Abstract
Introduction. The high-dose sequential (HDS) chemotherapy approach is characterized by early dose-intensification followed by autograft with peripheral blood progenitor cells (PBPC). The HDS program was introduced several years ago (Gianni & Bonadonna, 1989); subsequently, it has been increasingly used in the management of both non-Hodgkins (NHL) and Hodgkins Lymphoma (HL). The outcome of a large series of lymphoma patients treated with the HDS approach at 10 Centers associated to GITIL is reported.
Patients and Methods. Data have been collected on 1,266 patients, who received either the original or slightly modified HDS regimens. There were 213 HL and 1,053 NHL patients (630 intermediate/high-grade, 423 low-grade); median age was 46 yrs, 57% were male. Overall, 671 (53%) patients received HDS as salvage treatment after one or more recurrence; 595 (47%) had HDS front-line, either for high-risk clinical presentation or unfavorable histology, i.e. mantle-cell l. Most patients were autografted with PBPC, few received BM cells (alone or with PBPC); 158 (12%) patients did not undergo autograft, due to several reasons, namely: toxicity, disease progression, poor harvests.
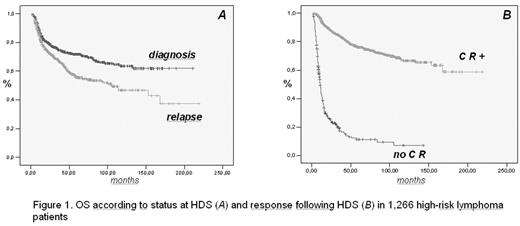
Results. Overall, 1,013 (80%) patients reached Complete Remission (CR) following the HDS program. Up to now, 93 (7%) patients died for early/late toxicities, 328 (26%) died for lymphoma, 844 are known to be alive; at a median follow-up of 5 yrs, the 5-yr Overall Survival (OS) projection is 64% (s.e. 2%). As shown in Figure 1 A and B, a significantly higher survival was observed in patients receiving HDS at diagnosis vs. those at relapse and in those achieving CR vs. no CR patients. On multivariate Cox survival analysis, these two parameters maintained a significant impact on the 5-yr survival (relapse status at HDS: HR 1.39, c.i.: 1.12–1.72; CR achievement: HR 0.12, c.i.: 0.10–0.16). Also some histological features (low grade vs intermediate/high; B-cell vs. T-cell) had a significant impact on OS, whereas other parameters, including sex, bone marrow involvement, HL vs NHL, use of hd-Ara-C, had no relevance.
Conclusions.
the HDS program including PBPC collection and re-infusion is feasible in a multicenter setting and allows prolonged survival in a good proportion of lymphoma patients presenting with unfavorable prognosis;
the long-term outcome is definitely good in patients achieving CR;
given their poor outcome, early salvage treatment options, including allogeneic transplant, should be considered for those patients unable to reach CR following a HDS treatment approach.
OS according to status at HDS (A) and response following HDS (B) in 1,266 high-risk lymphoma patients
OS according to status at HDS (A) and response following HDS (B) in 1,266 high-risk lymphoma patients
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal