Abstract
Abstract 2006
Several gene expression signatures predict survival in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), but the lack of practical methods for genome scale analysis has limited translation to clinical practice.
We examined the power of individual genes to predict survival across different therapeutic eras. In studying 787 patients with DLBCL, we built and validated a simple model employing one gene expressed by tumor cells and another expressed by host immune cells, assessing added prognostic value to the clinical International Prognostic Index (IPI). We validated models in an independent cohort using diagnostic formalin-fixed specimens.
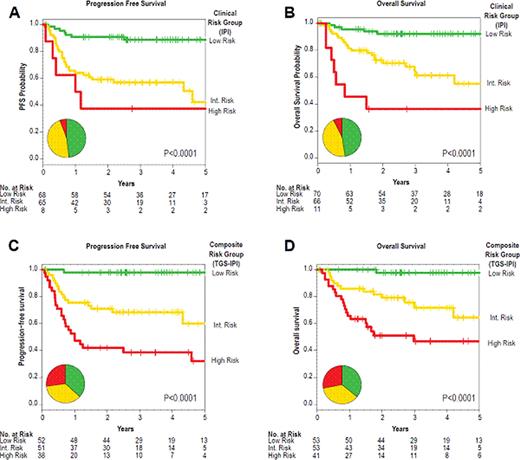
We verified expression of LMO2 as an independent predictor of survival and ‘Germinal Center B-cell’ subtype. We identified expression of TNFRSF9 from the tumor microenvironment, as the best in bivariate combination with LMO2. We studied distribution of TNFRSF9 tissue expression in 95 patients. A model integrating these two genes (TGS) was independent of ‘cell of origin’ classification, ‘stromal signatures’, IPI, and added to the predictive power of the IPI. This bivariate model and a composite score integrating the IPI (TGS-IPI) performed well in three independent cohorts of 545 previously described patients. Both models robustly stratified outcomes in a simple assay of routine specimens from 147 newly diagnosed patients as depicted.
Measurement of a single gene expressed by tumor cells (LMO2) and a single gene expressed by the immune microenvironment (TNFRSF9) powerfully predicts overall survival in patients with DLBCL. A simple test integrating these two genes with the IPI can readily be used to select patients of different risk groups for clinical trials.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal