Abstract
Abstract 841
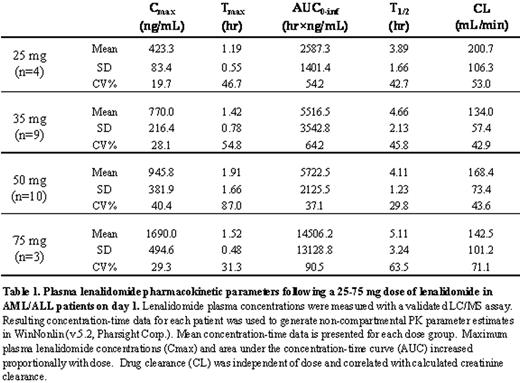
Lenalidomide is effective in myeloma and low-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), especially MDS with the 5q- cytogenetic abnormality, and may also have activity in acute leukemia. We designed a phase I dose escalation trial of lenalidomide in adults with relapsed or refractory acute leukemia to determine the maximum tolerable dose (MTD) and dose limiting toxicity (DLT), as well as to provide preliminary efficacy data in this setting. 35 adults with acute leukemia were enrolled: 31 with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and 4 with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Patients had a median age of 63 years (range, 22-79) and had received a median of 2 prior therapies (range, 1-4). 8 patients had relapsed after transplantation (7-allogeneic, 1-autologous). Patients were treated orally with lenalidomide on days 1-21 of 28 day cycles at the following dose levels: 25mg/day (N=4), 35mg/day (N=9), 50mg/day (N=19, including the expansion at the MTD), and 75mg/day (N=3). Patients were eligible to receive additional cycles of treatment beyond cycle 1 in the absence of disease progression defined as 25% increase in blasts relative to pretreatment. The median number of cycles received was 1 (range, 1-7). DLTs were assessed during cycle 1 of therapy. DLTs were sudden death (N=1, autopsy ruled out pulmonary embolism), rash (N=1), line-associated thrombosis (N=1), and fatigue (N=3). Grade 3 fatigue occurred in two patients at 75mg/day; 50mg/day was thus declared the recommended phase 2 dose and 10 additional patients were treated at this dose. The major toxicities associated with treatment were drug and disease associated myelosuppression and infection, as expected; these did not constitute DLT. In spite of concerns that higher dose lenalidomide would be associated with increased risk of thromboembolism, this toxicity was infrequent, even during multiple cycles of therapy. Two events occurred; both were line associated, and neither was life-threatening. Detailed pharmacokinetic results for the dose escalation cohorts in the trial are listed in the table below. Maximum plasma lenalidomide concentrations and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) increased proportionally with dose. Drug clearance was independent of dose and correlated with calculated creatinine clearance. Of 31 patients with AML there were 5 complete responses (CR) (by IWG criteria for AML; Cheson, JCO 2003). 3/3 with cytogenetically abnormal AML achieved cytogenetic CR (cCR) as well. Achievement of CR was delayed beyond 2 months from initiation of therapy in each case. The duration of CR was 2.4-8.8 months, with two responders still in CR at 2.4+ and 4.7+ months, respectively. At 25mg, a 74 year old with AML in 2nd relapse with widespread leukemia cutis but no blood/marrow involvement had resolution of disease after 2 cycles. At 35mg, a 69 year old with AML and trisomy 13 achieved cCR after 2 cycles. At 50mg, there were three CRs, including two patients who received lenalidomide as initial therapy for relapsed AML following allogeneic stem cell transplant. In both of these cases, lenalidomide therapy was associated with the onset of skin rash requiring temporary discontinuation of drug; CR was achieved after 2 to 3 cycles of therapy and was preceded by cytogenetic remission before count recovery occurred. A third CR at the 50mg level occurred in a 70 year old with AML who had lenalidomide discontinued after 2 cycles due to no apparent response. Subsequently, CR was achieved 1 month later with no intervening therapy. In conclusion, single agent lenalidomide induced CR in 16% (5/31) of relapsed/ refractory AML patients. None of the responders had 5q-. The DLT was fatigue; the MTD was 50mg daily for days 1-21. Achievement of CR without donor leucocyte infusion in 2/4 patients who received lenalidomide as initial therapy for AML relapse following allogeneic transplantation suggests a possible allogeneic immunomodulatory effect. We are now developing a CTEP-sponsored study of lenalidomide as maintenance following allogeneic transplantation for AML. The promising single agent efficacy reported here supports further study of lenalidomide in combination with other agents in high risk AML.
Blum:Celgene: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal