Abstract
Abstract 3718
Poster Board III-654
The combination of bortezomib (B) with rituximab (R), cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) produces complete response in >80% of patients with lymphoma, but has been associated with significant neurotoxicity (Ribrag, Cancer 2009). To examine whether adding B to RCHOP with modified vincristine dosing could be well-tolerated, we performed a Bayesian phase I trial and assessed neurotoxicity with functional and electrophysiological measures.
Untreated patient with follicular lymphoma(n=9) and other indolent NonHodgkin Lymphomas (NHL; n=8) and indications for treatment based on the GELF criteria or FLIPI score>3 received R 375mg/m2, cyclophosphamide 750mg/m2, doxorubicin 50mg/m2, vincristine 1.5mg on day 1, B 1.0-1.6mg/m2 days 1 and 8 and prednisone 100mg days 1-5 for 6-8 cycles. The maximum tolerated dose (MTD) was defined as the regimen at which <30% grade ≥3 non-hematological or grade ≥4 hematological toxicity (>14days) occurs. Dose escalation used the Escalation with Overdose Control Bayesian method with upper bound (Θ=0.3). Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy (FACT) Neurotoxicity (11-item; 4 point scale), NCI CTCAE general neurotoxicity score and electrodiagnostic studies were performed before treatment and after 4 cycles. Nerve conduction studies included recording of sensory and motor action potential from sural and peroneal nerves, with recording of SNAP and CMAP amplitudes. Electromyography was performed in distal muscles of the limbs.
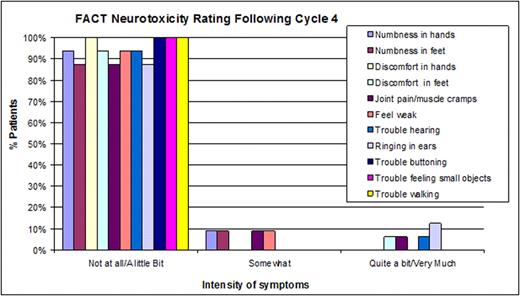
16 patients with indolent lymphoma enrolled in phase I and have completed ≥ 4 cycles; 11/16 pts have completed therapy to date. Median age was 56 years (range 28-71). 6 pts (43%) had stage IV disease, 5 pts (29%) had LDH > 200; 76% of pts had IPI scores of 1/2; 24% had IPI ≥3; 13 (93%) had FLIPI ≥2. Pts received RCHOP + B at 1.0 (n=1), 1.3 (n=6), or 1.6 mg/m2 (n=9). Overall response rate was 100% with 8/11 evaluable pts (73%) achieving a CR. Gr 4 neutropenia occurred in 3 pts (21%), Gr≥3 neuropathy in 1 pt (7%). Results from electrodiagnostic testing following cycle 4 were available in 8 pts. 3 pts (37.5%) displayed motor and sensory neuropathic changes after 4 cycles of therapy. 2 pts (25%) had a reduction in peroneal CMAP amplitude >50% compared to baseline and 1 pts (12.5%) had a reduction in sural SNAP amplitude >50%. Following cycle number 4, ≥88% of pts reported Little/No neuropathy for each FACT item (Figure 1) FACT self-reporting and NCI CTCAE neurotoxicity scores did not correlate with electrodiagnostic testing, indicating the importance of multi-modal neurological assessments to clearly identify pts' neuropathy.
1) B with RCHOP can safely be combined with vincristine at 1.5 mg with limited neurological toxicity compared to previously reported data. 2) BRCHOP has a high CR rate in indolent NHL worthy of exploring in phase 2 and phase 3 trials.
Flowers:Amos Medical Faculty Development Program grant from the American Society of Hematology/Robert Wood Johnson Foundation: Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; Genentech/Biogen-Idec (unpaid): Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal