Abstract
Abstract 216
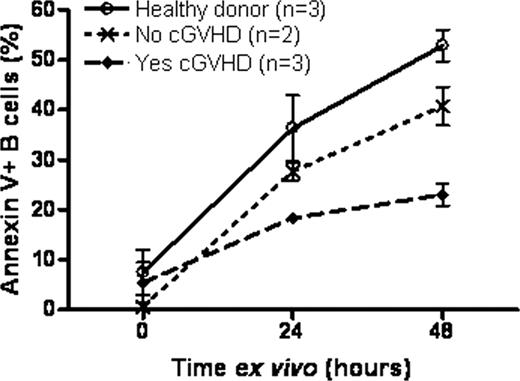
High BAFF levels correlate with the presence of activated B cells in patients who develop cGVHD after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. B cell reconstitution in these patients occurs under constant exposure to alloantigens, and we previously showed that B Cell Receptor (BCR) stimulated CD27+ B cells in cGVHD patients are activated, capable of spontaneous IgG production without requirement of further BCR or second signal stimulation. B cell survival is dependent on both BCR and BAFF signaling. BAFF is known to attenuate B cell apoptosis by counteracting pro-apoptotic Bcl-2-interacting mediator of cell death (Bim) protein, but it is not known whether BAFF can provide survival signals to activated B cells in cGVHD. Therefore, we examined the survival rates of B cells in cGVHD. CD19+ B cells were purified (>95% purity) by magnetic bead sorting. Rates of death were measured by flow cytometry staining with propidium iodide and Annexin V of unmanipulated B cells cultured without addition of cytokines over time. After 24 and 48 hours, the frequency of cells undergoing apoptosis (Annexin V+) B cells was significantly lower in samples from patients with cGVHD compared to those without cGVHD and to healthy individuals (one-way ANOVA p=0.007, Figure 1 ). In addition to Annexin V + cells, total death rates as measured by propidium iodide of unmanipulated purified CD27+ B cells were lower in cGVHD compared to healthy individuals. Importantly, we found that the frequency of propidium iodide stained CD27+ B cells did not increase 24 hours ex vivo if BAFF was added in cGVHD, but not in healthy, CD27+ B cells, consistent with BAFF mediated survival in these cells (Table 1 ). Further examination of CD27+ B cell subsets ex vivo was performed to determine if subpopulations we previously identified to uniquely circulate in cGVHD patients were more viable. The morphology of pre-germinal center (GC) CD27+IgD+CD38Hi cells and the antigen-inexperienced, most recent bone marrow emigrants, transitional CD27NegIgD+CD38Hi cells was compared. Unlike transitional cells, the pre-GC cells were enlarged, adherent and viable, consistent with an activated state. While the Bim isoforms are upregulated after BCR activation or by apoptosis-inducing drugs, Bim is degraded in response to BAFF signaling. Since steroids (previously shown to increase Bim in lymphocytes) are the only standard therapy for cGVHD and unfortunately often clinically ineffective, we first performed in vitro assays with dexamethasone and BAFF. Ninety-five percent of healthy CD19+ purified B cells were induced to apoptose (94.9% Annexin V+) with dexamathasone at 24 hours. Addition of BAFF blocked dexamethasone-induced apoptosis to the baseline levels found in untreated B cells (27.3% Annexin V+). Next, to determine whether in vivo BAFF survival signaling of B cells occurred in cGVHD patients, we examined protein levels of Bim by immunoblotting cell lysates from freshly purified unmanipulated CD19+ cells. B cells from healthy individuals did not generate the long form of Bim (BimL), likely due to the lack of BCR activation in these B cells, while 80% of patients with inactive cGVHD had increased BimL. In contrast, 75% of B cells from patients with active cGVHD lacked BimL. Thus, loss of BimL in cGVHD is likely BAFF-driven and may contribute to improved survival of potentially allo- or autoreactive B cells in cGVHD. Potential upstream activators of Bim degradation and inhibition such as mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK activating kinase (MEK) or NFkB, respectively, are currently being investigated. In addition to characterizing a potential therapeutic role for MEK and NFkB inhibitors, since Bim has been shown to be increased with proteasome inhibitor and BH3 mimetic induced cell death, these findings begin to delineate immunologic rationale for the therapeutic use of these agents to target B cells in cGVHD. Taken together, our data suggest that activated and potentially pathologic B cells in cGVHD utilize distinct survival pathways. Thus, activated B cells represent novel therapeutic targets in cGVHD.
Table 1.
| CD27+ B Cell Source . | % PI at Time 0 (mean +/-SD) . | % PI at 24 Hours (mean +/-SD) . | % PI at 48 Hours (mean +/-SD) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy | 12.8 +/- 10.7 (n=3) | 34.9 +/- 8.7 (n=2) | 34.3 +/- 9.6 (n=3) |
| Healthy +BAFF | 33.1 +/- 9.1 (n=2) | 42.2 +/- 11.4 (n=2) | |
| Yes cGVHD | 13.5 +/- 5.9 (n=3) | 20.5 +/- 3.1 (n=2) | 34.8 +/- 4.0 (n=3) |
| Yes cGVHD +BAFF | 14.8 +/- 5.4 (n=2) | 29.7 +/- 2.7 (n=2) |
| CD27+ B Cell Source . | % PI at Time 0 (mean +/-SD) . | % PI at 24 Hours (mean +/-SD) . | % PI at 48 Hours (mean +/-SD) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy | 12.8 +/- 10.7 (n=3) | 34.9 +/- 8.7 (n=2) | 34.3 +/- 9.6 (n=3) |
| Healthy +BAFF | 33.1 +/- 9.1 (n=2) | 42.2 +/- 11.4 (n=2) | |
| Yes cGVHD | 13.5 +/- 5.9 (n=3) | 20.5 +/- 3.1 (n=2) | 34.8 +/- 4.0 (n=3) |
| Yes cGVHD +BAFF | 14.8 +/- 5.4 (n=2) | 29.7 +/- 2.7 (n=2) |
Disclosures:
Off Label Use: NFkB inhibitor, MEK inhibitor, BH3 mimetic, bortezomib for chronic graft versus host disease.
Author notes
*
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
© 2010 by The American Society of Hematology
2010

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal