Abstract
Weibel-Palade bodies (WPBs) are the endothelial storage organelles that are formed upon von Willebrand factor (VWF) expression. Apart from VWF, WPBs contain a variety of hemostatic and inflammatory proteins. Some of these are thought to be targeted to WPBs by directly interacting with VWF in the secretory pathway. Previous studies have demonstrated that coexpression of factor VIII (FVIII) with VWF results in costorage of both proteins. However, whether cotrafficking is driven by intracellular FVIII-VWF assembly has remained unclear. We now have addressed this issue using recombinant VWF type 2N variants that are known to display reduced FVIII binding in the circulation. Binding studies using purified fluorescent FVIII and VWF type 2N variants revealed FVIII binding defects varying from moderate (Arg854Gln, Cys1060Arg) to severe (Arg763Gly, Thr791Met, Arg816Trp). Upon expression in HEK293 cells, all VWF variants induced formation of WPB-like organelles that were able to recruit P-selectin, as well as FVIII. WPBs containing FVIII did not display their typical elongated shape, suggesting that FVIII affects the organization of VWF tubules therein. The finding that VWF type 2N variants are still capable of cotargeting FVIII to storage granules implies that trafficking of WPB cargo proteins does not necessarily require high-affinity assembly with VWF.
Introduction
von Willebrand Factor (VWF) is a large, multimeric adhesive glycoprotein that is involved in the formation of a platelet plug after vascular injury.1 In addition, VWF functions as a molecular chaperone for factor VIII (FVIII) in the circulation, preventing its proteolytic degradation and premature clearance.2 Mutations and deletions in the gene encoding VWF are associated with an autosomally inherited bleeding disorder. Quantitative defects of VWF (type 1 and 3 von Willebrand disease [VWD]) affect both VWF as well as FVIII plasma levels, whereas qualitative defects (type 2 VWD) affect binding of VWF to platelets (type 2A, 2B, or 2M) or FVIII (type 2N, formerly referred to as Normandy variants).3
VWF is synthesized exclusively in megakaryocytes and vascular endothelial cells. The translation product is a 2813–amino acid prepropolypeptide that is proteolytically processed to generate a 22–amino acid signal peptide, a 741–amino acid propeptide (D1-D2), and a mature VWF subunit (D′-D3-A1-A2-A3-D4-B1-B2-B3-C1-C2-CK) that consists of 2050 amino acid residues.1,4 During its biosynthesis, VWF subunits are converted into high-molecular-weight multimers through the formation of intermolecular disulfide bonds at the amino terminal and carboxy terminal part of the molecule.1,5-7 In endothelial cells, high-molecular-weight VWF multimers are stored in elongated cigar-shaped secretory organelles called Weibel-Palade bodies (WPBs) that release their content upon appropriate physiologic stimulation.1
WPB formation is driven by synthesis of VWF.8,9 Depending on the endothelial environment, WPBs can contain a variety of other hemostatic proteins and inflammatory mediators.10 Some of these molecules, including VWF propeptide, interleukin-8, and P-selectin, have been shown to directly associate with VWF.7,11-14 These data suggest that VWF may select the content of the WPB by virtue of a direct association with WPB cargo in the secretory pathway. It has therefore been anticipated that FVIII, which forms a high-affinity protein complex with VWF in the circulation, should also be stored in VWF-containing organelles upon coexpression in the same cell.15,16 Indeed, it has been shown that FVIII can be costored in VWF-containing granules in a variety of cells.15-18 These findings raise the question as to whether intracellular cotargeting of FVIII to VWF-containing organelles is driven by assembly of the FVIII/VWF complex within the secretory pathway. Pertinent to this point is our observation that a FVIII variant carrying a Tyr1680Phe replacement is stored in WPBs despite the absence of high-affinity binding of FVIII to VWF.19
The aim of the present study was therefore to analyze the relationship between assembly of the VWF/FVIII complex and intracellular trafficking of FVIII to VWF-containing storage vesicles. To address this issue, we studied binding of various VWF type 2N variants to FVIII and the ability of these variants to redirect FVIII to intracellular VWF-containing storage organelles.
Methods
Materials
All chemicals used were of analytic grade. Pfu HotStart polymerase was from Stratagene (Cambridge, United Kingdom). Endotoxin Free Plasmid Isolation kits were from QIAGEN (Hilden, Germany). Oligonucleotide primers, dNTPs, expression vector pcDNA3.1(+), DMRIE-C reagent, geneticin G-418 sulfate, and trypsin were supplied by Invitrogen (Breda, The Netherlands). DNA-modifying enzymes were from Invitrogen, Fermentas (St Leon-Rot, Germany), and New England Biolabs (Ipswich, MA). DMEM/F12 medium, penicillin, streptomycin, and fetal calf serum were from BioWhittaker (Verviers, Belgium). Culture flasks and cell factories (6320 cm2) were purchased from Nunc A/S (Roskilde, Denmark). CNBr-Sepharose 4B and Q-Sepharose FF were obtained from Amersham Pharmacia Biotech (Roosendaal, The Netherlands). Microtiter plates (Immunolon) were from Dynatech (Plockingen, Germany) and (Maxisorp) from Nunc A/S. BIAcore3000 biosensor system and reagents (amino-coupling kit, research grade CM5 sensor chips) were from Biacore AB (Uppsala, Sweden).
Plasmid mutagenesis
P-selectin,20 FVIII-YFP with YFP replacing the B-domain,19 and VWF-CFP with CFP replacing the A2 domain19 in pcDNA3.1(+) have been described before. B-domain–deleted FVIII lacking the YFP moiety was created by removal of the YFP moiety by Quick Change (Stratagene) mutagenesis using appropriate primers. VWF-YFP in pcDNA3.1(+) was created by exchanging CFP for YFP amplified from pEYFP-N1 (Clontech, Mountain View, CA). Point mutations Arg763Gly, Arg854Gln, and Cys1060Arg in VWF-CFP were introduced by Quick Change mutagenesis using appropriate primers. Point mutations Thr791Met and Arg816Trp21,22 were ligated into VWF-CFP using HindIII and Bsu36I. The coding regions of all constructs were verified by sequence analysis. Sequence reactions were performed with BigDye Terminator Sequencing kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA).
Purification and analysis of recombinant proteins
Recombinant VWF and FVIII variants were purified as described.19 Purified FVIII and VWF preparations were analyzed by 7.5% SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) analysis followed by silver staining. Multimeric composition of purified VWF-CFP (variants) preparations was analyzed as described.23 VWF antigen was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using monoclonal anti-VWF antibody CLB-Rag2024 and polyclonal rabbit anti–human VWF antibody (DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark). FVIII antigen was quantified by anti–light chain ELISA using monoclonal anti-FVIII light chain antibodies CLB-CAg1225 and CLB-CAg117.26 FVIII activity was determined with a chromogenic assay according to the manufacturer's instructions (Chromogenix, Milan, Italy). Human pooled plasma from at least 30 donors, calibrated against the 5th International Standard for FVIII and VWF in plasma (WHO 02/150), was used as a standard. Protein concentrations were determined by the method of Bradford.27
FVIII/VWF binding
Pseudoequilibrium binding of FVIII to VWF in an ELISA-based format was assessed as described.19 Association and dissociation of FVIII-YFP interaction with VWF-CFP variants were monitored by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis using a BIAcore 3000 biosensor. VWF-CFP variants (22 fmol/mm2) were immobilized onto a CM5 sensor chip using the amine coupling method according to the manufacturer's instructions. Various concentrations of FVIII-YFP (1-5 nM), dialyzed to running buffer, were passed over the immobilized VWF-CFP variants in running buffer containing 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM CaCl2, 5% (vol/vol) glycerol, 0.005% (vol/vol) Tween, and 20 mM Hepes (pH 7.4) at 25°C with a flow rate of 20 μL/min. The sensor chip surface was regenerated by 3 repeated washes in the same buffer containing 1 M NaCl. Binding to VWF-CFP variants was corrected for binding in absence of VWF.
Cell culture, transfection, production levels, and intracellular retention
HEK293 cells were grown in DMEM-F12 medium supplemented with 10% FCS, 100 units/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin. HEK293 cell lines, stably expressing recombinant protein, were produced as described.28 Production levels and intracellular content of VWF variants were determined by transient transfection of HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were seeded at 2.5 × 105 cells per 10 cm2. Medium was refreshed 4 hours before transfection and cells were transfected 24 hours after seeding using the calcium phosphate coprecipitation method using 5 μg plasmid DNA.29 Medium was exchanged 24 hours after transfection and conditioned media were collected after additional 72-hour incubation. Cells were subsequently lysed on plate with ice-cold immunoprecipitation buffer (IPB; 1 M NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 10 mM Tris [pH 7.4], further containing 1% [vol/vol] Nonidet P40 and 1 tablet/50 mL protease inhibitor cocktail tablet [Roche, Mannheim, Germany]). Cell lysates were subjected to 3 freeze-thaw cycles. Conditioned media and cell lysates were centrifuged at 13 000g for 10 minutes prior to VWF quantification as described under “Purification and analysis of recombinant proteins.” Data were analyzed using a 2-tailed unpaired Student t test.
Intracellular FVIII/VWF type 2N binding
HEK293 cells coexpressing FVIII-YFP and VWF-CFP type 2N variants (80 cm2) were lysed with ice-cold lysis buffer (150 mM NaCl, 2.5 mM CaCl2, 0.1% [wt/vol] Tween20, 2% [vol/vol] human serum albumin [HSA], Cealb [Sanquin, Amsterdam, The Netherlands], 10 mM benzamidine, 5 mM N-ethylmaleimide, 20 μg/mL soybean trypsin inhibitor, and 50 mM Tris [pH 7.4], further containing 1% [vol/vol] Nonidet P40). Cell lysates were centrifuged at 13 000g for 10 minutes. To determine intracellular VWF/FVIII complex, cell lysates were serially diluted in lysis buffer without 1% (vol/vol) Nonidet P40 and incubated for 2 hours at 37°C in a CLB-RAg2024 –coated 96-well plate in the presence of 1 μg/mL horseradish peroxidase–labeled CLB-CAg12,25 a monoclonal anti-FVIII light chain antibody. After 3 short washes (1.5 seconds) with 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% (wt/vol) Tween20, and 50 mM Tris (pH 7.4), CLB-CAg12 was quantified as a measure for VWF/FVIII complex. VWF and FVIII antigen were quantified by ELISA as described under “Purification and analysis of recombinant proteins.” The amount of VWF/FVIII complex was plotted against the amount of VWF present in the various dilutions. The slope of the linear part of the dose-response curve was calculated by linear regression analysis and expressed as FVIII/VWF binding relative to wild-type VWF-CFP (Prism 4 software; GraphPad, San Diego, CA).
Immunofluorescence analysis
To determine the capability of VWF-CFP type 2N variants to induce the formation of elongated storage granules and ability to recruit P-selectin, HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with VWF-CFP type 2N variants alone or in combination with P-selectin using 5 μg of (each) plasmid DNA. To determine the capability of cotrafficking FVIII to storage granules, HEK293 cells stably expressing FVIII-YFP were transfected with the various VWF-CFP type 2N variants alone or in combination with P-selectin using 5 μg of (each) plasmid DNA. HEK293 cells were transiently transfected using the calcium phosphate coprecipitation method as described under “Cell culture, transfection, production levels, and intracellular retention.” Endothelial cells (HUVECs) were isolated from umbilical veins and cultured as described.30 For VWF-YFP and FVIII-YFP, HUVECs (106 cells) were transfected by nucleofection (Basic nucleofector kit for primary human endothelial cells; AMAXA, Cologne, Germany) using 5 μg plasmid DNA. For untagged FVIII, HUVECs (2.5 × 104 cells) were transduced with a lentiviral self-inactivating vector encoding human B-domain–deleted FVIII under control of the CAG promoter consisting of the chicken β-actin promoter, cytomegalovirus (CMV) enhancers, and a large synthetic intron.31 Cells were fixed in 3.7% paraformaldehyde 96 hours after transfection and prepared for immunofluorescence analysis as described.30 Monoclonal antibody CLB-RAg3530 was used to visualize VWF. Rabbit polyclonal antibody anti–human CD62-P (BD PharMingen, San Diego, CA) was used to visualize P-selectin. Monoclonal antibody CLB-Pro1732 was used to visualize VWF propeptide. FITC-labeled human monoclonal antibody EL14 IgG433 was used to detect untagged FVIII. Alexa 488– and Alexa 594–conjugated secondary antibodies were from Invitrogen. Cells were embedded in Vectashield mounting medium (Vector Laboratories, Burlington, CA) and viewed by confocal laser scanning microscopy using a Zeiss LSM510 equipped with a Plan Apochromat 63×/1.40 NA oil objective (Carl Zeiss, Heidelberg, Germany). Images were generated by making optical sections (Z-stacks with 0.4-μm intervals) and 3-dimensional analysis (Projections software, Zeiss LSM510 version 4.0; Carl Zeiss).
Results
Expression of VWF-CFP type 2N variants in HEK293 cells
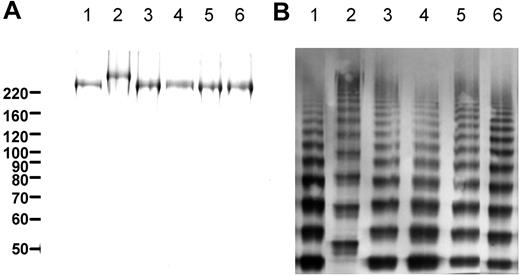
Expression of VWF in human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells results in the formation of elongated VWF-containing granules that resemble WPBs. These pseudo-WPBs contain internal striations and can recruit trans-membrane proteins such as CD63 and P-selectin.34 We therefore used HEK293 cells as a model system for VWF expression. VWF type 2N variants were created carrying an Arg763Gly, Thr791Met, Arg816Trp, Arg854Gln, or Cys1060Arg substitution. To facilitate visualization, variants were generated in fluorescently tagged VWF-CFP. Constructs were expressed in HEK293 cells and VWF levels in culture media and cell lysates were quantified. Transient expression of wild-type VWF-CFP resulted in the secretion of 5.8 (± 0.2) pmol VWF/106 cells per 72 hours (Table 1). A substantial portion of wild-type VWF-CFP (27% ± 2%) was retained within the cell (Table 1). Secretion levels of the VWF-CFP 2N variants were slightly reduced. The percentage of VWF, retained within the cell after 72 hours, was similar for all VWF-CFP variants (Table 1). HEK293 cell lines stably expressing the different VWF-CFP variants were generated and the variants were purified from conditioned medium using immunoaffinity chromatography. Analysis by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions revealed that the VWF-CFP variants were more than 95% pure (Figure 1A). All variants demonstrated a protein band at a monomeric size of approximately 220 kDa, with the exception of the Arg763Gly variant. (Figure 1A lane 2). This is consistent with lack of VWF propeptide cleavage due to substitution of the arginine residue at position 763.35,36 Multimeric analysis of the purified proteins demonstrated the presence of the full range of VWF multimer subunits with a similar distribution for all VWF-CFP 2N variants, again with the exception of the Arg763Gly variant (Figure 1B lane 2). Due to lack of propeptide cleavage, the individual size of the multimer subunits for the Arg763Gly variant was increased compared with wild-type VWF-CFP (Figure 1B).
VWF secretion and retention
| . | VWF secretion, pmol/106 cells per 72 h . | VWF retention, % of total/106 cells per 72 h . |
|---|---|---|
| VWF-CFP wild type | 5.8 ± 0.2 | 27 ± 2 |
| VWF-CFP Arg763Gly | 4.4 ± 0.5* | 30 ± 2 |
| VWF-CFP Thr791Met | 4.1 ± 0.2† | 28 ± 1 |
| VWF-CFP Arg816Trp | 4.1 ± 0.2† | 23 ± 3 |
| VWF-CFP Arg854Gln | 3.5 ± 0.1† | 27 ± 2 |
| VWF-CFP Cys1060Arg | 3.3 ± 0.3† | 29 ± 3 |
| . | VWF secretion, pmol/106 cells per 72 h . | VWF retention, % of total/106 cells per 72 h . |
|---|---|---|
| VWF-CFP wild type | 5.8 ± 0.2 | 27 ± 2 |
| VWF-CFP Arg763Gly | 4.4 ± 0.5* | 30 ± 2 |
| VWF-CFP Thr791Met | 4.1 ± 0.2† | 28 ± 1 |
| VWF-CFP Arg816Trp | 4.1 ± 0.2† | 23 ± 3 |
| VWF-CFP Arg854Gln | 3.5 ± 0.1† | 27 ± 2 |
| VWF-CFP Cys1060Arg | 3.3 ± 0.3† | 29 ± 3 |
HEK293 cells were transfected using 5 μg plasmid DNA. Conditioned medium and cell lysate were analyzed on VWF levels. Each value represents the mean plus or minus SD of 3 transfections. Statistically significant differences are indicated.
P < .05.
P < .001.
Purity and multimeric composition of VWF-CFP type 2N variants. (A) Purified VWF preparations were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under reducing conditions followed by silver staining. (B) Multimeric composition was analyzed by 2.5% agarose gel electrophoresis followed by Western blot analysis using rabbit polyclonal anti–human VWF. Lanes correspond with wild-type VWF-CFP (lane 1), Arg763Gly (lane 2), Thr791Met (lane 3), Arg816Trp (lane 4), Arg854Gln (lane 5), and Cys1060Arg (lane 6).
Purity and multimeric composition of VWF-CFP type 2N variants. (A) Purified VWF preparations were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under reducing conditions followed by silver staining. (B) Multimeric composition was analyzed by 2.5% agarose gel electrophoresis followed by Western blot analysis using rabbit polyclonal anti–human VWF. Lanes correspond with wild-type VWF-CFP (lane 1), Arg763Gly (lane 2), Thr791Met (lane 3), Arg816Trp (lane 4), Arg854Gln (lane 5), and Cys1060Arg (lane 6).
FVIII/VWF binding
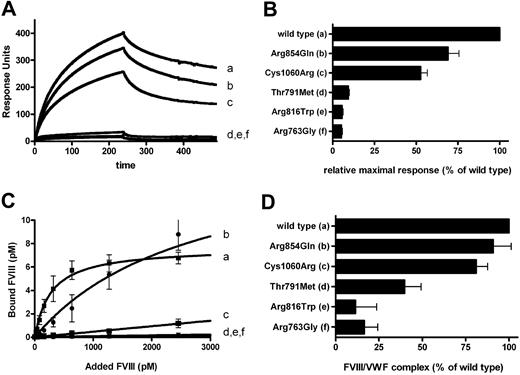
The interaction of the individual VWF-CFP type 2N variants with FVIII-YFP was assessed using 2 distinct techniques. First, surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis was used for comparison between mutants. Representative SPR experiments are shown in Figure 2A. For the interaction of FVIII-YFP to wild-type VWF-CFP, both association and dissociation displayed single exponential kinetics (Figure 2A curve a). However, FVIII binding appeared partially irreversible, suggesting fast reassociation of FVIII during the dissociation phase. The apparently fast binding further suggests that association is mass transport limited.37 Although this prohibits detailed quantitative assessment of binding kinetics, these SPR data remain particularly useful for qualitative, comparative analysis between mutants (Figure 2A curves b-f).38 These data are summarized in Figure 2B. All VWF type 2N variants displayed impaired FVIII binding, although to various extents. VWF substitution mutants Arg854Gln (b) and Cys1060Arg (c) had an apparently minor defect. In contrast, mutants Thr791Met (d), Arg816Trp (e), and Arg763Gly (f) displayed less than 10% residual binding (Figure 2B). We further analyzed the binding of purified FVIII-YFP to immobilized VWF-CFP type 2N variants in a pseudoequilibrium binding assay (Figure 2C). As described previously and in agreement with our SPR data, FVIII-YFP readily bound to wild-type VWF-CFP with high affinity (Figure 2C curve a). As was apparent from our SPR data, all VWF-CFP type 2N variants demonstrated a binding defect, which varied considerably depending on the amino acid replacement. The apparent affinity for the VWF-CFP variant carrying an Arg854Gln replacement was mildly reduced, with an 8-fold increased apparent dissociation constant (Figure 2C curve b). Binding also occurred to an appreciable extent for the variant carrying a Cys1060Arg replacement (Figure 2C curve c), whereas no binding could be observed for the variants carrying an Thr791Met, Arg816Trp, or Arg763Gly replacement (Figure 2C curves d-f). Thus, these 3 variants fail to assemble with FVIII under the conditions of Figure 2, whereas the other 2 display reduced affinity.
FVIII-YFP binding to VWF-CFP type 2N variants. VWF variants include wild-type VWF-CFP (a), Arg854Gln (b), Cys1060Arg (c), Thr791Met (d), Arg816Trp (e), and Arg763Gly (f). (A) FVIII-YFP was passed over a chip to which 22 fmol/mm2 VWF-CFP type 2N variants were coupled. Association and dissociation were both followed for 240 seconds. Depicted is a representative SPR experiment showing the average curve of 3 injections of 5 nM FVIII-YFP. (B) Summary of binding for all VWF-CFP type 2N variants. Percentage of binding was calculated relative to wild-type VWF-CFP after 235 seconds of association. Each value represents the mean of 9 injections (1-5 nM FVIII-YFP) and the SEM is indicated. (C) FVIII-YFP (0-3 nM) was incubated for 2 hours with recombinant VWF-CFP variants bound to monoclonal antibody CLB-RAg20. The amount of FVIII bound to VWF was measured by chromogenic assay and calculated using plasma-derived FVIII as a standard. Each value represents the mean of 3 experiments and the SEM is indicated. The curves were fitted to a standard hyperbola using nonlinear regression analysis. (D) Cell lysates containing FVIII-YFP and VWF-CFP type 2N variants were assessed on FVIII/VWF complex as described under “Intracellular FVIII/VWF type 2N binding.” *The extent of intracellular FVIII/VWF type 2N complex is expressed relative to wild-type VWF-CFP. Each value represents the mean plus or minus SD of 3 experiments.
FVIII-YFP binding to VWF-CFP type 2N variants. VWF variants include wild-type VWF-CFP (a), Arg854Gln (b), Cys1060Arg (c), Thr791Met (d), Arg816Trp (e), and Arg763Gly (f). (A) FVIII-YFP was passed over a chip to which 22 fmol/mm2 VWF-CFP type 2N variants were coupled. Association and dissociation were both followed for 240 seconds. Depicted is a representative SPR experiment showing the average curve of 3 injections of 5 nM FVIII-YFP. (B) Summary of binding for all VWF-CFP type 2N variants. Percentage of binding was calculated relative to wild-type VWF-CFP after 235 seconds of association. Each value represents the mean of 9 injections (1-5 nM FVIII-YFP) and the SEM is indicated. (C) FVIII-YFP (0-3 nM) was incubated for 2 hours with recombinant VWF-CFP variants bound to monoclonal antibody CLB-RAg20. The amount of FVIII bound to VWF was measured by chromogenic assay and calculated using plasma-derived FVIII as a standard. Each value represents the mean of 3 experiments and the SEM is indicated. The curves were fitted to a standard hyperbola using nonlinear regression analysis. (D) Cell lysates containing FVIII-YFP and VWF-CFP type 2N variants were assessed on FVIII/VWF complex as described under “Intracellular FVIII/VWF type 2N binding.” *The extent of intracellular FVIII/VWF type 2N complex is expressed relative to wild-type VWF-CFP. Each value represents the mean plus or minus SD of 3 experiments.
VWF type 2N variants induce the formation of elongated storage granules that are able to cotarget VWF propeptide and P-selectin
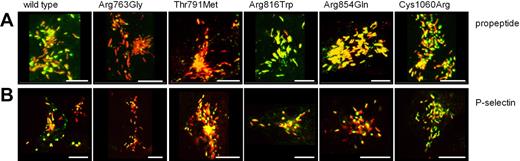
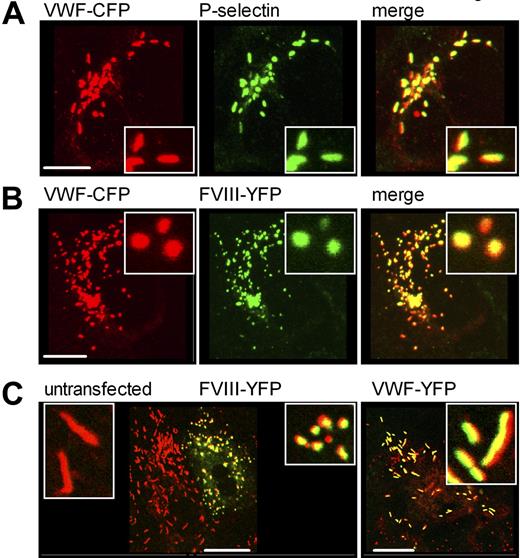
We subsequently addressed the question whether VWF-CFP type 2N variants are stored in pseudo-WPBs in HEK293 cells. We analyzed the subcellular localization of the VWF-CFP type 2N variants 96 hours after transfection. In the majority of the cells, VWF-CFP could be visualized only in pseudo-WPBs. All VWF-CFP type 2N variants were able to induce the formation of elongated cigar-shaped storage vesicles that in addition to VWF also contained VWF propeptide (Figure 3A). Weak propeptide staining was observed for the VWF-CFP type 2N variant carrying an Arg763Gly replacement, which may be caused by a reduced accessibility of the binding site of CLB-Pro17 in this variant (Figure 3A). In addition, we assessed if the trans-membrane protein P-selectin could be recruited to the VWF-containing storage organelles by performing a cotransfection of individual VWF-CFP type 2N variants with P-selectin. All VWF-CFP type 2N variants were able to recruit P-selectin to elongated cigar-shaped VWF-containing granules (Figure 3B), indicating that VWF type 2N replacements have no effect on the formation of Weibel-Palade–like organelles or on the ability to recruit additional WPB cargo.
VWF-CFP type 2N variants induce the formation of storage organelles that recruit VWF propeptide and P-selectin in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were transfected with VWF-CFP type 2N variants alone (A) or in combination with P-selectin (B). Cells were stained for VWF propeptide (in green, A) using monoclonal antibody CLB-Pro17 and for P-selectin (in green, B) using rabbit polyclonal anti–human CD62P antibody. VWF-CFP type 2N variants are depicted in red (A,B). Shown is the merge of double-fluorescent detection of representative 3-dimensional projections (Z-stacks 0.4 μm). Regions of colocalization are shown in yellow. The scale bar represents 10 μm.
VWF-CFP type 2N variants induce the formation of storage organelles that recruit VWF propeptide and P-selectin in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were transfected with VWF-CFP type 2N variants alone (A) or in combination with P-selectin (B). Cells were stained for VWF propeptide (in green, A) using monoclonal antibody CLB-Pro17 and for P-selectin (in green, B) using rabbit polyclonal anti–human CD62P antibody. VWF-CFP type 2N variants are depicted in red (A,B). Shown is the merge of double-fluorescent detection of representative 3-dimensional projections (Z-stacks 0.4 μm). Regions of colocalization are shown in yellow. The scale bar represents 10 μm.
VWF-CFP type 2N variants are capable of cotrafficking FVIII-YFP to VWF-containing storage granules that retain the ability to recruit P-selectin
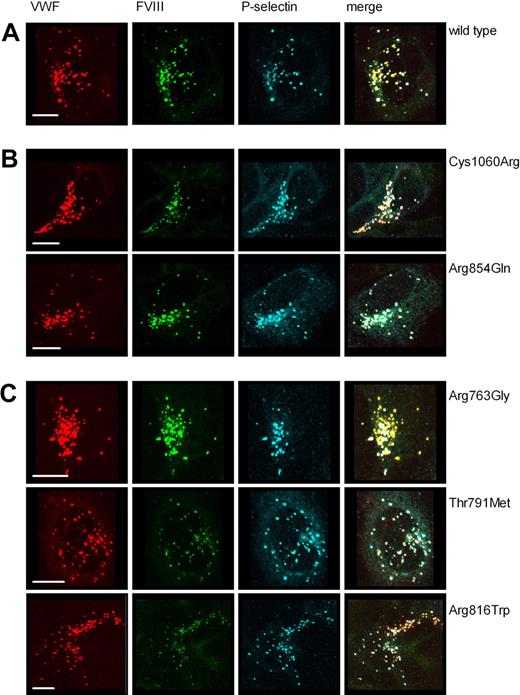
As we described previously,19 expression of FVIII-YFP alone in HEK293 cells resulted in a faint staining with FVIII immunolocalized at the level of the trans-Golgi network. Upon coexpression of wild-type VWF-CFP, intracellular localization of FVIII-YFP was rerouted to granular staining together with VWF-CFP in Weibel-Palade body–like organelles (Figure 4A).19 These storage organelles can also contain P-selectin (Figure 4A), indicating that the presence of FVIII does not alter the general ability of VWF to recruit other WPB cargo molecules. These data further demonstrate that the presence of FVIII and P-selectin is not mutually exclusive. To address the role of the VWF type 2N replacements in cotrafficking of FVIII, we cotransfected individual VWF-CFP–type 2N variants with P-selectin in a HEK293 cell line stably expressing FVIII-YFP and analyzed the subcellular distribution of FVIII-YFP and P-selectin. VWF-CFP type 2N variants with a moderately reduced capacity to bind to FVIII-YFP (Arg854Gln and Cys1060Arg) retained the ability to trigger intracellular rerouting of FVIII to costorage in VWF-containing vesicles (Figure 4B). Surprisingly, also the VWF-CFP 2N variants that displayed a severely impaired binding to FVIII-YFP (Arg763Gly, Thr791Met, and Arg816Trp) were able to change the intracellular routing of FVIII from trans-Golgi network toward storage in VWF-containing granules (Figure 4C). Irrespective of the VWF type 2N replacement, VWF-containing organelles were able to simultaneously corecruit FVIII-YFP and P-selectin to the same vesicle (Figure 4B,C). In fact, most of the VWF-containing granules contained both FVIII and P-selectin, indicating that both FVIII as well as P-selectin readily cosegregate with VWF type 2N variants (Figure 4B,C).
VWF-CFP type 2N variants induce formation of storage organelles that recruit both factor VIII-YFP and P-selectin. HEK293 cells stably expressing FVIII-YFP were transfected with P-selectin and wild-type VWF-CFP (A), P-selectin and VWF type 2N variants that display a moderately reduced binding to FVIII (Arg854Gln, Cys1060Arg) (B), or P-selectin and VWF type 2N variants that display a severely reduced binding to FVIII (Arg763Gly, Thr791Met, Arg816Trp) (C). Cells were stained for P-selectin using rabbit polyclonal anti–human CD62P antibody. Shown is triple fluorescent detection of representative 3-dimensional projections (Z-stacks 0.4 μm). VWF-CFP, FVIII-YFP, and P-selectin are shown in red, green, and blue, respectively. Triple fluorescent detection is shown in the color merges (regions of triple colocalization are shown in white). The scale bar represents 10 μm.
VWF-CFP type 2N variants induce formation of storage organelles that recruit both factor VIII-YFP and P-selectin. HEK293 cells stably expressing FVIII-YFP were transfected with P-selectin and wild-type VWF-CFP (A), P-selectin and VWF type 2N variants that display a moderately reduced binding to FVIII (Arg854Gln, Cys1060Arg) (B), or P-selectin and VWF type 2N variants that display a severely reduced binding to FVIII (Arg763Gly, Thr791Met, Arg816Trp) (C). Cells were stained for P-selectin using rabbit polyclonal anti–human CD62P antibody. Shown is triple fluorescent detection of representative 3-dimensional projections (Z-stacks 0.4 μm). VWF-CFP, FVIII-YFP, and P-selectin are shown in red, green, and blue, respectively. Triple fluorescent detection is shown in the color merges (regions of triple colocalization are shown in white). The scale bar represents 10 μm.
Intracellular VWF/FVIII binding
To assess whether FVIII and VWF type 2N variants can associate within the cell in a manner comparable with the binding of purified proteins, we studied the extent of FVIII/VWF type 2N complex in cell lysate (Figure 2D). In cell lysate from HEK293 cells that coexpressed FVIII-YFP and wild-type VWF-CFP, the complex of FVIII and VWF was readily detected (Figure 2D). Compared with wild-type VWF-CFP, the VWF-CFP variants containing the Arg854Gln and Cys1060Arg replacement demonstrated similar levels of VWF/FVIII complex, whereas the VWF type 2N variants containing the Thr791Met, Arg816Trp, and Arg763Gly replacement clearly displayed much lower FVIII binding (Figure 2D). These data indicate that VWF and FVIII can associate prior to secretion with binding characteristics similar to those of the proteins purified from conditioned medium.
VWF-containing vesicles that contain FVIII-YFP are round
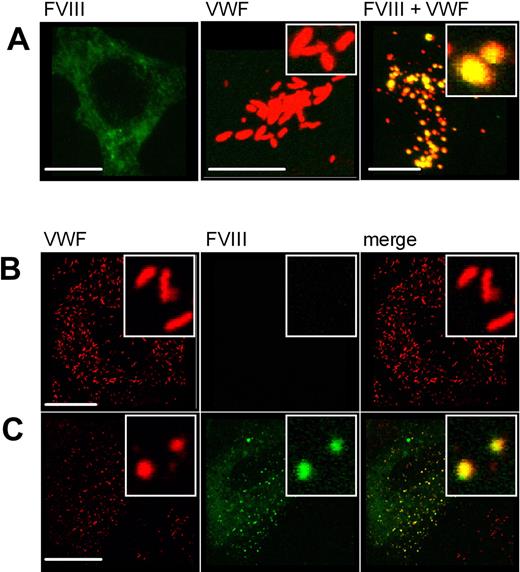
Evaluation of the generated CLSM data revealed a different morphology for FVIII-containing organelles (compare Figure 3B and Figure 4A-C) as opposed to P-selectin and VWF-containing granules. These observations are visualized in detail in Figure 5A through C. Whereas granules containing VWF-CFP and P-selectin were elongated and cigar shaped (Figure 5A), the vesicles containing VWF and FVIII demonstrated a loss in elongated structures and the appearance of round WPB-like structures (Figure 5B). This phenomenon was observed in virtually all VWF/FVIII-containing vesicles. Figure 4A through C demonstrates that the formation of round FVIII-containing organelles was independent of the presence of VWF type 2N replacements. To exclude that these observations result from the use of HEK293 cells as a model system for VWF expression and storage, we additionally studied FVIII-YFP expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). In agreement with studies in HEK293 cells, storage of FVIII-YFP in authentic Weibel-Palade bodies induced a transition from elongated to round organelles (Figure 5C left panel). In contrast, expression of VWF-YFP resulted in storage in normal Weibel-Palade bodies (Figure 5C right panel), indicating that the transition of elongated into round structures did not result from the YFP moiety but originated from the presence of FVIII itself. To further exclude that the observed morphologic change of the WPB was mediated by the YFP/CFP tags, HEK293 cells were also transfected with untagged VWF and FVIII (Figure 6A). As in Figure 5A and B, WPBs are elongated in absence of FVIII (middle panel) and spherical in presence of FVIII (right panel). This demonstrates that FVIII, and not the YFP/CFP tags, induces the morphologic change of WPBs upon coexpression of VWF and FVIII-YFP. Finally, untagged FVIII was also expressed in HUVECs that endogenously produce VWF. Again, WPBs are elongated in absence of FVIII (Figure 6B) and spherical in presence of FVIII (Figure 6C).
Factor VIII-YFP induces morphologic transition from elongated cigar-shaped structures to round circular-shaped organelles. (A) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with VWF-CFP and P-selectin. Cells were stained for P-selectin using rabbit polyclonal anti–human CD62P antibody. Shown is double-fluorescent detection of representative 3-dimensional projections (Z-stacks 0.4 μm). VWF-CFP, P-selectin, and regions of colocalization are shown in red, green, and yellow, respectively. The scale bar represents 10 μm. (B) HEK293 cells stably expressing FVIII-YFP were transfected with VWF-CFP. Shown is double-fluorescent detection of representative 3D projections (Z-stacks 0.4 μm). VWF-CFP, FVIII-YFP, and regions of colocalization are shown in red, green, and yellow, respectively. The scale bar represents 10 μm. (C) HUVECs were nucleofected with FVIII-YFP (left panel) or VWF-YFP (right panel). Endogenous VWF was stained using monoclonal antibody CLB-Rag35. Shown is the merge of double-fluorescent detection. Endogenous VWF is shown in red, FVIII-YFP (left panel) and VWF-YFP (right panel) are depicted in green, and regions of colocalization are yellow. The inset shows the morphology of vesicles. The scale bar represents 20 μm.
Factor VIII-YFP induces morphologic transition from elongated cigar-shaped structures to round circular-shaped organelles. (A) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with VWF-CFP and P-selectin. Cells were stained for P-selectin using rabbit polyclonal anti–human CD62P antibody. Shown is double-fluorescent detection of representative 3-dimensional projections (Z-stacks 0.4 μm). VWF-CFP, P-selectin, and regions of colocalization are shown in red, green, and yellow, respectively. The scale bar represents 10 μm. (B) HEK293 cells stably expressing FVIII-YFP were transfected with VWF-CFP. Shown is double-fluorescent detection of representative 3D projections (Z-stacks 0.4 μm). VWF-CFP, FVIII-YFP, and regions of colocalization are shown in red, green, and yellow, respectively. The scale bar represents 10 μm. (C) HUVECs were nucleofected with FVIII-YFP (left panel) or VWF-YFP (right panel). Endogenous VWF was stained using monoclonal antibody CLB-Rag35. Shown is the merge of double-fluorescent detection. Endogenous VWF is shown in red, FVIII-YFP (left panel) and VWF-YFP (right panel) are depicted in green, and regions of colocalization are yellow. The inset shows the morphology of vesicles. The scale bar represents 20 μm.
Morphology of Weibel-Palade bodies upon expression of untagged FVIII and VWF. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with untagged FVIII (left panel), untagged VWF (middle panel), or both (right panel). Cells were stained for FVIII (green) using monoclonal antibody EL14 and for VWF (red) using monoclonal antibody CLB-RAg20. Shown is the merge of double-fluorescent detection of representative 3-dimensional projections (Z-stacks 0.4 μm). The scale bar represents 10 μm. (B) HUVECs (control) were transduced with untagged FVIII (C). Cells were stained for VWF (red, left panel) and FVIII (green, middle panel) using antibodies as in panel A. The right panel represents the merge of double-fluorescent detection. Regions of colocalization are represented in yellow. The scale bar represents 20 μm. The inset shows the vesicle morphology.
Morphology of Weibel-Palade bodies upon expression of untagged FVIII and VWF. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with untagged FVIII (left panel), untagged VWF (middle panel), or both (right panel). Cells were stained for FVIII (green) using monoclonal antibody EL14 and for VWF (red) using monoclonal antibody CLB-RAg20. Shown is the merge of double-fluorescent detection of representative 3-dimensional projections (Z-stacks 0.4 μm). The scale bar represents 10 μm. (B) HUVECs (control) were transduced with untagged FVIII (C). Cells were stained for VWF (red, left panel) and FVIII (green, middle panel) using antibodies as in panel A. The right panel represents the merge of double-fluorescent detection. Regions of colocalization are represented in yellow. The scale bar represents 20 μm. The inset shows the vesicle morphology.
Discussion
With regard to the VWF-CFP type 2N variants used in this study, we can distinguish between 2 distinct categories. One group, consisting of the variants Arg763Gly, Thr791Met, and Arg816Trp, displays a severe defect in FVIII binding (Figure 2A-C), which is in agreement with previous studies.21,22,35 A second group, consisting of the variants Arg854Gln and Cys1060Arg, still shows appreciable binding to FVIII (Figure 2A-C). The data concerning the Arg854Gln variant are in agreement with previous studies reporting a 4- to 8-fold reduction in FVIII binding.39-41 A VWF variant carrying a Cys1060Arg replacement has been previously reported to be severely impaired in FVIII binding.42 Under our experimental conditions, this variant demonstrated impaired, but still appreciable, binding to FVIII under pseudoequilibrium conditions (Figure 2C) and a relatively minor defect in FVIII binding in SPR analysis (Figure 2A,B). The results of these binding assays are consistent with the observation that patients carrying a homozygous Arg854Gln replacement have higher residual FVIII levels in plasma than patients carrying a homozygous Arg816Trp replacement.43 Although mass transport limitations may underestimate defects in association between mutants, our SPR data indicate that some of the VWF type 2N replacements (Arg854Gln and Cys1060Arg) induce relatively minor differences in binding kinetics (Figure 2A,B). Because FVIII plasma levels are so low (0.3 nM), however, even a minor loss in affinity in the subnanomolar range may already compromise the stability of the FVIII/VWF complex in the circulation.
All VWF-CFP type 2N variants were able to induce the formation of elongated storage granules that resemble WPBs in terms of morphology and ability to recruit the trans-membrane protein P-selectin (Figure 3B). This is not surprising as VWF type 2N variants are generally considered to be structurally and functionally normal with the exception of binding to FVIII. However, in this respect it is noteworthy to mention that Michaux et al have recently demonstrated that the D′D3 region of VWF interacts with the luminal domain of P-selectin thereby providing a targeting motif for P-selectin to gain entry into the WPBs.12 Based on those data, Michaux et al speculated that VWF type 2N variants may display a dysfunctional VWF/P-selectin interaction.12 However, our experimental data indicate that intracellular cotrafficking of P-selectin to VWF-containing granules is normal for VWF type 2N variants. We therefore expect that VWD type 2N patients have normal exposure of P-selectin and subsequent leukocyte recruitment after WPB exocytosis.
To our surprise, despite the variety in binding defects, all VWF-CFP type 2N variants were able to target FVIII-YFP to VWF-containing storage organelles (Figure 4), indicating that high-affinity VWF/FVIII complex assembly is not the driving force behind FVIII/VWF costorage. This finding may seem unexpected in view of previous reports that suggest that several WPB members, including VWF propeptide,7,11 P-selectin,12 osteoprotegerin,14 and interleukin-8,13 are cotargeted with VWF as a result of a direct interaction in the secretory pathway. However, the affinities thereof have not been rigorously assessed12,14 or estimated to be in the micromolar range.13 If affinity in the micromolar range indeed results in complex assembly of VWF with its cargo in the secretory pathway, it is conceivable that residual low-affinity interactions between FVIII and VWF type 2N variants, although not sufficient to stabilize the VWF/FVIII complex in the circulation, support intracellular cotrafficking. This is supported by our data that, even for VWF type 2N variants, some complex with FVIII is present in the cell lysate, albeit reduced (Figure 2D).
An alternative hypothesis is that cotrafficking of FVIII to VWF-containing granules does not require assembly of the FVIII/VWF complex, but is secondary to the VWF-induced biogenesis of secretory granules. These contain—in addition to VWF—a variety of other cargo proteins and membrane constituents that may contribute to FVIII targeting. In this respect, we should mention that previous experiments by Rosenberg et al16 demonstrated that cotrafficking of FVIII to VWF-containing storage organelles in murine pituitary tumor AtT20 cells does depend on high-affinity interaction. The observation that FVIII trafficking in HEK293 cells and HUVECs does not depend on high-affinity interaction,19 although this is required for cotargeting in AtT20 cells,16 suggests that cell-specific elements contribute to FVIII targeting to VWF-containing granules. Targeting of P-selectin displays similar cell-dependent targeting differences between AtT20 cells, HEK293 cells, and HUVECs.12,44,45 In addition, AtT20 cells differ from HEK293 cells and CV-1 cells in that they do not form pseudo–Weibel-Palade bodies upon expression of the VWF Arg763Gly variant.9,46 It therefore seems conceivable that targeting of FVIII to VWF-containing granules involves an additional key player that is absent in AtT20 cells, but present in HEK293 cells and HUVECs.
Another remarkable observation is that FVIII-containing WPBs have lost their characteristic elongated shape (Figures 5B,C and 6A,C). The shape of the WPB has been suggested to result from tubular packing of VWF strings.47 Recently, Huang et al48 have provided evidence that this tubule assembly results from association of 2 individual VWF propeptide moieties with one D′D3 dimer of VWF. We therefore hypothesize that the spherical shape of the FVIII-containing WPBs is caused by disturbed tubular packing of VWF due to the presence of FVIII. Whether this disturbance results from binding of FVIII to the D′D3 region of VWF, thereby preventing the D′D3 region to assist in tubule assembly remains to be established. The fact that the presence of P-selectin, which has also been proposed to bind to the D′D3 region of VWF,12 has no effect on WPB shape suggests that P-selectin and FVIII are differently orientated within the WPB. Alternatively, the luminal domain of P-selectin, being much smaller than FVIII, does not preclude the D′D3 region to interact with VWF propeptide. The importance of proper interaction between propeptide and mature VWF may also explain why round WPBs are formed upon expression of VWF variants that are defective in VWF propeptide, including VWF variants carrying Δpro or Y87S substitution.47 The question remains whether the morphologic change into round WPBs has any impact on the physiology of VWF secretion, or on the hemostatic properties of the released VWF. This may be particularly relevant in gene transfer aiming at FVIII expression in endothelial cells. Similar changes in WPB morphology have recently been described in a study on WPB exocytosis. Babich et al49 demonstrated that WPBs become spherical upon partial loss of cargo through a so-called lingering kiss event. Why presence of FVIII induces a similar morphologic change remains unknown. However, it suggests that WPB morphology depends on its intraorganelle content. Future studies on cargo-induced morphology may contribute to understanding the complexity of WPB sorting.
Although it is clear that the liver constitutes the major site of FVIII biosynthesis,50 administration of desmopressin (DDAVP) results in concomitant increased VWF and FVIII plasma levels, which would be compatible with cosynthesis in—and regulated secretion from—endothelial cells.51 Our observation that WPBs undergo a morphologic change upon expression of FVIII would seem to argue against endogenous production of FVIII in endothelial cells, because WPBs are generally elongated and cigar shaped. On the other hand, it is not known how much FVIII is needed for the transition of elongated to spherical morphology of WPBs. It may be that the amount of FVIII produced in endothelial cells is just too low to interfere with WPB shape. Moreover, it should be noted that most reports regarding endothelial cells have used HUVECs, although it has become increasingly recognized that endothelial cells are organ specific and display high intravascular variations in gene expression.52 It remains possible that FVIII expression is restricted to a particular lineage of the vascular tree. The data presented in this study demonstrate that costorage pools of FVIII and VWF can be generated even in absence of high-affinity interaction. This provides a molecular explanation for the observed DDAVP-mediated release of FVIII and VWF in VWD type 2N patients43,53 and is compatible with the existence of FVIII/VWF costorage pools in vivo.
An Inside Blood analysis of this article appears at the front of this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
Dr C. Mazurier (LFB, Lille, France) is acknowledged for providing VWF constructs containing Thr791Met and Arg816Trp replacements and Dr N. A. Kootstra for providing the lentiviral FVIII construct. We thank Ms Carmen van der Zwaan for help with protein purifications and Ms Birgit Ruhdorfer for technical assistance. Dr G. Storm is acknowledged for constructive comments. We thank Mrs Marlies van Schagen for the multimeric analysis of VWF variants.
Part of this work was supported by the Trombosestichting Nederland (Voorschoten, The Netherlands), grant no. 2004-2 (A.B.M.).
Authorship
Contribution: M.B. performed experiments, analyzed data, made the figures, and wrote the paper; A.B.M. designed research and analyzed data; and J.V. and K.M. designed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Koen Mertens, Sanquin Research, Department of Plasma Proteins, Plesmanlaan 125, 1066 CX, Amsterdam, The Netherlands; e-mail: k.mertens@sanquin.nl.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal