Abstract
Background: The pharmacokinetic impact of multidrug resistance-1 (MDR1) gene single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) has been already investigated in solid organ transplantation field, however, data is still lacking in an allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT) setting.
Methods: A total of 82 patients receiving an allogeneic HLA-identical sibling (n=70) or unrelated SCT (n=12) with graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis of cyclosporine-A (CSA) plus methotrexate (MTX) were included in the current study. Two SNPs of MDR1 gene (C3435T and G2677T/A) were analyzed using PCR/RFLP assay.
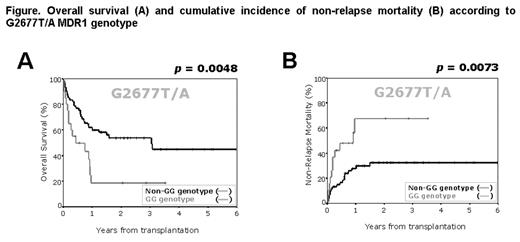
Results: As regards G2677T/A SNP, GG genotype showed a higher incidence of NRM compared to non-GG genotype (67% vs. 32%, p=0.0073), yet not C3435T (p=0.2026) or MDR1 haplotype (p=0.2238). Accordingly, overall survival (OS) was significantly correlated with G2677T/A genotype (p=0.0048), yet not with C3435T (p=0.5041) or MDR1 haplotype (p=0.4086). However, no difference in the relapse incidence was noted according to G2677T/A, C3435T genotype or MDR1 haplotype. In a multivariate analysis, those patients without GG genotype at G2677T/A were found to have favorable prognosis in terms of OS (p=0.003) or NRM (p=0.031) along with occurrence of chronic GVHD (p<0.001 for OS, p=0.001 for NRM), standard disease risk (p=0.045 for OS) or acute grade 0,1 GVHD (p=0.019 for NRM). However, no correlation was found between the blood concentrations of CSA and MDR1 genotype and CSA neurotoxicity and MDR1 genotype.
Conclusion: The G2677T/A genotype seemed to be associated with the transplantation outcomes, especially NRM. Further study is warranted to clarify its mechanism of MDR1 SNPs other than pharmacokinetic aspects.
Overall survival (A) and cumulative incidence of non-relapse mortality (B) according to G2677T/A MDR1 genotype
Overall survival (A) and cumulative incidence of non-relapse mortality (B) according to G2677T/A MDR1 genotype
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal