Abstract
Abstract 1523
Poster Board I-546
Sickle cell anemia (SCA) is a genetic disorder characterized by recurring episodes of vaso-occlusive crisis (VOC) that can lead to hospitalization or sudden death. Hypoxia is an accepted trigger of sickling and degrees of nighttime hypoxia correlate with strokes and frequency of VOC. To better understand the mechanism of events leading to VOC, we simulated the occurrence of nocturnal hypoxia in SCA patients by administration of five breaths of 100% nitrogen. Tidal volume (Vt), arterial oxygen saturation, electrocardiogram (ECG), and microvascular perfusion (PU) by Laser-Doppler were continuously recorded.
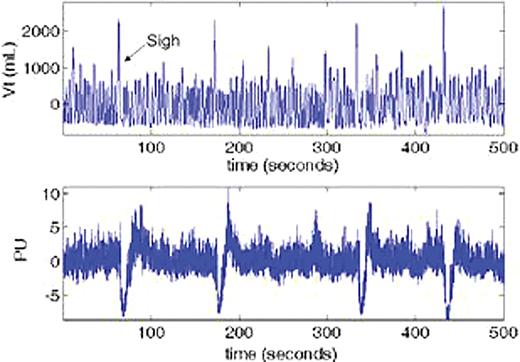
We had anticipated a drop in PU after each controlled episode of hypoxia. However, we observed multiple prominent drops in PU in SCA subjects (n=8) that were not as clearly evident in controls (CTL; n=9), and found no direct relationship between hypoxia and change in PU (p = NS). As deep breaths or sighs can trigger reflex peripheral vasoconstriction, we examined Vt respiratory tracings obtained simultaneously and observed that PU drops frequently followed sighs (see Figure) in SCA subjects, but rarely in CTL. A statistical algorithm was used to find all sighs and vasoconstrictive events (PU drops) during each 40-minute experimental session. PU drops were associated with sighs in 7 of 8 SCA patients and in 4 of 9 CTL subjects (P < 0.001, Poisson regression analysis). Five CTL and 1 SCA subjects had infrequent sighs and no association between sighs and PU drops. The likelihood ratio of sigh-associated PU drops was significantly higher in SCA than CTL subjects (median = 59.9 % vs. < 1 % for SCA vs. CTL, P = 0.008, rank-sum test) whereas the frequency of sighs was not significantly different between the two groups (median = 2.2 % vs. 1.3 % for SCA vs. CTL, P = 0.16, rank-sum test), indicating that SCA patients are much more likely to have sigh-associated peripheral vasoconstriction. Since the sigh-vasoconstrictor response is controlled by the autonomic nervous system (ANS), we measured heart rate variability (HRV) which is an accepted index of sympathetic/parasympathetic balance. These studies showed substantial reduction of parasympathetic modulation of HRV during hypoxia in SCA but not in CTL subjects (p < 0.01), indicating a marked abnormality of the ANS in SCA.
In overview, the likelihood of coupling between spontaneous sighs and subsequent vasoconstrictive events (PU drops) is much higher in SCA patients than in CTL. Thus, we speculate that a drop in perfusion secondary to increased neural coupling between the lung and vasculature may be an initiating event in VOC. Hypoxia may secondarily promote VOC by altering ANS sensitivity and increasing the probability that a sigh will in turn lead to reflex peripheral vasoconstriction. In a background of HbS, transient decreases in perfusion may prolong red cell residence time in the microvasculature, leading to HbS polymerization, sickling and vascular occlusion.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal