Abstract
Blastoid-variant mantle-cell lymphoma (MCL-BV), unlike most B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL-Bs), is refractory to conventional chemotherapy and associated with a very poor prognosis. Development of new therapies has been hampered by the lack of valid animal models. We have developed a novel murine model of MCL-BV by crossing interleukin 14α (IL-14α) transgenic mice with c-Myc transgenic mice (double transgenic [DTG]). IL-14α is a B-cell growth factor that is expressed in a number of high-grade lymphomas, including MCL-BV. Ninety-five percent of IL-14α transgenic mice develop CD5+ large B-cell lymphomas by 18 months of age. Sixty percent of c-Myc transgenic mice develop pre-B-cell lymphomas by 12 months of age. Close to 100% of DTG mice develop an aggressive, rapidly fatal lymphoma at 3 to 4 months of age that is CD5+, CD19+, CD21−, CD23−, sIgM+. The tumor is found in the blood, bone marrow, liver, spleen, lymph nodes, gastrointestinal tract, and lungs and rarely in the brain, similar to the involvement seen in human MCL-BV. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangements document the monoclonality of the tumor. Cyclin D1 is highly expressed in these tumors, as it is in MCL-BV. DTG represents a novel model for MCL-BV that should reveal important insights into the pathogenesis of the lymphoma and contribute to the development of new forms of therapy.
Introduction
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) are one of only a small number of human cancers that have been increasing in incidence over the last 3 decades.1,2 NHLs are a heterogeneous group of lymphoid tumors, more than 80% of which are derived from the B-lymphoid lineage (NHL-B). Most NHL-Bs are derived from the B2 subset of mature B cells, usually associated with germinal centers (GCs).3,4 Two important forms of NHL-B, small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL/CLL) and mantle-cell lymphoma (MCL), usually express CD5 and appear to be derived from the B1 subset.4–6 SLL/CLL and MCL, while sharing CD5+, B1 cell lineage characteristics, have quite different cellular, genetic, and clinical characteristics. SLL/CLL is an indolent lymphoma often associated with low-grade B-cell leukemia, which is sensitive to chemotherapy with a relatively good survival.7,8 MCL, however, is an aggressive lymphoma that is quite refractory to standard chemotherapy with an overall poor prognosis, although newer therapies have recently improved these patients' outlook.9,10
Clinically, MCL presents with a male predominance in the sixth decade of life, with a mean survival of 40 months. A more aggressive form, the blastoid-variant MCL (MCL-BV), presents at an earlier age and has a mean survival of less than 20 months. Besides involvement of the bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen, there is frequently involvement of the colon and lungs. Approximately 25% of patients have a leukemic phase to their disease and 6% of patients develop central nervous system involvement.9,11
Mantle-cell lymphoma is strongly associated with chromosomal abnormalities including the translocation t(11;14) and deletion of 11q22-23.12–14 The involvement of the ATM and cyclin D1 genes in this disease has been postulated from these abnormalities.13 The deletion of 13q14 commonly seen in B-CLL also occurred in 70% of patients with MCL, suggesting overlapping genetic disorders in these 2 diseases.15 Increased expression of bcl2 and c-Myc is seen in most cases of MCL,9,16–20 with the antiapoptotic bcl2 often increased in expression in many lymphoid malignancies.21 Myc proteins participate in oncogenesis in a wide variety of tumors by a number of different mechanisms, including increasing the entry of cells into the cell cycle, regulating the transcription of many relevant genes, and inducing genomic instability.22–26 The NF-κB family of transcription factors are central mediators in the growth and survival of MCL,27–30 consisting of 5 members: c-rel, RelA (p65), RelB, NF-κB1 (p50/p105), and NF-κB2 (p52/p100).31
Currently, there are no spontaneous animal models for MCL, although xenotransplantation models have been produced in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice growing human MCL cells.32,33 In addition, a candidate MCL model has recently been created in Eμ–cyclin D1 transgenic Balb/c mice treated with 3 monthly intraperitoneal injections of the tumor promoter pristane.34
Interleukin 14 was identified in a Burkitt lymphoma cell line and initially called high–molecular-weight B-cell growth factor (HMW-BCGF).35 It acts as a growth factor for germinal center B-lymphocytes, B1 cells, and memory B cells.35,36 IL-14 is also a potent growth factor for B-CLL in vitro.37 Two transcripts are derived from the IL14 gene, which have been designated IL-14α and IL-14β. Transgenic mice expressing IL4A constructed with the pEμSR vector develop autoimmunity and large B-cell lymphomas by 18 months of age.38 The expression of IL-14α mRNA has been identified in high-grade B-cell tumors in vivo, and IL-14 antisense oligonucleotides inhibit these tumors in vitro.39
We describe here the development of lymphoid malignancies closely resembling the blastoid variant of MCL (MCL-BV) in IL-14α × c-Myc double-transgenic mice (DTG), each produced using the vector pEμSR that directs transgene expression in the B-cell compartment.40 The DTG mice develop an aggressive, monoclonal, CD5+, CD19+, IgM+, and cyclin D1+ B-cell lymphoma early in life that involves the bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen, lungs, colon, and, rarely, the central nervous system. Increased expression of bcl-2, ATM, RelA, and NF-κB2 is noted along with the translocation of the NF-κB proteins to the lymphoma cell nucleus. This is the first animal model that spontaneously develops lymphoma consistent with human MCL-BV.
Patients, materials, and methods
Patient cells were obtained under protocols approved by the institutional review board (IRB) at the M. D. Anderson Cancer Center. Informed consent was provided in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Mice
C57BL/6 (B6) mice were obtained from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME) and housed in the Laboratory Animal Facility at State University of New York at Buffalo (SUNY Buffalo) in accordance with institutional guidelines. IL-14α transgenic mice were made as described.38 C-myc transgenic mice were purchased from Charles River Laboratories (Wilmington, MA). Female c.b.-17-ICR/SCID mice at 3 weeks of age were purchased from Taconic Farms (Germantown, NY). The mice were maintained in the M. D. Anderson Cancer Center SCID Mouse Core Facility, which consists of a standard barrier vivarium, under sterile pathogen-free conditions suitable for immune-deficient rodents in accordance with institutional guidelines.
Total RNA purification and semiquantitative reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
Dependent on the source of samples, 2 different methods were used to collect total RNA. TRIzol purified total RNA from the whole spleen of mice, according to the manufacturer's instructions (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). Total RNA from cells harvested from the spleens of mice was purified with the QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit, according to the manufacturer's instructions (Qiagen, Valencia, CA).
RT-PCR was performed as described.38 The following primers were used for cyclin D1, bcl-2, ATM, RelA, RelB, NF-κB1, NF-κB2, IL-14α, c-Myc, PAK, and actin: cyclin D1 forward primer, 5′-AGAAATCCAATGGGGTTGGA; cyclin D1 reverse primer, 5′-CTACGTAGCCTTCAACACAT; Bcl-2 forward primer, 5′-GACTTCGTAGCAGTCATCCT; Bcl-2 reverse primer, 5′-TGCGCATCTTGGCCTTGAGA; ATM forward primer, 5′-GCTGCTTGACTTTGGCACTTAGCA; ATM reverse primer, 5′-ATCAGACTGTCACAACCACCACCA; RelA forward primer, 5′-ACCATCAGGGCAGATCTCAAACCA; RelA reverse primer, 5′-ACCGAAGCAGGAGCTATCAACACA; RelB forward primer, 5′-GCGGATTTGCCGAATCAACAAGGA; RelB reverse primer, 5′-AGCTGCTCAACTCTCCAAGGACAT; NF-κB1 forward primer, 5′-TGAAGCAGCTGACAGAAGACACGA; NF-κB1 reverse primer, 5′-TGAGTTTGCGGAAGGATGTCTCCA; NF-κB2 forward primer, 5′-TGGTGTCATTGAGCAGATAGCCCA; NF-κB2 reverse primer, 5′-TTCCTGTATGTGTCCACCAGGCTT; IL-14α forward primer, 5′-CACAAGGACCTACAACAGCAGC; IL-14α reverse primer, 5′-TGATGCTTCTGTGCTCGG; c-Myc forward primer, 5′-GACGCGGGGAGGCTATTCTG; c-Myc reverse primer, 5′-AGGGTGTGACCGCAACGT; Pak forward primer, 5′-CGCTTGCTTCAAACATCAAA; Pak reverse primer, 5′-TCCCTCATGACCAGGATCTC; actin forward primer, 5′-GTGGGGCGCCCCAGGCACCA; and actin reverse primer, 5′-CTCCTTAATGTCACGCACGATTTC.
RT-PCR products were separated on 1% agarose gels and visualized by UV light after incorporation of ethidium bromide, as described.41
Morphologic and immunohistochemical analysis
Lymphoma tumor tissue and mouse organs were harvested from IL-14α transgenic, c-myc transgenic, and DTG transgenic mice; placed in 10% formalin (Baxter Diagnostics, Issaquah, WA); and embedded in paraffin. Thin sections were prepared on slides and the slides were stained with the HISTOMOUSE-MAX kit (Invitrogen) as instructed by the manufacturer. Antimouse CD5 and B220 antibodies were purchased from BD Pharmingen (Heidelberg, Germany). Anti–cyclin D1 antibody was purchased from Lab Vision (Fremont, CA).
Flow cytometry
Cells collected from spleens, lymph nodes, or tumor tissue of the mice were stained with panels containing antimouse antibody CD19-APC, CD138-PE, CD21-FITC, CD5-PE-Cy5, CD23-PE, IgD-FITC (BD Pharmingen); CD38-PE-Cy5 (eBioscience, San Diego, CA); and IgM-PE (ABcam, Cambridge, United Kingdom) and analyzed on a BD Biosciences FACSCalibur machine and Winlist software (Verity Software House, Topsham, ME).
Immunoglobulin gene rearrangements
Ig gene rearrangements for clonal B-cell determination of mouse tumor were performed by high-fidelity PCR using 0.1 mg of DNA extracted from normal C57BL/6J mouse liver, spleen, and transgenic mouse tumors using the DNeasy Tissue kit (Qiagen). The primers for immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in the lymphomas from the IL-14α transgenic mice were DHL (5′GGAATTCGMTTTTTGTSAAGGGATCTACTACTGTG), J3 (5′GTCTAGATTCTCACAAGAGTCCGATAGACCCTGG); and DHR (5′TTTTGYTGMTGGATATAKCACTGAG), J3 (5′GTCTAGATTCTCACAAG-AGTCCGATAGACCCTGG). PCR was performed as described42 with the following protocol: incubation at 95°C for 5 minutes then 95°C for 1 minute, 55°C for 1minute, and 72°C for 2 minutes for 35 cycles, followed by extension at 72°C for10 minutes. The PCR products were analyzed on 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis.
Spectral karyotyping
Spectral karyotyping (SKY) was performed as previously described.43 In short, metaphase chromosome spreads were prepared from murine lymphoma cells using standard hypotonic treatment and fixation. They were then denatured with 70% formamide and hybridized with the murine SKY probes (Applied Spectral Imaging, Carlsbad, CA). Chromosomes were isolated by high-resolution flow sorting and tagged with different combinations of digoxigenin, Texas red, Cy5, biotin/streptavidin, and Cy5.5. SKY images were captured using the Spectral Curve/Interferometer, and karyotypes were prepared using SKYView software (Applied Spectral Imaging).
Western blot for human IL-14α
The Western blot for human IL-14α in lymphoma cells was performed as previously described.39
NF-κB translocation
Translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus was detected using electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) analysis and Western-blot analysis as previously described.29 Antibodies to NF-κB proteins were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotech (Santa Cruz, CA).
Oversight
The animal studies were all approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, SUNY at Buffalo School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. Lymphoma cells were obtained from patients at the M. D. Anderson Cancer Center according to the local IRB.
Microscopy
Images were visualized under an Olympus BX41 microscope (Olympus, Melville, NY) equipped with a 40×/0.65 or 40×/1.25 oil-immersion Olympus Uplan F1 objective lens. Permount imaging medium (Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA) and haematoxylin-eosin stain (H&E stain) were used. Images were captured with an Olympus Q color 5 camera, acquired with Olympus Q Capture software version 2.7, and processed with Adobe Photoshop CS2 software (Adobe Systems, San Jose, CA).
Results
Characteristics of the malignancy in IL-14α TG × c-Myc TG (DTG) mice
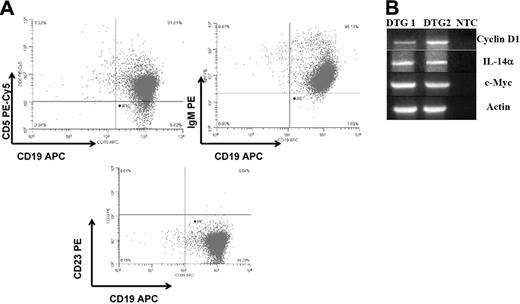
Since IL-14 is expressed in high-grade B-cell lymphomas, many of which also express c-Myc, we evaluated whether c-Myc could accelerate tumor formation in IL-14α TG mice.39 Previous studies had demonstrated that 95% of C57BL/6 IL-14α TG mice develop CD5+, CD19+, sIgM+, cyclin D1–negative large B-cell lymphomas by 16 to 18 months of age.38 We crossed c-Myc transgenic mice, produced with the same vector as the IL-14α transgenic mice,40 with IL-14α TG mice to obtain double-transgenic mice (DTG). Every DTG mouse is characterized by an initial leukemic phase (Figure 1A) and develops a B-cell malignancy within 4 months, preceding the appearance of dramatic, widespread lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly (Figure 1B). DTG mice at 2 months of age have high peripheral white blood cell counts that are 1.5 to 3 times higher than littermate controls with 10% to 50% leukemic blasts. Lymphoma can readily be demonstrated in the bone marrow (Figure 1C), spleen (Figure 1D), gastrointestinal tract (Figure 1E), and liver (Figure 1F) in all DTG mice. This pattern of organ involvement is characteristically seen in the most aggressive forms of MCL.11,12,44,45 The morphology of these tumors closely resembles human MCL-BV, with diffuse structural effacement of lymphoid tissue with large (blastoid) lymphoma cells showing large ovoid or cleft nuclei with a vesicular chromatin pattern and often prominent nucleoli (Figure 1G).46 There are often prominent large histiocytes admixed throughout the tumor. To characterize this tumor further and to distinguish it from the tumors of the IL-14α TG mice and c-myc TG mice, we compared the histology (Figure 2A), expression of cell-surface markers (Figure 2B), and gene-expression profile (Figure 2C) of these 3 tumors. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangements demonstrated that the tumors of the IL-14α TG mice, the c-myc TG mice, and the DTG mice were all monoclonal in origin (Figure 2F). The histology of tumors from the IL-14α TG mice was most consistent with large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL), demonstrating atypical large transformed B-lymphoid cells with large vesicular nuclei, slightly basophilic cytoplasm, morphologic variability, and easily found mitotic figures (Figure 2A).38 The histology of the tumors from the c-myc TG mice was most consistent with an aggressive pre-B-cell lymphoma (Figure 2A) and demonstrated relatively monomorphic, medium-sized atypical lymphoid cells with a moderate amount of basophilic cytoplasm, regular oval-to-round nuclei, and easily found mitotic figures.40 The histology of the tumors from the DTG mice was very different from the tumors of the IL-14α TG mice or c-myc TG mice (Figures 1 and 2A). The tumors of the IL-14α TG mice, c-myc TG mice, and DTG mice all expressed CD5 (Figure 2D) and CD19 (Figure 2B,D).38 The tumors of the IL-14α TG and DTG mice expressed sIgM, but the tumors from the c-myc TG mice did not, as would be expected of a pre-B-cell tumor (Figure 2D).40 None of these tumors expressed CD21, CD23, or sIgD (Figures S1–S2, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article). The cell-surface phenotype of the DTG tumors is consistent with MCL-BV.9,11,47,48
Clinical appearance of tumors in DTG mice. (A) Peripheral-blood smear from a 3-week-old DTG mouse showing leukemic atypical large blastic lymphoid cells morphologically similar to lymphomas subsequently arising in peripheral lymphoid tissues (original magnifications: left, ×400, right, ×1000). (B) Gross necropsy photo of DTG mouse, showing widespread and extensive peripheral lymphadenopathy indicative of lymphomatous involvement as histologically shown in panel D. Arrows indicate lymph nodes. (C) Bone marrow from a 3-month-old DTG mouse showing large “blastoid” lymphoma cells (original magnification, ×1000). (D) Histopathologic H&E-stained paraffin section of the spleen showing diffuse effacement of an enlarged lymph node diffusely replaced with large “blastoid” lymphoma cells with admixed large “pink” histiocytes characteristic of MCL-BV (original magnification, ×400). (E) Lymphomatous involvement in the gastrointestinal tract showing diffuse involvement of the lamina propria and submucosa (original magnification, ×400). (F) Liver involvement in DTG mice, showing perivascular infiltrates of lymphoma cells (original magnification, ×400). (G) Comparison of DTG lymphoma cell line with 2 representative MCL-BV cell lines from patients showing morphologic similarity between human MCL-BV and the DTG murine model (H&E; original magnification, ×1000).
Clinical appearance of tumors in DTG mice. (A) Peripheral-blood smear from a 3-week-old DTG mouse showing leukemic atypical large blastic lymphoid cells morphologically similar to lymphomas subsequently arising in peripheral lymphoid tissues (original magnifications: left, ×400, right, ×1000). (B) Gross necropsy photo of DTG mouse, showing widespread and extensive peripheral lymphadenopathy indicative of lymphomatous involvement as histologically shown in panel D. Arrows indicate lymph nodes. (C) Bone marrow from a 3-month-old DTG mouse showing large “blastoid” lymphoma cells (original magnification, ×1000). (D) Histopathologic H&E-stained paraffin section of the spleen showing diffuse effacement of an enlarged lymph node diffusely replaced with large “blastoid” lymphoma cells with admixed large “pink” histiocytes characteristic of MCL-BV (original magnification, ×400). (E) Lymphomatous involvement in the gastrointestinal tract showing diffuse involvement of the lamina propria and submucosa (original magnification, ×400). (F) Liver involvement in DTG mice, showing perivascular infiltrates of lymphoma cells (original magnification, ×400). (G) Comparison of DTG lymphoma cell line with 2 representative MCL-BV cell lines from patients showing morphologic similarity between human MCL-BV and the DTG murine model (H&E; original magnification, ×1000).
Histopathologic and immunohistochemical characteristics of the DTG lymphomas in relation to the B-cell lymphomas in parental IL-14α TG and c-myc TG mice. (A) H&E-stained paraffin sections (original magnification, × 400). (B) Sections stained with anti-B220 (original magnification, × 400). (C) Sections stained with anti–cyclin D (original magnification, × 400). DTG tumor staining is more uniform and intense than that of the c-myc TG tumor. IL-14α TG tumor is negative. (D) Flow cytometry of tumors from IL-14α TG, c-myc TG, and DTG mice showing CD19/CD5 and CD19/sIgM staining. (E) Semiquantitative RT-PCR of C57/BL6 spleen and tumors from IL-14α TG, DTG, or c-myc TG mice analyzed for cyclin D1 and actin, as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” (F) Immunoglobulin gene rearrangements performed on tumors from IL-14α TG, c-myc TG, and DTG mice showing monoclonality of all of these tumors, as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.”
Histopathologic and immunohistochemical characteristics of the DTG lymphomas in relation to the B-cell lymphomas in parental IL-14α TG and c-myc TG mice. (A) H&E-stained paraffin sections (original magnification, × 400). (B) Sections stained with anti-B220 (original magnification, × 400). (C) Sections stained with anti–cyclin D (original magnification, × 400). DTG tumor staining is more uniform and intense than that of the c-myc TG tumor. IL-14α TG tumor is negative. (D) Flow cytometry of tumors from IL-14α TG, c-myc TG, and DTG mice showing CD19/CD5 and CD19/sIgM staining. (E) Semiquantitative RT-PCR of C57/BL6 spleen and tumors from IL-14α TG, DTG, or c-myc TG mice analyzed for cyclin D1 and actin, as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” (F) Immunoglobulin gene rearrangements performed on tumors from IL-14α TG, c-myc TG, and DTG mice showing monoclonality of all of these tumors, as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.”
One of the characteristics of MCL-BV is the expression of bcl-1/cyclin D1.5,9,49 We evaluated cyclin D1 expression in the tumors of the IL-14α TG, c-myc TG, and DTG mice. The tumors of the DTG mice express high levels of cyclin D1 at both the RNA (Figure 2E) and protein level (Figure 2C), whereas the tumors of IL-14α TG mice do not. A small percentage of the tumor cells from the c-myc TG mice express cyclin D1 at a low level, as visualized by immunohistochemistry (Figure 2C). The DTG lymphomas are distinct from the lymphoid tumors of either the IL-14α TG mice or c-myc TG mice, from which the DTG mice were derived. Several lymphoma cell lines have been developed from the tumors of the DTG mice that retain the characteristics of the primary tumors, with expression of CD5, CD19, sIgM, and cyclin D1 (Figure 3). Early in vitro–explanted cultures initially showed mixtures of lymphoid tumor cells with large macrophage-like cells, as in the histopathologic sections, that in time evolved into cultures of predominantly MCL-BV cells.
Characteristics of tumor cell lines derived from DTG mice. (A) Flow cytometry evaluating CD19/CD5, CD19/sIgM, and CD19/CD23. (B) Semiquantitative RT-PCR evaluating cyclin D1, IL-14α, and c-Myc, as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.”
Characteristics of tumor cell lines derived from DTG mice. (A) Flow cytometry evaluating CD19/CD5, CD19/sIgM, and CD19/CD23. (B) Semiquantitative RT-PCR evaluating cyclin D1, IL-14α, and c-Myc, as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.”
Cytogenetic studies and spectral karyotyping on cultured DTG/MCL cells
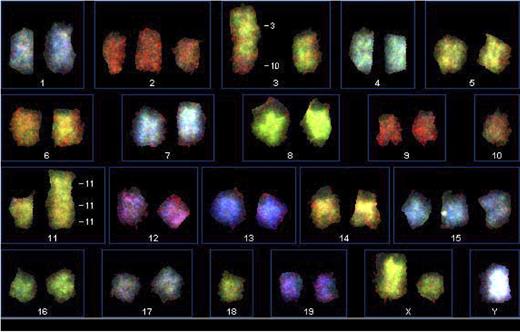
Because MCL-BV is strongly associated with chromosomal abnormalities including the translocation t(11;14) and deletion of 11q22-23,12–14 we undertook preliminary cytogenetic analysis and karyotyping of tumor cells from several of the DTG lymphoma cell lines. The chromosomal range on the DTG lymphoma cell lines studied was 37-41 and the modal number was 40. Figure 4 shows spectral karyotyping of a representative DTG cell line of 4 studied. Additional cytogenetic data are shown in Figures S1–S2. These studies revealed a complex karyotype with multiple chromosomal abnormalities in the DTG lymphoma cells. Chromosomal abnormalities seen in all the preparations include trisomy 15 and a 3:10 translocation. Other chromosomal abnormalities are seen variably in the different tumor cell lines. We did not identify a syntenic equivalent chromosomal t(11;14) translocation in any of the cell lines studied so far. The chromosome 3 abnormality could potentially involve ATM, a gene frequently implicated in the pathophysiology of MCL, particularly MCL-BV,13,42,50–52 and PAK, a gene involved with increased transcription and translation of cyclin D1.53
Spectral karyotyping (SKY) of a DTG cell line. SKY was performed as outlined in “Patients, materials, and methods.” A 3:10 translocation, trisomy 15, trisomy 2, and 11:11 translocation were observed.
Spectral karyotyping (SKY) of a DTG cell line. SKY was performed as outlined in “Patients, materials, and methods.” A 3:10 translocation, trisomy 15, trisomy 2, and 11:11 translocation were observed.
Additional molecular studies on the DTG/MCL murine lymphomas
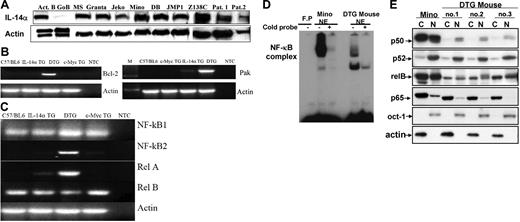
Several potential oncogenes are frequently expressed in MCL-BV in addition to cyclin D1, particularly in MCL-BV. We have demonstrated that IL14A is expressed in several human MCL-BV cell lines, as well as primary MCL-BV cells (Figure 5A). The MYC gene is frequently expressed in MCL-BV and represented in our model through the expression of the pEμSR c-myc transgene.9,19,33,51,54 Bcl-2 or its antiapoptotic family members is often expressed in MCL and is expressed in our animal model as well (Figure 5B).17,55 Recent studies have suggested that various NF-κB proteins are constitutively activated in MCL-BV and are important for the growth of these tumors.29,56–58 We have demonstrated that the mRNA for the NF-κB family members RelA and NF-κB2 are overexpressed and constitutively activated in the tumors from the DTG mice but not from the IL-14α TG or c-myc TG mice (Figure 5C). To demonstrate that NFκB is constitutively active in the DTG tumors, we also demonstrated nuclear translocation of these proteins by EMSA analysis and Western blotting in the DTG lymphoma cells (Figure 5D-E).58–60 Because of the translocation involving chromosome 3 and the potential involvement of PAK in regulation of cyclin D1, we evaluated the expression of PAK in the DTG tumors. Figure 5B demonstrated that PAK is overexpressed in DTG tumors and weakly expressed in IL-14α TG tumors but is not expressed in c-myc TG tumors.
Gene expression in MCL-BV. (A) Demonstration of IL-14α expression in MCL-BV cell lines and fresh tumors from various patients, performed as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” (B) Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis of bcl-2 and Pak expression in spleen from C57BL/6 mice, and tumors from IL-14a TG, DTG, and c-Myc TG mice, performed as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” NTC indicates negative control (no primers). (C) Expression of NF-κB components in the lymphoma of a DTG mouse. Total RNA purified from the indicated mouse was analyzed for NF-κB1, NF-κB2, p65, and RelB by semiquantitative RT-PCR. (D) Translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus in DTG lymphoma cells. EMSA analysis was performed as described in “Patients, materials, and methods” using nuclear extracts purified from Mino cells or DTG lymphoma cells. FP indicates free probe. (E) Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were purified from Mino cells or 3 different cell lines derived from the lymphoma of DTG mouse and analyzed for NF-κB components by Western blotting as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.”
Gene expression in MCL-BV. (A) Demonstration of IL-14α expression in MCL-BV cell lines and fresh tumors from various patients, performed as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” (B) Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis of bcl-2 and Pak expression in spleen from C57BL/6 mice, and tumors from IL-14a TG, DTG, and c-Myc TG mice, performed as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” NTC indicates negative control (no primers). (C) Expression of NF-κB components in the lymphoma of a DTG mouse. Total RNA purified from the indicated mouse was analyzed for NF-κB1, NF-κB2, p65, and RelB by semiquantitative RT-PCR. (D) Translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus in DTG lymphoma cells. EMSA analysis was performed as described in “Patients, materials, and methods” using nuclear extracts purified from Mino cells or DTG lymphoma cells. FP indicates free probe. (E) Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were purified from Mino cells or 3 different cell lines derived from the lymphoma of DTG mouse and analyzed for NF-κB components by Western blotting as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.”
Transplantation of DTG lymphoma cells into immune-deficient SCID mice
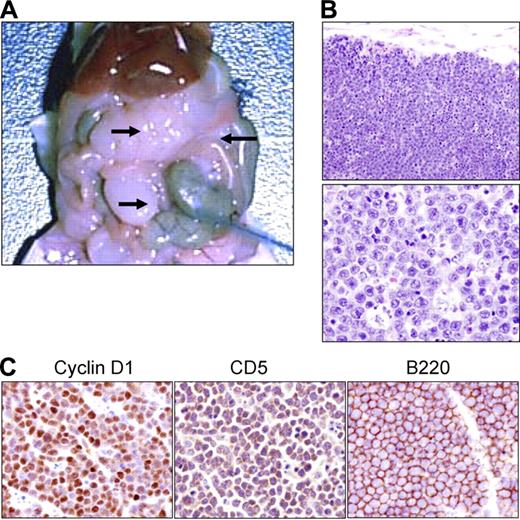
Although the DTG lymphoma appears to display all of the requisite characteristics of an aggressive NHL-B, it was important to determine if the DTG lymphoma cells could be successfully transplanted. For these studies, DTG lymphoma cells from 1 of the recently established DTG cell lines were adoptively transferred into immune-deficient c.b.17 SCID mice, as previously described.32 However, while most human lymphoma cells (including MCL) required xenotransplantation at doses of 10 × 106 to 20 × 106 or greater cells per mouse, DTG tumor cells transplanted at this dose repeatedly killed the SCID mice in 2 to 3 days. The maximum number of DTG tumor cells that could be successfully transplanted into a SCID mouse, without killing the mouse, is 10 × 106, and we have successfully transplanted some DTG tumors at 5 × 106 cells/mouse. Lymphoid tumors appeared within 2 weeks after transplantation and arose primarily within the peritoneal cavity, attached to mesentery and external to the bowel (Figure 6A-B). Immunohistochemistry of the tumors growing in the SCID mice expressed B220, CD5, and cyclin D1, identical to the original DTG lymphoma (Figure 6C).
Transplantation of DTG lymphoma cells into immune-deficient SCID mice. (A) Necropsy of a SCID mouse that received a transplant of cells from a cell line derived from a DTG mouse lymphoma (arrows). (B) H&E paraffin sections of the SCID peritoneal tumor bearing the DTG tumor cells from low (top panel; original magnification, ×100) to high magnification (bottom panel, original magnification, ×400). (C) Immunohistochemical analysis of the transplanted lymphoma from a SCID mouse showing the expression of cyclin D1, CD5, and B220 (original magnification, ×400).
Transplantation of DTG lymphoma cells into immune-deficient SCID mice. (A) Necropsy of a SCID mouse that received a transplant of cells from a cell line derived from a DTG mouse lymphoma (arrows). (B) H&E paraffin sections of the SCID peritoneal tumor bearing the DTG tumor cells from low (top panel; original magnification, ×100) to high magnification (bottom panel, original magnification, ×400). (C) Immunohistochemical analysis of the transplanted lymphoma from a SCID mouse showing the expression of cyclin D1, CD5, and B220 (original magnification, ×400).
Discussion
In these studies, we demonstrate the production of a murine lymphoma model that recapitulates clinical, histologic, and genetic features of MCL-BV, a morphologic variant of classical MCL. Transgenic mice expressing oncogenes known to be up-regulated in MCL, such as cyclin D1, Myc, and Bcl2, have produced lymphomas resembling various NHL-B histotypes, but none of these resembled MCL.17,40,61–66 We evaluated lymphomagenesis in IL-14α transgenic mice because IL-14 was originally identified in a Burkitt lymphoma cell line, induces proliferation of B cells, enhances expression of bcl-2, and shows constitutive expression in a wide range of B-cell malignancies.35,39 The IL-14α transgenic mice develop a lymphoma in older mice resembling human large B-cell lymphoma.38 To further analyze the role of IL-14 in lymphomagenesis, we bred the IL-14α transgenic mice with c-Myc transgenic mice, since c-Myc is dysregulated in Burkitt and other lymphomas67 and c-Myc facilitates the development of cancer without necessarily dictating the phenotype of the tumor.63,64,66,68–71 The rapid onset and the high rate of penetrance (close to 100%) of MCL-BV in the DTG mice suggest that IL-14α is playing a critical role in the development of these tumors.
The DTG/MCL-BV murine model closely resembles the human counterpart except for the lack of the syntenic equivalent translocation t(11;14) involving the cyclin D1 gene. Interestingly, MCL has been described in a small number of patients without the t(11;14) translocation. In all of these cases, cyclin D1 was not highly expressed and utilization of other D cyclins was implicated in the pathophysiology of the tumors.72,73 In the tumors of DTG mice, however, cyclin D1 is overexpressed (Figures 2C, 2E, 3B, 6C), so another mechanism(s) for cyclin D1 dysregulation besides t(11;14) must be present. The expression of cyclin D1 is complex and may require constitutive nuclear expression to induce B-cell lymphoma. A number of genes have been implicated in the regulation of cyclin D1 transcription and translation, including PAK, which may be involved in the 3:10 translocation identified by SKY (Figure 4) and is overexpressed in the DTG tumors (Figure 5B).74–76
Recent studies have suggested that besides cyclin D1, both NFκB and ATM are critical for MCL.5,11,29,57 A characteristic deletion 11q22-q23 found in MCL involves ATM.5,13 The t(3:10) translocation identified in the DTG tumors may involve ATM as well (Figure 4). The levels of ATM expression were not, however, found to be significantly different among normal spleen and tumors from c-Myc TG, IL-14α TG, and DTG mice (data not shown). In contrast, significant elevations of RelA and NF-κB2 mRNA were identified in the DTG tumors (Figure 5C). NFκB was constitutively activated and expressed in the nucleus of these tumors, as has been described in many NHL-B lymphomas, suggesting that it was active in the disease process (Figure 5D-E).
While closely reproducing many features of MCL-BV, the tumors of the DTG mice provide a novel model to dissect the molecular events leading to this type of malignancy. In addition, this murine model suggests that MCL-BV may arise de novo in bone marrow (BM), rather than only as a progression from classic (small-cell) MCL. Since MCL does not occur spontaneously in mice, the DTG mice provide a unique opportunity to understand the development of the MCL-BV phenotype in the murine lymphoid lineage. How IL-14 and c-Myc interact to produce this phenotype may provide important clues to the pathogenesis of MCL-BV. The DTG mice provide an important model to test therapeutic agents for MCL-BV. Many questions remain to be answered including what cells are these tumors derived from and why these tumors are so widespread in the body at clinical presentation. It is important to determine why these tumors are so biologically and clinically aggressive and so refractory to therapies that have been effective in other forms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The online version of this manuscript contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Cancer Institute grants CA-RO1-100836 and CA-16672-26 (R.J.F.) and grants from the Lymphoma Research Foundation (New York, NY; R.J.F), Wendt Foundation (J.L.A.), and Troupe/Kaleida Health Foundation (J.L.A.). The authors would like to thank various individuals for assistance with these studies. Linda Yoshimura, Tao Wang, Hua Zeng, Shangguo Tang, Stephen Brooks, and Donald Sykes helped with various technical aspects of the work. The authors would also like to thank Linda Ludwig, Oleh Pankewycz, and Dr Sen Pathak for helpful suggestions and comments regarding this work. Tracey Roth provided editorial assistance in the preparation of this manuscript. Lan V. Pham was supported by the Odyssey program and a Kimberly-Clark Foundation Award for Scientific Achievement at the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center.
National Institutes of Health
Authorship
Contribution: R.J.F. designed research and wrote the paper; L.S., Y.C.L.-L., and L.V.P. performed research and wrote the paper; A.M., H.-J.Z., A.T.T., C.Z., and L.H. performed research; J.K.C. analyzed data; and J.L.A. designed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Julian L. Ambrus Jr, SUNY at Buffalo School of Medicine Room 308 MLB, BGH 100 High Street, Buffalo, NY 14203; e-mail: jambrus@buffalo.edu.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal