Abstract
Abstract 1992
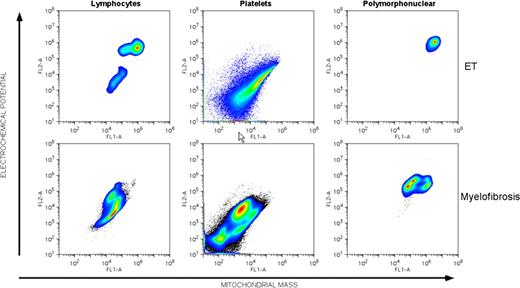
The myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) can have a variable natural history. Polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia, in particular, are conditions that can extend over decades, but some patients have clinical progression to myelofibrosis or acute myeloid leukemia. As first articulated by Warburg, cancers are metabolically distinguished from normal tissues by the use of glycolysis under aerobic conditions. To metabolically characterize the blood cells of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms, we measured the mitochondrial membrane potential using the cyanine dye, JC-1. In examining cells derived from the blood and/or marrow of 159 patients with primary myelofibrosis, polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia, we found that the mitochondrial membrane potential (FL2/FL1=electrochemical potential/mitochondrial mass) was elevated compared to the blood cells of normal individuals. Thirty five percent of patients with polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia had normal MMP. In contrast, 97% of patients with primary myelofibrosis, post-polycythemia myelofibrosis, post-essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis and acute myeloid leukemia following an MPN had evidence of cell populations with higher mitochondrial membrane potential. Cells with distinctly higher mitochondrial membrane potential could be indentified in platelets and polymorphonuclear leukocytes; however the MMP of lymphocytes was normal, indicating that the alteration in metabolic state likely occurred in a multipotential myeloid stem cell. Cell populations were confirmed by co-staining with anti-CD19, -CD45, -GlycophorinA and -β3-integrin antibodies. Sequential analysis of patient samples found that the acquisition of higher mitochondrial membrane potential was stable and persistent over 2 years or more of follow up and that elevated membrane potential predisposed patients to disease progression. The balance of patients (65%) with ET had evidence of increased MMP suggesting the possibility of disease in an early state of evolution to a more aggressive condition. The increased MMP did not correlate with the presence of mutation in JAK2. These results indicate that clinically advanced MPN can be characterized by changes in mitochondrial physiology that might be identified non-invasively by flow cytometric staining with JC-1. In addition, the early nature of these changes may help to identify therapeutic targets.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal