Abstract
Background and Aims: Impairment of cell-mediated immunity has long been recognized in classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma (cHL), but it is still under discussion whether the ineffective immune clearance of Hodgkin/ Reed-Sternberg (H/R-S) cells is exclusively resulting from the immunosuppressive environment at the tumor site or might be due to a primary T cell defect. Therefore, we applied a microarray approach in order to analyze circulating T lymphocytes for specific dysregulation.
Material and Methods: CD3+ T cells isolated from peripheral blood samples of untreated patients with cHL were analyzed for their gene expression profile in comparison to 2 control groups consisting of healthy donors and patients with sarcoidosis by applying Affymetrix HG-U95Av2 GeneChip. Fold change values of normalized differentially expressed genes (p<0.01; ANOVA analysis) were calculated from the mean expression of duplicates for each group. To further elucidate molecular differences ANOVA selected transcripts have been grouped by using 2D hierarchical clustering.
Results:Among more than 12,500 genes 541 transcripts were detected as differentially expressed (p<0.01, CI>99%; ANOVA analysis). A hierarchical clustering identified within 541 selected transcripts specific expression profiles clearly discriminating between cHL and the control groups (Figure 1.): The identified transcripts fell into several functional classes of genes important in cell cycle regulation (i.e., cyclin A/B1, Cdc2), translational control (i.e., RPL23, LOXL1, ARAF1), intercellular communication/receptor (i.e., CXCR3, CXCR5), and most importantly immune response (i.e., cathepsin C, LTß, MIP1ß, SAP).
Conclusions: The molecular study identified that circulating T lymphocytes of cHL seem to be globally affected in cell cycle transition, proliferation and Th1/Th2 balance with induction of immune regulatory genes. Altogether these results are arguing for a primary cellular defect contributing to an ineffective immune clearance of H/R-S cells.
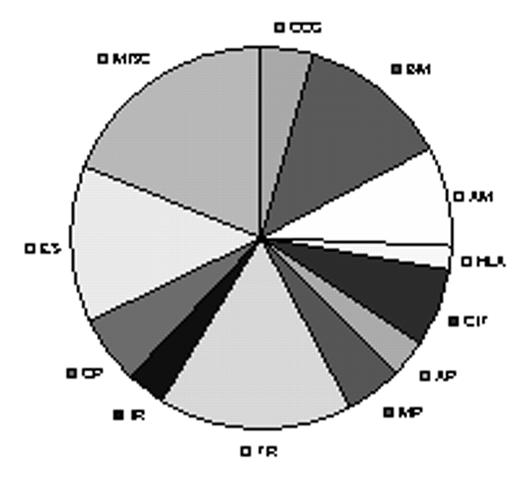
Distribution of the 541 differentially expressed genes discriminating between cHL and control groups
CCG, Cytokines/chemokines, growth factors and receptors; BM, bioynthesis and metabolism; adhesion and motility; HLA, HLA and heat shock proteins; CIT, Calcium and ion channel binding and other transporters; AP, apoptosis and proteolytic systems; MP, membrane proteins and other proteins; TR, transcriptional regulation; IR, other immune related genes; CP, cell proliferation and regulation genes; ES, enzymes and other signal molecules; MISC, miscellaneous.
Distribution of the 541 differentially expressed genes discriminating between cHL and control groups
CCG, Cytokines/chemokines, growth factors and receptors; BM, bioynthesis and metabolism; adhesion and motility; HLA, HLA and heat shock proteins; CIT, Calcium and ion channel binding and other transporters; AP, apoptosis and proteolytic systems; MP, membrane proteins and other proteins; TR, transcriptional regulation; IR, other immune related genes; CP, cell proliferation and regulation genes; ES, enzymes and other signal molecules; MISC, miscellaneous.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal