Abstract
Rituximab, anti-CD20 mAb, has become an essential drug for the treatment of Non Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL). Although transient B cells depletion frequently occurs after Rituximab treatment, it usually resolves after 6-9 months. Nevertheless, high frequency of non-neutropenic infections and persistent hypogammaglobulinaemia during follow-up period have been recently reported. However, impaired humoral response to the recall and primary antigens was found in NHL patients during (or few months after), Rituximab treatment.
Influenza vaccination is generally recommended in Lymphoma patients, but no data are available about the activity of this vaccine after Rituximab-based chemotherapy (RIT).
To assess humoral response to influenza vaccine after RIT in complete remission (CR) NHL pts, as compared to healthy subjects.
Considered that disease status might affect the immune response, only NHL pts without evidence of disease and that had completed RIT no less than 6 months before the accrual were eligible. Healthy volunteers served as an age-matched control group. All the subjects were vaccinated with the same commercially available influenza vaccine (contained 2 A and 1 B viral strains). Hemagglutinin inhibition assays were performed before and 4 weeks after vaccination. The EMEA parametres for assessment of vaccines were determined. Seroconversion rate (SC), seroprotection rate (SP), and mean fold increase after Beyer correction/logarithmic transformation (BMFI) were evaluated to compare the two groups. Circulating lymphocytic subpopulations, NK and Dendritic cells, were assessed by immuno-cytofluorometry to evaluate the presence of potentially relevant phenotypic perturbations after vaccination and between the two groups.
During 2008/09 epidemic season, 31 patients (PTS) and 34 healthy controls (CTR) were enrolled and analyzed. The median period after RIT administration was 29 months (range 7- 54).
SC, SP and BMFI were lower in PTS group compared with CTR group (p <0.05 or less in 7/9 evaluated parameters). However, according with the EMEA criteria after age stratification, only the PTS weren't sufficiently protected. PTS that received Fludarabine-Rituximab regime had a high probability not to respond to any of the 3 vaccine strains and a lower SC as compared to PTS treated with the others regimes (p<0.05).
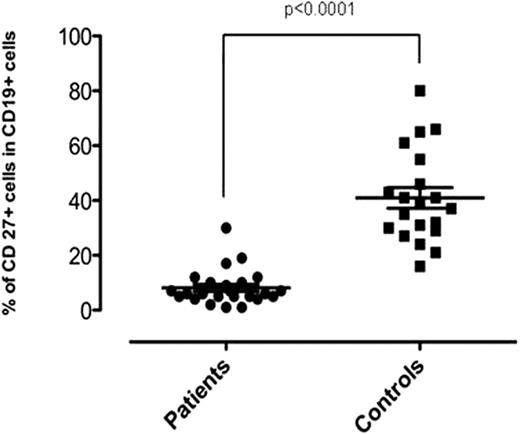
Interestingly, while peripheral CD27- naïve B-cells were present, CD27+ memory B-cell populations were significantly depleted in the patients (p<0.0001) [Fig].
Patients treated with RIT, especially those treated with Rituximab-Fludarabine regimens, have a significant lack of humoral response to influenza vaccine compared with healthy controls, even long time after treatment administration. In these patients the vaccination does not appear to confer adequate protection. The profound depletion in CD27+ B memory cells observed in these patients may explain, in part, this humoral failure. These results raise the concern that PTS treated with RIT, even if in complete remission or on follow since a long time, may be at particular risk of infection, therefore needing careful surveillance, during this period of H1N1 swine-flu spreading.
| Antigens . | Parametres . | PTS . | CTR . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AH1N1 | SC % | 29.0 | 41.2 | ns |
| SP % | 74.2 | 94.1 | <0.05 | |
| BMFI | 1.84±0.92 | 4.69±1.54 | <0.0001 | |
| AH3N2 | SC % | 22.6 | 52.9 | <0.05 |
| SP % | 64.5 | 94.1 | <0.01 | |
| BMFI | 0.6±0.9 | 1.9±1.25 | <0.0001 | |
| B | SC % | 3.2 | 29.4 | <0.01 |
| SP % | 22.6 | 44.1 | Ns | |
| BMFI | 0.59±0.7 | 1.84±0.91 | <0.0001 |
| Antigens . | Parametres . | PTS . | CTR . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AH1N1 | SC % | 29.0 | 41.2 | ns |
| SP % | 74.2 | 94.1 | <0.05 | |
| BMFI | 1.84±0.92 | 4.69±1.54 | <0.0001 | |
| AH3N2 | SC % | 22.6 | 52.9 | <0.05 |
| SP % | 64.5 | 94.1 | <0.01 | |
| BMFI | 0.6±0.9 | 1.9±1.25 | <0.0001 | |
| B | SC % | 3.2 | 29.4 | <0.01 |
| SP % | 22.6 | 44.1 | Ns | |
| BMFI | 0.59±0.7 | 1.84±0.91 | <0.0001 |
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This icon denotes an abstract that is clinically relevant.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal