Abstract
Multiple Myeloma (MM) is an incurable disease that warrants novel treatments. MM survival is dependent on resistance conferred by interactions with the bone marrow (BM) microenvironment (stroma and/or extracellular matrix proteins): Environment Mediated-Drug Resistance (EM-DR). We have shown that adhesion to fibronectin inhibits CD95-induced caspase-8 activation resulting in apoptosis by regulating the cellular localization and availability of c- FLIPL (
Shain K. et al. J Immunol. 2002;168(5):2544–53
). TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand/Apo-2L (TRAIL/Apo-2L) is a member of the TNF superfamily of death ligands that induce apoptosis of resistant MM cell lines and patient’s cells while cultured in suspension. TRAIL/Apo-2L also inhibits the growth of human plasmocytomas in xenografted NOD/SCID mice (Mitsiades C. et al. Blood 2001; 98(3):795–804
). To explore if the tumor microenvironment confers resistance to TRAIL/Apo-2L mediated apoptosis, we treated RPMI 8226 cells with recombinant human killer TRAIL (Alexis Biochemicals). In a series of 3 experiments, we observed a 50.8 ± 10 % specific apoptosis, measured by annexin/PI staining, when cells were treated with TRAIL (10ng/mL) in suspension (Su) media. In contrast, a dramatic resistance to TRAIL mediated apoptosis (6.9 ± 1.2 %) was observed when RPMI 8226 cells were adhered (Ad) to stroma cells (HS-5 and HS-5 transfected with green fluorescent protein-GFP) suggesting the EM-DR phenotype. We hypothesized that EM-DR can potentially be reversed by Bortezomib, a proteosome inhibitor, via NF-κB inhibition resulting in reduced transcription of cellular adhesion proteins genes (Mitsiades et al. Blood 2002; 99(11): 4079–4086
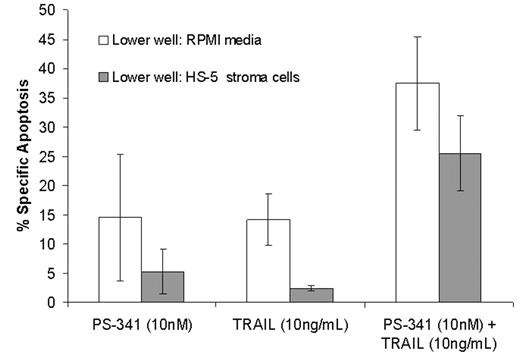
). Resistance to drug-induced apoptosis was also observed when RPMI 8226 cells were adhered to HS-5 and HS5-GFP and treated with Bortezomib alone at 5, 10 and 15nM (55.6 ± 11.6 % Su and 12.1 ± 1.6 % Ad). Microarray analysis of RPMI 8226 cells treated with Bortezomib showed that death receptor 4 (DR4) and DR5 expression was up-regulated suggesting a potential interaction between Bortezomib and TRAIL pathway. When RPMI 8226 cells were treated with Bortezomib (10nM) for 20 Hrs and subsequently treated with TRAIL for additional 4 Hrs, we observed an enhancement to 77.7 ± 3.64 % (Su) and 47.22 ± 13.6 % (Ad) specific apoptosis. In addition, in a series of 3 experiments using transwell inserts, RPMI 8226 cells (upper well) separated from HS-5 (lower well) were treated with Bortezomib (10nM), TRAIL (10ng/ML) or Bortezomib and TRAIL combined as described above. Results were comparable with direct contact experiments described, suggesting that cytokines and/or chemokines released by stroma may be responsible for EM-DR phenotype (Figure 1). Further mechanistic studies elucidating TRAIL and Bortezomib combination are currently under investigation. These preclinical studies provide the basis for clinical trial testing the combination of these agents.Author notes
Corresponding author
2005, The American Society of Hematology
2004

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal