Abstract
Abstract 1325
Poster Board I-347
Glanzmann's thrombasthenia (GT) is a rare platelet dysfunction caused by deficiency of gp IIb/IIIa. Treatment with platelet glycoprotein (gp) IIb/IIIa antagonists is common practice in patients undergoing urgent percutaneous cardiac intervention and causes a phenotypic defect similar to GT. Urgent need of acute open-heart surgery may cause excessive bleeding due to the presence of gpIIb/IIIa antagonists and access to platelet transfusion may cause delay.
The present laboratory study explores treatment modalities for reversal of GT and platelet gpIIb/IIIa antagonists, based on recombinant factor VIIa (rFVIIa), fibrinogen, as well as combination of the two drugs.
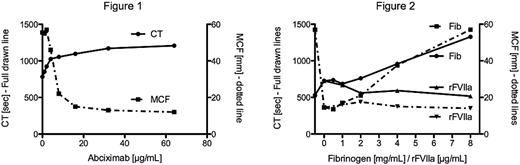
A patient with severe GT, and healthy volunteers provided whole blood (WB) samples for the study. Blood samples were taken in tubes containing 3.2% citrate and corn trypsin inhibitor (final conc. 18.3 μg/mL) to abolish artificial contact activation. Blood samples from healthy volunteers were spiked with aliquots of buffer (HEPES 20mM, NaCl 150mM, pH=7.4) and abciximab reaching final concentrations of 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, and 64 μg/ml. Subsequently, blood samples treated with abciximab 32 μg/ml were spiked with fibrinogen concentrate (0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8 mg/mL) or rFVIIa (1, 2, 4, 8 μg/mL) as well as the combination of fibrinogen and rFVIIa. Haemostatic capacity was evaluated by recording dynamic WB ROTEM thromboelastometry using activation with minute amounts of tissue factor (TF, Innovin̈, final dilution 1:17,000) as well as clot stability using TF + tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA, final concentration 2 nM). WB platelet adhesion was visualized by Impact-R̈. Data was visualized graphically and interpreted using descriptive statistics.
Titration experiments with abciximab increased the clotting time (CT) and reduced the maximum clot firmness (MCF) (Figure 1). The patients clotting profiles were comparable to the highest dose of abciximab. In vitro addition of fibrinogen concentrate dose dependently reversed the MCF, but further prolonged the CT (Figure 2). In contrast, rFVIIa significantly shortened the CT, whereas is had limited effect on the MCF (Figure 2). Combined intervention with fibrinogen (4mg/mL) and rFVIIa (4μg/ml) completely reversed the coagulopathy (CT=745 sec, MCF= 69mm) induced by GT or abciximab as evaluated by thromboelastometry. Test run following activation with TF and t-PA showed that abciximab significantly reduced the total area under the elasticity curve from 139×103 to 36×103. Furthermore, addition of fibrinogen dose dependently increased clot stability to 153×103. In contrast, rFVIIa only induced minor increases in clot stability to 50×103. Experiments with Impact R showed that GT and addition of abciximab abolished platelet adhesion and aggregation. No changes were observed following addition of rFVIIa, fibrinogen or their combination. Furthermore, no changes were seen following prolonging the standard duration of the measurement from 2 to 8 mins, neither following increasing the shear from 720/sec to 1500/sec.
Our laboratory studies suggest that urgent reversal of Glanzmann's thrombasthenia and gpIIb/IIIa antagonists may be achieved by combined haemostatic intervention of fibrinogen concentrate and rFVIIa. The mechanisms seem to depend on fibrin polymerisation and improved clot stability rather than shear stress induced impacts on platelet adhesion and aggregation. Future clinical studies are needed to verify the findings.
Off Label Use: Fibrinogen is not licensed for use in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal