Abstract
Increasing evidence supports the existence of elevated numbers of regulatory T cells (Treg cells) in solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. Whereas the biology of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ Treg cells in murine models seems to be rather straightforward, studies in human diseases are more difficult to interpret due to expression of CD25 on activated effector T cells as well as Treg cells. More importantly, early studies in human tumors were mainly focused on CD4+CD25+ Treg cells lacking interrogation of more specific markers such as FOXP3 expression. Although the increase of Treg cells seems to be a characteristic feature in most tumors, little is known about the molecular and cellular mechanisms responsible for the increase and maintenance of elevated levels of Treg cells in cancer. We will discuss earlier data in the context of recent findings in Treg-cell biology with a particular emphasis on CD4+CD25highFOXP3+ Treg cells in human malignancies.
Introduction
In 1971, Gershon and Kondo identified so-called “suppressor” cells when they transferred antigen-specific tolerance to naive animals by transferring antigen-experienced T cells.1 Due to conflicting results, the concept of T-cell suppression vanished into relative obscurity in the late 1980s. However, reports describing murine T cells responsible for suppression of antitumor immune responses2 and the identification of human CD4+ T-cell clones suppressing autologous cytotoxic antitumor immune responses3 clearly suggested that in vivo mechanisms of tumor-driven cellular immune suppression must exist.
Sakaguchi et al were the first to stir up again the interest in now termed “regulatory” T cells (Treg cells) by identifying a population of CD4+ T cells highly expressing CD25 and preventing autoimmunity in a murine model.4 Numerous reports in the following years enlightened major aspects of Treg-cell biology, characterizing different T-cell subpopulations with regulatory properties including naturally occurring CD4+CD25high Treg cells, induced Treg cells, eg Tr1 and TH3 cells, as well as CD4+CD25high Treg cells developing in the periphery by conversion of CD4+CD25– T cells. All these different T-cell populations with regulatory function coexist and contribute to immune suppression.5-8
In the mouse, CD25 is a good marker for Treg cells, as animals are held under pathogen-free conditions. However, humans are constantly exposed to foreign antigens, leading to a significant fraction of recently activated CD25+ effector T cells. In search of more specific Treg-cell markers, the transcription factor FOXP3 has been identified as uniquely expressed in Treg cells in the mouse9-11 and expression has been proposed as a lineage marker already in developing Treg cells.12,13 However, caution about its specificity still is recommended because recent reports in humans demonstrated induction of FOXP3 in activated conventional T cells without suppressive activity.14-16
Characteristics of CD4+CD25highFOXP3+ Treg cells are their anergic state, their ability to actively inhibit CD4+CD25– T cells, CD8+ T cells, dendritic cells (DCs), natural killer (NK) cells, natural killer T (NKT) cells, and B cells in a cell-to-cell contact and dose-dependent manner.17-22 Phenotypically CD4+CD25highFOXP3+ Treg cells are characterized as antigen-experienced memory T cells, although lately some reports have described naive CD4+CD25highFOXP3+ T cells in mice as well as humans.23,24 Among the cell-surface markers associated with Treg-cell phenotype and function, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) and glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein (GITR) are the most prominent molecules.25-28 Additionally, IL-10 and TGF-β, although rarely expressed in vitro, might have functional importance for Treg cells in vivo, particularly in the context of disease.29,30 Major topics of current research are the characterization of Treg-cell defects in autoimmune diseases and their role in infectious diseases and transplantation tolerance, particularly after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation.5,6,31-34 Although research in Treg-cell biology is intensifying, it is still unclear whether Treg cells in human tumors are primed mainly in the thymus or emerge in the periphery due to antigen-specific stimulation. The lack of more specific cell-surface markers is a major reason that many functionally relevant aspects of Treg cells are still unknown. In this review, we focus mainly on naturally occurring CD4+CD25highFOXP3+ Treg cells with particular emphasis on novel aspects in malignant disease as well as potentials for improving antitumor immunity by targeting Treg cells.
Increase of Treg cells in cancer-bearing mice
Treg cells protect the host from autoimmune disease by suppressing self-reactive cells. As such, Treg cells may also block antitumor immune responses. Particularly in the context of cancer, Treg-cell frequencies and function are important because increased numbers might favor tumor development or growth and influence the course of the disease. Currently, a number of important questions are under intense investigation. Is the increase of Treg-cell frequencies an early event at the onset of disease or more likely a response of the immune system during tumor progression? Do organ-specific and more importantly, do tumor-specific Treg cells, play a role? How does therapy influence Treg-cell numbers, particularly in already established tumors? Is there a possibility of long-term depletion of Treg cells and is this connected to induction of autoimmunity?
The development of Treg cells during tumor progression has been addressed in a fibrosarcoma model in C57BL/6N mice as well as in a colon adenocarcinoma model in BALB/c mice. Transfer of unfractionated tumor-draining lymph node (LN) cells isolated on day 9 after tumor challenge achieved complete rejection of established tumors, whereas even 4-fold higher numbers of cells harvested on day 12 seldom prevented lethal tumor progression. This treatment failure was due to cotransfer of tumor-induced Treg cells, indicating that during this relatively short time span of tumor development the induction of a highly suppressive Treg-cell population occurred.35 Relatively early induction of Treg cells during tumor development has significant impact in human disease as the time point of Treg-cell induction in cancer patients would certainly precede the time of diagnosis in the majority of patients.
The suppressive effect of naturally occurring Treg cells against tumor-specific CD8+ T cells was established in a poorly immunogenic B16 melanoma model. Treg cells efficiently suppressed cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL)–mediated concomitant immunity against a rechallenge with the same tumor, demonstrating that precursor Treg cells in naive hosts gave rise to effective suppressors during tumor development. These findings clearly suggest that Treg cells are major regulators of concomitant tumor immunity.36 Further evidence for the interference of Treg cells with CD8+ T cell-mediated antitumor immune responses in vivo was established in a transgenic murine colon carcinoma model where Treg cells abrogated CD8+ T cell–mediated tumor rejection by specifically suppressing cytotoxicity of CTLs.37
Selective accumulation of Treg cells in the tumor environment was studied in a murine fibrosarcoma model where the majority of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) at late stage of tumor progression were Treg cells. Their depletion during the effector rather than priming phase successfully enhanced antitumor immunity. Blockade of IL-10 and TGF-β partially reversed the suppression imposed by CD4+ T cells. Furthermore, local depletion of CD4+ T cells inside the tumor led to eradication of well-established tumors and development of long-term antitumor memory. This study suggested that suppression of antitumor immunity by Treg cells occurs predominantly at the tumor site and that local reversal of suppression, even late during tumor development, can be an effective treatment.38 This has been confirmed in a murine pancreatic cancer model, suggesting that the tumor actively promotes the accrual of Treg cells through several mechanisms involving activation of naturally occurring Treg cells as well as conversion of non-Treg cells into Treg cells.39
Analysis of tumor-draining LNs demonstrated that both antitumor effector T cells and FOXP3+ Treg cells are primed in the same LNs during tumor progression. These tumor antigen-specific Treg cells possessed the same functional properties as Treg cells that arise naturally in the thymus.40 Whether there is a systemic increase of Treg cells in cancer-bearing mice is not yet clearly defined because conflicting data have been reported. In a colon carcinoma model, an expansion of Treg cells was observed only in the spleen but not in peripheral blood (PB).41 In contrast, in a murine transgenic model of prostate dysplasia, increased frequencies of Treg cells and enhanced production of inhibitory cytokines were observed in PB, resulting in impaired T-cell function, which also correlated with tumor progression.42
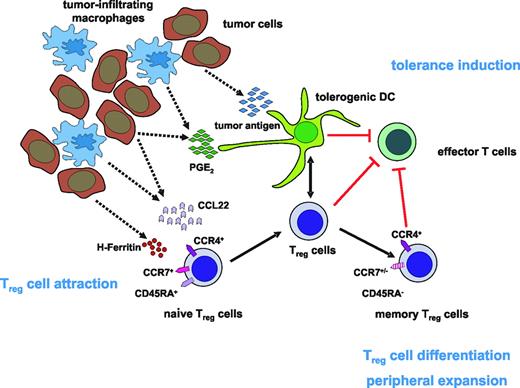
Although these experiments focused on accumulation and function of Treg cells, the trafficking behavior of Treg cells and their cellular interactions and localization to and within the tumor microenvironment and in tumor-draining LNs were not studied in these models. Immunohistochemistry revealed FOXP3+ Treg cells in close proximity to CD11c+ DCs, FOXP3–CD4+ T cells, and CD8+ T cells in the T-cell regions of lymphoid tissues in normal and tumor-bearing mice.43 Further insights into the signals involved in Treg-cell attraction to tumor sites came from studies in a lung cancer model. Tumor-derived prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) resulted in an increase of Treg-cell activity and Foxp3 expression (Figure 1). Assessment of E-prostanoid (EP) receptor requirements revealed that absence of EP4 receptor led to reduced induction of Foxp3, whereas absence of EP2 ablated expression. In vivo, COX2 inhibition reduced Treg-cell frequency and activity, attenuated Foxp3 expression, and decreased tumor burden. Transfer of Treg cells or administration of PGE2 to mice receiving COX2 inhibitors reversed these effects, indicating that COX2 inhibition suppressed Treg-cell activity and might be useful to enhance antitumor responses.44 Interestingly, PGE2 also enhanced the in vitro inhibitory function of human Treg cells and induced a regulatory phenotype in CD4+CD25– T cells. Furthermore, PGE2 exposure induced FOXP3 in CD4+CD25– T cells and up-regulated its expression in Treg cells. Similarly, incubation with supernatants from COX2-overexpressing lung cancer cells secreting PGE2 significantly induced FOXP3, indicating that PGE2 can indeed modulate FOXP3 expression and Treg function.45
Treg-cell depletion leads to restoration of antitumor immunity
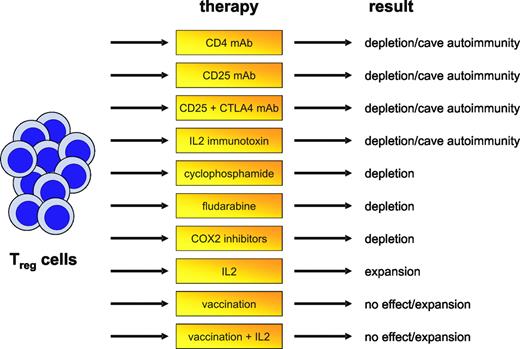
Even before the identification of CD4+CD25+ Treg cells, early data indicated that nonspecific depletion of CD4+ T cells can lead to the induction of efficient antitumor immunity (Figure 2).46 More specifically targeting Treg cells by administration of CD25 monoclonal antibody (mAb) abrogated immunologic unresponsiveness to tumors and induced spontaneous development of tumor-specific CD8+ effector T cells and NK cells.47 Interestingly, depletion of Treg cells led to cross-reactive tumor immunity against tumors of diverse origins.48 Timing of Treg-cell elimination also seems to be an important aspect. Administration of CD25 mAb later than 2 days after inoculation of myeloma cells caused no tumor regression, irrespective of Treg-cell depletion.49 As already outlined, this might be due to the induction of antitumor tolerance at a relatively early time point of tumor development, resulting in inefficient activation of effector cells. Furthermore, the number of Treg cells after CD25 depletion is restored over time and the capacity to mount an antitumor response progressively diminishes.50
Model of the accumulation of Tregcells in human tumors. One of the possible scenarios for how Treg-cell attraction to the tumor site and expansion of Treg cells occurs may be the release of CCL22 as well as H-ferritin by tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating macrophages leading to the accumulation of CCR4+ naive Treg cells in the tumor microenvironment. Interaction with PGE2-induced tolerogenic DCs then gives rise to the differentiation and peripheral expansion of naive Treg cells into memory Treg cells. Together with tolerogenic DCs, these Treg cells than inhibit the generation of effector T cells, resulting in the induction of tolerance against the tumor.
Model of the accumulation of Tregcells in human tumors. One of the possible scenarios for how Treg-cell attraction to the tumor site and expansion of Treg cells occurs may be the release of CCL22 as well as H-ferritin by tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating macrophages leading to the accumulation of CCR4+ naive Treg cells in the tumor microenvironment. Interaction with PGE2-induced tolerogenic DCs then gives rise to the differentiation and peripheral expansion of naive Treg cells into memory Treg cells. Together with tolerogenic DCs, these Treg cells than inhibit the generation of effector T cells, resulting in the induction of tolerance against the tumor.
Depletion of Treg cells together with other immunostimulatory approaches, for example, CTLA-4 blockade, has also been tested. Combination of Treg-cell depletion and CTLA-4 blockade was synergistic and resulted in maximum tumor rejection. The observed synergism indicates that both pathways represent 2 alternatives for suppression of autoreactive T cells so that simultaneous intervention might be a promising concept for the induction of therapeutic antitumor immunity.51 Because immune responses to malignant tumors often are weak and ineffective, solely depleting Treg cells might not always result in tumor regression. Approaches combining Treg-cell depletion with other immunologic interventions, for example, transfer of activated T cells or DC-based vaccinations, therefore might be more beneficial.52-54
Reduction of Treg cells is associated with the immunostimulatory effect of cyclophosphamide
It has long been recognized that cyclophosphamide exerts an immunostimulatory effect.55 Early data indicated that cyclophosphamide preferentially destroys CD4+ suppressor T cells causing immunologically mediated regression of immunogenic lymphomas in mice.56 In a rat colon cancer model, administration of cyclophosphamide depleted Treg cells and delayed the outgrowth of tumors.57 Combining cyclophosphamide and immunotherapy even cured the mice, whereas both strategies applied alone had no curative effect.57,58 Low-dose cyclophosphamide not only decreases numbers of Treg cells but also leads to decreased function, enhanced apoptosis, and decreased homeostatic proliferation.59 This suggests that cyclophosphamide might be successfully integrated into chemoimmunotherapy, as recently shown by Dudley et al.60 The combination of adoptive transfer of ex vivo activated tumor-specific T cells to patients with lymphopenic melanoma after chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide and fludarabine induced tumor regression in up to 50% of patients treated.
Influence of treatment of Treg-cell frequency. Different approaches affecting Treg-cell frequencies and function have been proposed in recent years and tested either in murine models or first clinical trials. Targeting of Treg cells in human tumors, however, does not always result in reduced Treg-cell numbers but may also, under given circumstances, be linked to the induction of autoimmunity or the expansion or development of Treg cells.
Influence of treatment of Treg-cell frequency. Different approaches affecting Treg-cell frequencies and function have been proposed in recent years and tested either in murine models or first clinical trials. Targeting of Treg cells in human tumors, however, does not always result in reduced Treg-cell numbers but may also, under given circumstances, be linked to the induction of autoimmunity or the expansion or development of Treg cells.
Collateral damage needs to be accounted for after Treg-cell depletion
Because Treg cells are an important cellular mechanism suppressing autoantigen-specific conventional T cells from attacking self tissues, nonspecific depletion of these cells might be a too crude approach to be used without leading to significant collateral damage. The fine balance between benefit and harm of manipulating Treg cells was elegantly demonstrated in the following experiment: transfer of a mixture of CD4+CD25– and CD4+CD25+ T cells prevented effective adoptive immunotherapy of established melanoma. In contrast, adoptive transfer of CD4+CD25– T cells together with tumor- as well as self-reactive CD8+ T cells into CD4+ T cell–deficient hosts followed by vaccination induced both regression of established melanoma but also severe and undesired autoimmunity.61 Similarly, depletion of Treg cells with CD25 mAb in a mammary gland tumor model resulted in tumor regression but significantly increased susceptibility to autoimmune thyroiditis. This in vivo priming to both tumor- and self-antigens attests to the presence of otherwise undetectable immune effectors that are under negative regulation and demonstrates that modulation of Treg cells is a powerful strategy in cancer therapy, but may also significantly increase autoimmune complications.62,63
Broadly expressed self-antigens are recognized by tumor-associated Treg cells
For most current tumor models the antigens recognized by Treg cells are not known. In a series of elegant experiments, Nishikawa et al demonstrated that immunization with tumor-associated self-antigens and tumor-specific CTL epitopes heightened CD8+ T-cell responses and increased resistance to tumor challenge in a CD4+ T cell–dependent manner. In contrast, immunization with self-antigens alone increased the susceptibility to tumor challenge,64 leading to the development of highly active Treg cells with enhanced expression of Foxp3. Induction of Treg cells was also associated with acceleration of tumor development, which was abolished by depletion of CD4+ T cells or CD25+ T cells. Acceleration of tumorigenesis was not only observed in self-antigen vaccinated mice but could also be adoptively transferred with Treg cells derived from immunized mice.65
Human Treg cells in cancer: current knowledge and open questions
Even in the early 1990s, T cells with regulatory function were reported in patients with cancer; however, these reports were not followed up until the identification of CD4+CD25+ Treg cells in the mid-1990s.4 Since then, an increase of Treg cells in cancer patients has been reported by numerous investigators. In contrast to the murine system, definition of human Treg cells has been more difficult, and assessment of the most specific marker—namely, FOXP3—has not been performed in many of the early studies. Although human CD4+CD25high T cells are most enriched for FOXP3+ T cells, there are still significant numbers of FOXP3+ cells within the CD4+CD25low T-cell population. In the absence of more specific cell-surface markers, it is not yet possible to study human FOXP3+ Treg cells irrespective of their CD25 expression. These limitations also explain why Treg cells in humans currently need to be characterized by a combination of FOXP3 and CD25 expression as well as analysis of inhibitory function of T-cell populations enriched for FOXP3+ cells, mainly by sorting CD25high T cells.
Comparability of previous reports is further challenged by use of different antibodies to detect CD25 or different gating strategies when assessing CD25+/CD25high cells. Similarly, function of Treg cells has been assessed with numerous in vitro approaches, making it rather difficult to compare results of different studies. To reconcile our recent findings about Treg cells, it is most important to identify specific cell-surface markers for Treg cells that allow us to isolate these cells and functionally test them in the context of malignant disease.
Increased frequencies of Treg cells in solid cancers
Woo et al66 were the first to report increased percentages of CD4+CD25+ Treg cells in TILs in non–small-cell lung cancer and ovarian cancer. These Treg cells were shown to secret TGF-β, providing first evidence that Treg cells contribute to immune dysfunction in patients with cancer.66 Further characterization of these cells showed constitutive high-level expression of CTLA-4. More importantly, Treg cells mediated potent inhibition of T-cell proliferation.67 Supporting this initial report, a larger study concluded that prevalence of CD4+CD25+ Treg cells is increased not only in the tumor microenvironment of patients with invasive breast or pancreas cancers but also in PB, suggesting that the increase of Treg cells is a generalized phenomenon.68
In malignant melanoma, an increase of functional CD4+CD25+ Treg cells was observed,69 which was further linked to increases in the serum level of H-ferritin.70 Release of H-ferritin by melanoma cells led to activation of IL-10–producing functional Treg cells as a potential mechanism of Treg-cell induction in cancer patients.71 A more recent study demonstrated FOXP3 mRNA expression in the increased subset of CD4+CD25high Treg cells in patients with melanoma, confirming the previous reports.72
In patients with gastrointestinal malignancies, the relative increase of Treg cells might actually be explained by a significant reduction of CD4+CD25– T cells. Interestingly, in patients with gastric carcinoma, poor prognosis and decreased survival rates were closely correlated with higher Treg-cell frequencies.73,74 After curative resections, previously elevated Treg cells numbers were significantly reduced. In contrast, prevalence of Treg cells increased again in patients having a relapse after tumor resection.75 These findings underline the close correlation of tumor growth and Treg-cell frequencies.
Curiel et al demonstrated that CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ Treg cells suppress tumor-specific T-cell immunity in ovarian cancer, contribute to tumor growth, and accumulate during progression.76 Furthermore, increased frequencies of Treg cells were associated with a high death hazard ratio and reduced survival. Treg cells preferentially moved to and accumulated in tumors and ascites, but rarely entered draining LNs in later cancer stages. Tumor cells and surrounding macrophages produced the chemokine CCL22, which mediated trafficking of Treg cells to the tumor via CCR4 (Figure 1). This specific recruitment of Treg cells might represent a mechanism by which tumors may foster immune privilege.
For patients with squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck, a significantly elevated frequency of FOXP3+GITR+ Treg cells was shown.77 These Treg cells were significantly more sensitive to apoptosis than non-Treg cells, which might hint at a rapid turnover in the peripheral circulation.77 How the higher sensitivity to apoptosis influences Treg-cell frequencies, however, has not been addressed yet.
Increased numbers of Treg cells have also been reported in PB and TILs of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.78 Although the increase of Treg cells seems to be a common theme in solid tumors, there are clear but yet unexplained differences between individual tumor entities. In a comparative study, differences in Treg-cell frequencies were shown for malignant pleural effusions from patients with mesothelioma compared with carcinomatous pleural effusions from patients with non–small-cell lung cancer or breast cancer.79
Overall, previous work has clearly established that Treg cells are increased in most human solid tumors. Furthermore, there seems to be a stage-dependent increase of Treg cells with frequencies of Treg cells probably correlated to overall survival. However, little is known about the mechanisms leading to this increase. A first study by Wolf et al might help us to understand the underlying molecular mechanisms.80 This study showed that increased frequencies of Treg cells in PB of cancer patients are due to active proliferation rather than redistribution from other compartments (ie, secondary lymphoid organs or bone marrow). This finding, in combination with the proposed attraction of Treg cells to the tumor via CCL22/CCR4 and induction of Treg cells by PGE2 or H-ferritin, might be one possible mechanism responsible for expansion of Treg cells in cancer patients (Figure 1).
Treg cells in hematologic malignancies
Whereas the question of Treg cells in solid tumors sparked interest relatively early, studies addressing Treg cells in hematologic malignancies have been conducted only recently.
The first study by Marshall et al demonstrated large populations of both IL-10–secreting Tr1 and CD4+CD25+ Treg cells in Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) infiltrating lymphocytes and peripheral-blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Suppressive function was mediated by IL-10 secretion, cell-to-cell contact, and CTLA-4 expression.81 The difficulty of applying FOXP3 as a Treg cell–specific marker in human diseases is exemplified by a second study in HL.82 The frequency of FOXP3+ cells was determined in lymphoma-afflicted LNs. Low frequencies of FOXP3+ cells and high frequencies of CTLs in the reactive background of LNs were correlated with poor overall survival. However, costaining for FOXP3 and CD4 or CD25 was not performed, limiting the significance of this finding because FOXP3 expression in humans might not be confined to Treg cells only.14 Alternatively, Treg cells might actually play a beneficial role in HL, which is characterized by a chronic inflammatory response, similar to Helicobacter-associated lymphoma.
In patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) we recently established a stage-dependent increase of CD4+CD25highFOXP3+CTLA4+GITR+ Treg cells with full suppressive capacity. However, when patients with CLL were treated with fludarabine, frequencies of Treg cells decreased and Treg cells showed impaired function. Ongoing studies are addressing the question of how fludarabine mediated this effect.83 The increase of CTLA-4+ Treg cells in untreated CLL patients, which correlated with advanced disease stage and unfavorable cytogenetics, was recently confirmed by others.84 Similarly, in patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (B-NHLs) increased frequencies of FOXP3+CTLA4+ Treg cells have been observed. PD1 expression was partly responsible for the suppressive activity of these LN-infiltrating Treg cells. Furthermore, as reported for ovarian cancer, the tumor cells released CCL22 and thereby attracted CCR4+ Treg cells into the area of the lymphoma (Figure 1).85 For patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) higher frequencies of CD4+CD25high Treg have been observed. Similar to observations in solid tumors, Treg cells of patients with AML were less resistant to apoptosis but showed higher proliferation compared with healthy individuals.86
Comparable to other hematologic malignancies, we were also able to demonstrate increased frequencies of CD4+CD25highFOXP3+ Treg cells in patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) or multiple myeloma (MM).24 Independent of prior therapy or stage of disease Treg cells exhibited a strong inhibitory capacity. Moreover, the increase of Treg cells was also dependent on stage and resulted from peripheral expansion. We also established for the first time that naive CD4+CD25highFOXP3+ Treg cells coexpressing CD45RA and CCR7 are expanded in MM patients, further supporting the concept of peripheral expansion of this T-cell compartment. The importance of identifying more specific markers as well as more standardized functional assays is supported by a recent report on FOXP3+ cells in PB from patients with MM.87 Due to an alternative experimental approach only assessing FOXP3 in context of CD4+ T cells but not CD25+ cells, these data are difficult to compare with other studies on naturally occurring CD4+CD25high Treg cells. Although this report came to the conclusion that Treg cells are dysfunctional in MM patients, the assays chosen to assess Treg-cell function allowed for alternative explanations of the observed results including already described defects in conventional autologous T cells in MM patients.88
Taken together, these data established the concept of increased Treg cells in solid tumors as well as hematologic malignancies. However, some of the early studies need to be validated by using more specific markers such as FOXP3 as well as more sophisticated and standardized functional assays.
Specificity of Treg cells in human tumors
So far, little is known about the antigen-specificity of human Treg cells. Wang et al reported the identification of LAGE1-specific CD4+CD25+GITR+ fully functional Treg-cell clones in cancer patients.89 Ligand-specific activation and cell-to-cell contact were required for Treg cells to exert suppressive activity, suggesting that the presence of tumor-specific Treg cells at tumor sites may have profound effects on the inhibition of T-cell responses against cancer. In a second study, a CD4+CD25+ Treg-cell line was established from a patient with colorectal carcinoma. This T-cell line was tumor-cell dependent in its growth but did not lyse autologous tumor cells and suppressed proliferative responses of allogeneic lymphocytes and autologous CTLs as well as the induction of CTLs from autologous PBMCs. These effects were mediated by TGF-β and did not require cell-to-cell contact, which would be in line with induced regulatory capacity.90 Clearly, further work is needed to understand how the enrichment of Treg cells in cancer patients occurs and if accumulation or preferential induction of clonal, oligoclonal, or polyclonal tumor-specific Treg cells plays a role during tumor progression.
The question of whether induction of Treg cells might be inversely correlated with the induction of tumor-antigen specific immunity during cancer development in vivo was addressed by Nishikawa et al.91 Using NY-ESO-1 as a model, the authors demonstrated that the in vitro generation of NY-ESO1-speficic TH1 cells in NY-ESO-1–seropositive cancer patients was independent of Treg-cell depletion, indicating that tumor antigen-associated Treg cells were not enriched in patients naturally mounting an immune response against this antigen. In contrast, Treg-cell depletion in NY-ESO1–seronegative patients was always required for induction of NY-ESO-1–specific TH1 cells, which suggests the existence of Treg cells specifically suppressing the expansion of tumor-antigen–specific T cells. Moreover, NY-ESO-1–specific TH1 cells were derived from naive precursors in seronegative patients, whereas preexisting memory populations were detectable exclusively in NY-ESO-1–seropositive patients. The memory populations were also less sensitive than naive populations toward Treg cell–mediated suppression. These results strongly support the hypothesis that tumor-specific Treg cells exist in patients with tumors and actively suppress antigen-specific antitumor immunity.
Influence of treatment on Treg-cell frequency and function
As already outlined, a correlation of increased Treg cells with greater disease burden and poorer overall survival has been reported. In CLL, we have observed reduced frequencies of functionally impaired Treg cells after fludarabine treatment; however, not every chemotherapeutic agent seems to induce this effect, because in CLL or MM no other treatment including autologous stem cell transplantation induced similar effects. In line with this observation, frequency and suppressive function of Treg cells in tumor-draining LNs derived from patients with cervical cancer were not influenced by chemotherapy or combined chemoradiation.92
Recent work has demonstrated that IL-2 signaling is required for thymic development, peripheral expansion, and suppressive activity of Treg cells.93 During immune reconstitution after chemotherapy, IL-2 therapy led to a homeostatic peripheral expansion of Treg cells and to a markedly increased Treg-cell compartment. IL-2 therapy induced expansion of existent Treg cells in healthy hosts and this expansion was further augmented by lymphopenia. Treg cells generated by IL-2 therapy expressed FOXP3 at levels observed in healthy individuals and these Treg cells also were of similar potency, suggesting that IL-2 and lymphopenia are modulators of Treg-cell homeostasis.94 Similarly, in patients with melanoma or renal-cell carcinoma (RCC), the frequency of fully functional Treg cells was significantly increased after IL-2 treatment, which was also accompanied by an increase of FOXP3, demonstrating that administration of high-dose IL-2 increases the frequency of circulating FOXP3+ Treg cells.95 This might also explain why therapy with IL-2 in patients with RCC has not yet fully lived up to expectations because significant induction of Treg cells might counteract potential antitumor effects of IL-2.
Surprisingly, vaccination of melanoma patients with DCs either loaded with synthetic peptides or tumor lysates was also shown to induce increased frequencies of Treg cells, concomitant with the expansion of tumor-specific CTLs. Whether this enhances antitumor tolerance and negatively influences the induction of clinically efficient antitumor immune responses needs further attention, because the mechanisms of this phenomenon are not yet understood.96
First clinical studies toward selective elimination of Treg cells
Murine models have established that selective elimination of Treg cells alone or in combination with other treatment options might induce regression of already established tumors. First pilot studies have been initiated in cancer patients to selectively eliminate Treg cells. A promising and specific approach might be targeting of CD25 on the surface of Treg cells. Danull et al used IL-2 diphtheria toxin conjugate DAB(389)IL-2 (denileukin diftitox) to selectively eliminate CD25-expressing Treg cells from the PBMCs of cancer patients without inducing toxicity on other cells that expressed CD25 at only intermediate to low levels.97 DAB(389)IL-2 significantly reduced the number of Treg cells present in the PB of patients with metastatic RCC and abrogated Treg cell– mediated immunosuppressive activity in vivo. Moreover, elimination of Treg cells followed by vaccination with RNA-transfected DCs significantly improved stimulation of tumor-specific T-cell responses when compared with vaccination alone.
In summary, this first clinical study specifically eliminating Treg cells has shown promising results that need to be further evaluated. An important aspect of future studies will be to clearly describe the therapeutic window of deleting Treg cells as a major gatekeeper of self-antigen recognition.
Future directions
In patients with tumors, characterization of Treg cells has focused mainly on coexpression of CD4 and CD25, whereas differentiation status, frequencies of Treg-cell subtypes, eg, natural or induced Treg cells, Tr1, or TH3 cells are less well characterized. To better understand and study Treg-cell biology in relation to tumor development and progression, it will be most critical to identify more specific cell-surface markers. Assessment of FOXP3, lacking in many of the early studies, is certainly a minimum requirement for future studies; however, it does not allow for subsequent functional testing of FOXP3+ cells.
One of the most burning questions concerning Treg cells in cancer remains the specificity of these cells. Although tumor specificity was demonstrated for single Treg-cell clones, so far our understanding is still limited. The lack of specific cell-surface markers allowing us to follow such cells in vivo is again the major hurdle.
The recent finding demonstrating recruitment of CCR4-expressing naive Treg cells by tumor cells secreting CCL22 was intriguing. Similarly, the role of PGE2 expressed by tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages on development of Treg cells demonstrated that there is a rather coordinated cross-talk between tumor environment and Treg cells. It is very likely that additional signals and interactions with other cells, such as tolerogenic DCs, are involved in recruitment of Treg cells to the tumor site. Whether this is a uniform process in all cancer types or whether organ-specific mechanisms might also play a role is only one of the many still unanswered questions of Treg-cell biology in human cancer.
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, April 6, 2006; DOI 10.1182/blood-2006-02-002774.
Supported by the Sofja Kovalevskaja Award of the Alexander von Humboldt-Foundation, the Wilhelm-Sander Stiftung, and the Nationales Genomforschungsnetz (J.L.S.).

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal