Abstract
Introduction: Beta thalassaemia major (TM) is a hereditary anaemia affecting 60 000 births worldwide each year. Survival is dependent upon lifelong blood transfusions resulting in iron overload. Cardiac siderosis can result in a cardiomyopathy which is the leading cause of death in TM. The validated cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) T2* technique allows non-invasive and reproducible quantification of myocardial iron. Assessment of myocardial iron loading is essential in determining appropriate chelation therapy. This technique has the potential to become the new gold standard in the assessment of cardiac siderosis but is currently available at only a few sites worldwide. For maximal healthcare benefit its inter-scanner reproducibility must be demonstrated before being widely disseminated.
Objective: To demonstrate that CMR T2* quantification of myocardial iron can be reproducibly transferred to MR scanners of different manufacturers in different centres. This project was sponsored by the Thalassemia International Federation.
Methods: The previously described multi breath-hold gradient echo T2* technique was installed on MR scanners (all 1.5Tesla) at 6 different centres. Scanner details were as follows: Site 1, Phillips Intera (Turin, Italy), Site 2, Siemens Sonata (Philadelphia, USA), Site 3 GE Signa (Limassol, Cyprus) Site 4, Phillips Intera (Nicosia, Cyprus), Site 5, GE Signa (Cagliari, Sardinia) and Philips Intera (Genova, Italy). 34 patients (mean age 30+/− 5.7years) were scanned in total. All patients were subsequently re-scanned at the standardization centre in London, UK (Siemens Sonata, 1.5T) within 31 days of their original scan.
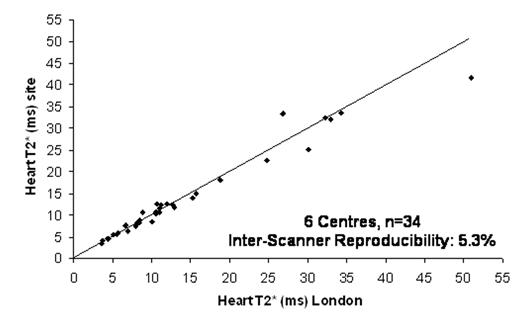
Results: The T2* sequence was successfully installed on all 6 scanners. Myocardial T2* values ranged from 3.6ms to 51ms (14.2 +/− 11ms). The overall inter-scanner reproducibility (SD/mean) was 5.3% (figure 1). The mean difference between T2* values at the standardization centre and visited sites was 0.32ms.
Conclusion: We have demonstrated that the multi breath-hold T2* technique for the quantification of myocardial iron can be reproducibly transferred to 1.5T MR scanners at different sites and of different manufacturers. There is therefore real potential to roll out this technique worldwide to facilitate maximal healthcare impact in the management of patients with iron overload conditions such as thalassaemia.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal