Abstract
Allogeneic SCT remains an effective strategy for inducing durable remission in CML. RIC regimens are less myelosuppressive, but adequately immunosuppressive, allowing for engraftment with acceptable treatment-related mortality (TRM) in older pts who otherwise would not be candidates for SCT. The long-term antitumor effect of this approach is not well-established. This is relevant in CML, since many pts present for SCT with advanced disease after failing tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI).
Patients, Methods: We evaluated outcomes of 64 CML pts (40 M/24 F) with median age 52 yrs (range 18–72) treated from June 1996 to April 2005 with FAI (fludarabine 120 mg/m2, Ara-C 8 gm/m2, idarubicin 36 mg/m2), FM140 (fludarabine 120 mg/m2, melphalan 140 mg/m2 +/− Ara-C 2 gm/m2) or FM180 (fludarabine 120 mg/m2, melphalan 180 mg/m2) and unmanipulated stem cells. Disease stage at time of study entry was first chronic (n=13), second chronic (n=17), accelerated (n=29), or blast phase (n=5), with median time from diagnosis to SCT of 2.6 yrs (range 0.5–20.3). Stem cell source was bone marrow (n=38) or peripheral blood (n=26), and donor type was matched related (n=30), 1 Ag mismatched related (n=4), or matched unrelated (n=30). Graft vs. host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis consisted of tacrolimus and mini-dose methotrexate in all but 6 pts (CSA-based).
Anti-thymocyte-globulin was added to all pts other than matched related. Maintenance therapy with TKIs following SCT was not used. Multivariate analysis was done using Cox proportional hazards regression.
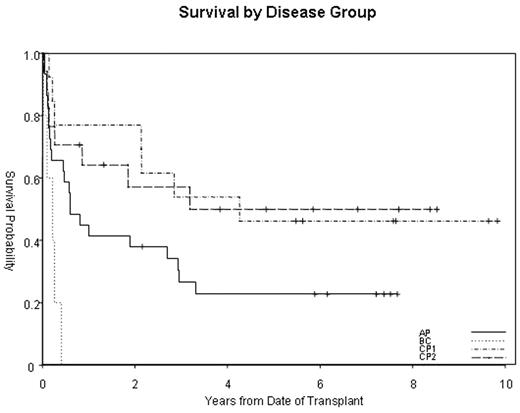
Results: 22 pts were alive at a median follow up of 7 yrs from SCT (range 0.8–9.8). OS and PFS were 48% and 30%, respectively, at 2 yrs, and 33% and 30%, respectively, at 5 yrs. The cumulative incidence of acute GVHD grades II–IV and III–IV were 31% and 14%, respectively, and chronic GVHD was 32% (22% for extensive). TRM at 100 days, 1-, 2-, and 5- yrs were 2%, 14%, 20%, and 33%, respectively. There was no association between pt age, donor source, preparative regimen, or time to SCT and TRM. Disease recurrence accounted for 12 of 42 deaths. There were 3 cases of graft rejection, with 1 death from graft rejection. Only disease stage at time of SCT was significantly predictive in multivariate analysis for both OS and PFS. Pts with advanced disease had worse OS (HR 2.36, 95%CI 1.25–4.46, p=0.008, see figure) and PFS (HR 1.91, 95%CI 1.05–3.49, p=0.035) than pts in chronic phase. In multivariate for PFS, pts who developed grade I or II acute GVHD were less likely to progress compared to pts who did not develop any GVHD: grade I (HR 0.324, 95%CI 0.13–0.84, p=0.027) and grade II (HR 0.286, 95%CI 0.11–0.78, p=0.014).
Conclusion: RIC SCT provides adequate disease control in chronic phase CML pts. The development of some GVHD is protective in this setting. TRM rates are acceptable but continue to increase over time. Alternative treatment strategies need to be explored in pts with accelerated or blast phase disease. Results may be improved with addition of TKI therapy post SCT.
Survival by Disease Group
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal