Abstract
Abstract 2780
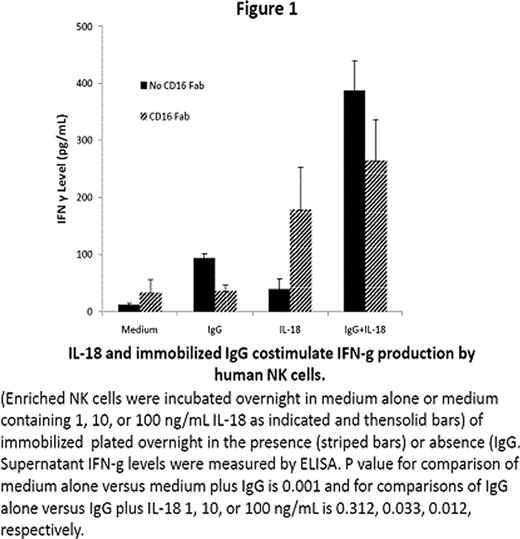
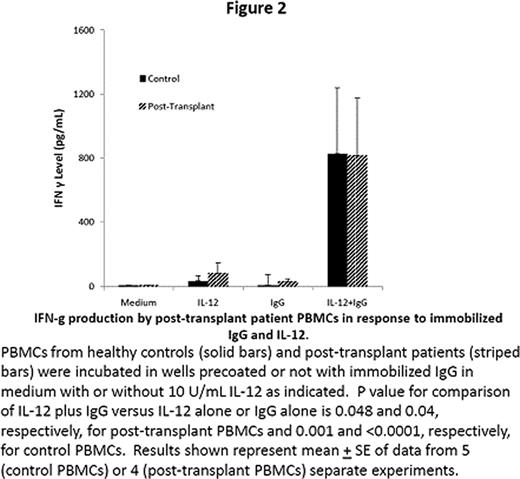
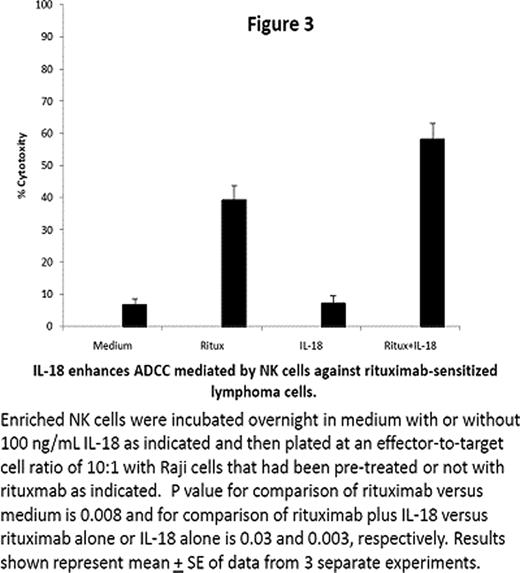
NK cells play an important role in innate and adaptive immune responses. Most human NK cells express CD16, an Fc receptor for IgG that mediates lysis of antibody-coated target cells and costimulates interferon (IFN)-g production in response to cytokines. IL-18 is an immunostimulatory cytokine with antitumor activity in preclinical animal models. The effects of IL-18 on human NK cell function were examined. Here we show that NK cells stimulated with immobilized IgG in vitro secreted IFN-g; such IFN-g production was partially inhibited by blocking CD16 with monoclonal antibodies. IL-18 augmented IFN-g production by NK cells stimulated with immobilized IgG or CD16 antibodies (Figure 1). NK cell IFN-g production in response to immobilized IgG and/or IL-18 was inhibited by chemical inhibitors of Syk, extracellular signal-related kinases (ERK), p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K). Stimulation with IL-18 or immobilized IgG could augment IL-12-induced IFN-g production by STAT4-deficient lymphocytes obtained from lymphoma patients after autologous stem cell transplantation (Figure 2). IL-18 also augmented the in vitro lysis of rituximab-coated Raji cells by human NK cells (Figure 3). These observations that IL-18 can co stimulate IFN-g production and cytolytic activity of NK cells activated through Fc receptors makes it an attractive cytokine to combine with monoclonal antibodies for treatment of cancer.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal