Abstract
Abstract 1818
Poster Board I-844
The current International staging system (ISS) for myeloma utilises the measurement of beta 2 microglobulin (B2M) and albumin, whilst total immunoglobulin or M-spike measurements are not generally considered to be prognostic. In contrast, some studies have reported that levels of serum free light chains, expressed as a k/l ratio, do provide prognostic information for myeloma patients. The development of antibodies which bind to conformational epitopes spanning the junctional regions between bound κ or λ light chains and their respective heavy chain partners has allowed the specific measurement of serum IgGκ, IgGλ, IgAκ and IgAλ concentrations. In turn, this has enabled the calculation of IgGκ/IgGλ and IgAκ/IgAλ ratios (heavy/light chain or HLC ratios) for individual patients. In this study, the prognostic value of HLC ratios was compared with the ISS.
Archived, frozen presentation sera from 339 patients enrolled on the IFM 2005-01 trial were assayed. B2M and albumin were measured in all sera. In addition, IgGk & IgGl concentrations were measured in sera from the 245 IgG myeloma patients (166 IgGk, 79 IgGl). IgAk and IgAl concentrations were measured in the sera from the 94 IgA myeloma patients (60 IgAk, 34 IgAl). These measurements were made on a Siemens BNTMII nephelometer, using reagents from the Binding Site, UK. HLC ratios (IgGk/IgGl or IgAk/IgAl) were calculated for all patients. Association of the various serum markers with progression free survival (PFS) was assessed using Kaplan Meier and Cox regression analysis (SPSS v14.0).
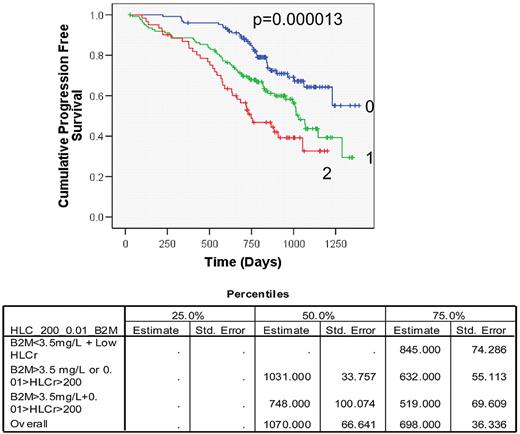
Kaplan Meier analysis indicated that more abnormal HLC ratios were associated with reduced PFS (>median for IgGk and IgAk patients, <median for IgGl and IgAl patients; P=0.007). Using more extreme ratios (>200 or <0.01), the significance was increased (P=0.002). Cox regression analysis, confirmed the association of the latter HLC ratios with reduced PFS (P<0.001) and indicated that the association was independent of and more significant than that of B2M or albumin. The combined use of the extreme HLC ratios, and B2M>3.5mg/L in a risk stratification model, showed significant differences in PFS for patients with 0,1 or 2 adverse risk factors (P=0.000013; Fig.1). A more complex risk stratification model combining HLC ratios with the ISS also showed significant differences in PFS according to the number of risk factors (P=0.0001). Prognosis for overall survival could not be examined meaningfully with these patients because of limited mortality (13.5%) at this time point.
The use of HLC ratios provides a measure of tumour immunoglobulin production plus immunoparesis. It is probably the combination of these 2 factors which gives the prognostic value. HLC measurements were readily made on an automated nephelometer and they may form a useful addition to the current ISS assessments.
Bradwell:The Binding Site Group Ltd: Shareholder. Harding:The Binding Site Group Ltd: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal