treg cells intravenously. On day 0, 107 human apheresis PBMCs were injected intravenously. Mice were regularly monitored, weighed and graded according to a GvHD scale developed by Dr. James Ferrara (University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center).
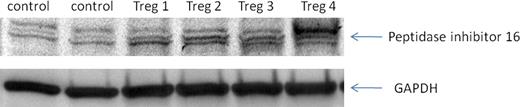
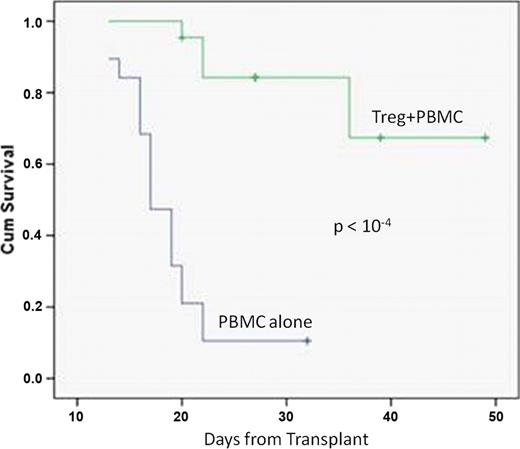
(a) Ex vivo Treg expansion of up to 700 fold was achieved yielding approximately 2.5×108 Treg cells from an average frozen UCB unit. Analysis of the ex vivo expanded product after 14 days revealed: (i) 95% co-expressed FOXP3/CD4/CD25 (flow cytometry), and (ii) expression of peptidase inhibitor 16, known to be uniquely associated with FOXP3 expression (western blot, Figure 1). Further, addition of UCB Tregs showed suppression of two-way allo-MLR by 93% (measured by tritiated thymidine and CFSE studies). (b) In the NSG GvHD model, mice receiving PBMC showed: (i) a significant (P=0.0002, student's paired t-test) 30% reduction in body weight, (ii) gross evidence of GvHD (average Ferrara score of 6) and (iii) reduced survival, when compared to mice receiving intravenous injection of Tregs on day -1. By comparison, mice receiving Tregs on day -1: (i) did not lose weight, (ii) scored consistently lower on the Ferrara scale (average score of 3) and (iii) had significantly improved survival (70% survival vs. 15%; P < 10-4, figure 2). Xenogenic transplanted mice showed clear histopathological evidence of GvHD in skin, gut, liver, spleen, lung, esophagus, and bone marrow whereas histopathology remained comparable to controls in the Treg rescued mice.
Infusion of 3rd party UCB Tregs markedly reduced the severity of xenoGVHD in a mouse transplant model. These preclinical data support the initiation of a phase I/II clinical trial to assess the efficacy of third party allogenic UCB Tregs in a traditional transplant setting.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal