We made the hypothesis that donor and recipient gene polymorphisms that drive the host response to microorganisms could be associated with infections after bone marrow transplantation (BMT). HLA-identical BMT was performed for patients with acute (n = 39) or chronic leukemia (n = 68). Genotyping was performed in 107 D/R DNA pairs for gene polymorphisms of cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α] and TNF-β, interleukin-1 receptor antagonist [IL-1Ra], IL-6, and IL-10), adhesion molecules (CD31 and CD54), Fcγreceptors (FcγRIIa, IIIa, IIIb), mannose-binding lectin (MBL), and myeloperoxidase (MPO). First infection (overall) and first episodes of bacterial, viral, or invasive fungal infection were studied retrospectively for 180 days after BMT. Univariate and multivariate analyses, using death as a competing event, were performed to study risk factors. In multivariate analysis, first overall infections were increased in patients with the FcγRIIa R-131 genotype (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.92; P = .04), and severe bacterial infections were increased when the MPO donor genotype was AG or AA (HR = 2.16; P = .03). Viral and invasive fungal infections were not influenced by any genetic factor studied. Interestingly, we also found that (1) time to neutrophil recovery was shorter when donors were FcγRIIIb HNA-1a/HNA-1b (HR = 1.77; P = .002); (2) donor IL-1Ra (absence of IL-1RN*2) increased the risk for acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (II-IV) (HR = 2.17; P = .017); and (3) recipient IL-10 (GG) and IL-1Ra genotypes increased the risk for chronic GVHD (P = .03 and P = .03, respectively). Finally, 180-day transplantation-related mortality rates were increased when donors were FcγRIIIb HNA-1a/HNA-1a or HNA-1b/HNA-1b (HR = 2.57; P = .05) and donor MPO genotype was AA (HR = 5.14; P = .004). In conclusion, donor and recipient gene polymorphisms are informative genetic risk factors for selecting donor/recipient pairs and could help in the understanding of mechanisms involved in host defenses of BM transplant recipients.
Introduction
Early infection, engraftment, and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) are major determinants of early outcomes after allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT). Risk factors affecting these complications depend on patient- (such as age, disease, cytomegalovirus [CMV] status), donor- (such as HLA compatibility, type of donor, sex), and treatment- (intensity of conditioning regimen, GVHD prophylaxis, source of stem cells) related factors.
Huge advances in human genomics and in the understanding of the inflammatory response have led to an expanding list of genetic risk factors associated with inflammatory and infectious diseases in the past 5 years. In allogeneic SCT, genetic factors such as donor and recipient gene polymorphisms of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines have been associated with the incidence and severity of GVHD in HLA-identical bone marrow transplantation (BMT).1 2However, the influence of such donor and recipient gene polymorphisms on other outcomes, including engraftment and infection after SCT, has not been described.
Recently, candidate gene studies and human genome analyses have been used to identify genes implicated in susceptibility or resistance to infectious agents. Rarely has a single gene defect been directly related to devastating consequences, such as interferon-gamma receptor mutations leading to fatal infections with ubiquitous mycobacteria.3 More often, disease susceptibility is multifactorial. Genetic variants that modify the level or function of the mediators have been associated with susceptibility to and outcome of severe sepsis and septic shock. For example, in bacterial infections, Fc gamma receptor (FcγR) and mannose-binding protein allotype have been linked to the risk for severe pneumococcal infections4 and meningococcal infections in children,5 respectively. Polymorphisms of cytokine genes such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), TNF-β, and interleukin-1 (IL-1) or intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) have been reported to influence the level of secreted mediators, to unbalance the inflammatory cascade, and to alter the susceptibility to bacterial, viral, and fungal infections.6
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) is an enzyme that plays an important role in human defense against microorganisms7; however,MPO gene polymorphisms have not been associated with infectious episodes, though it has been recently associated with the risk for lung cancer.8 9
We hypothesized that donor and recipient polymorphisms of genes that have a central role in innate immunity or phagocyte biology could influence the incidence of bacterial, viral, and fungal infections and other outcomes after HLA-identical BMT. We thus studied a panel of candidate gene polymorphisms (TNF-α, TNF-β, IL-1 receptor antagonist [IL-1Ra]), IL-6, IL-10, platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 [PECAM-1], intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1], FcγR (IIa, IIIa, IIIb), mannose-binding lectin [MBL], and myeloperoxidase [MPO]) in 107 HLA-identical BM transplant recipients/donors. We analyzed the association of any gene polymorphism with the incidence of infections and other outcomes after BMT.
Patients, materials, and methods
Patient, donor, and transplantation characteristics
Criteria for the inclusion of patients in this study were (1) nonmanipulated, HLA-identical BMT was performed at Hôpital Saint Louis from January 1994 to August 1999, with a minimum 6-month follow-up; (2) patient had acute or chronic leukemia; (3) donor and recipient DNA were stored; and (4) available clinical data and infectious episodes were reported within the first 180 days of transplantation. One hundred seven patients and their respective donors met these eligibility criteria. Patient, donor, and transplantation characteristics are listed in Table1. Approval of these studies was obtained from the institutional review board at Hôpital Saint Louis and informed consent was provided according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Patients, disease, and transplantation characteristics
| Characteristics . | n = 107 . |
|---|---|
| Recipient | |
| Median age, y (range) | 35 (3-56) |
| Median weight, kg (range) | 65 (15-126) |
| Male (%) | 67 (63) |
| Children, 15 y or younger (%) | 17 (16) |
| Positive CMV serology (%) | 46 (43) |
| Underlying diagnosis | |
| Chronic leukemia (%) | 68 (64) |
| Acute leukemia (%) | 39 (36) |
| Disease stage | |
| Early (%) | 82 (77) |
| Intermediate (%) | 20 (19) |
| Advanced (%) | 5 (5) |
| Donor | |
| Median age, y (range) | 34 (2-65) |
| Male (%) | 56 (52) |
| Female donor to male recipient (%) | 31 (29) |
| Sex match (%) | 56 (52) |
| ABO match (%) | 72 (67) |
| ABO major incompatibility (%) | 17 (16) |
| Positive CMV serology (%) | 56 (55) |
| Transplantation | |
| Conditioning | |
| TBI + CY ± others (%) | 32 (30) |
| Bu + CY (%) | 58 (54) |
| GVHD prophylaxis | |
| CSA + MTX (%) | 94 (88) |
| CSA + MTX + other (%) | 6 (6) |
| CSA ± corticosteroids (%) | 7 (6) |
| Graft composition | |
| Median NC, 108/kg (range) | 2.4 (0.2-8.1) |
| Median CD34, 106/kg (range) n = 83 | 3.6 (0.07-17.9) |
| Characteristics . | n = 107 . |
|---|---|
| Recipient | |
| Median age, y (range) | 35 (3-56) |
| Median weight, kg (range) | 65 (15-126) |
| Male (%) | 67 (63) |
| Children, 15 y or younger (%) | 17 (16) |
| Positive CMV serology (%) | 46 (43) |
| Underlying diagnosis | |
| Chronic leukemia (%) | 68 (64) |
| Acute leukemia (%) | 39 (36) |
| Disease stage | |
| Early (%) | 82 (77) |
| Intermediate (%) | 20 (19) |
| Advanced (%) | 5 (5) |
| Donor | |
| Median age, y (range) | 34 (2-65) |
| Male (%) | 56 (52) |
| Female donor to male recipient (%) | 31 (29) |
| Sex match (%) | 56 (52) |
| ABO match (%) | 72 (67) |
| ABO major incompatibility (%) | 17 (16) |
| Positive CMV serology (%) | 56 (55) |
| Transplantation | |
| Conditioning | |
| TBI + CY ± others (%) | 32 (30) |
| Bu + CY (%) | 58 (54) |
| GVHD prophylaxis | |
| CSA + MTX (%) | 94 (88) |
| CSA + MTX + other (%) | 6 (6) |
| CSA ± corticosteroids (%) | 7 (6) |
| Graft composition | |
| Median NC, 108/kg (range) | 2.4 (0.2-8.1) |
| Median CD34, 106/kg (range) n = 83 | 3.6 (0.07-17.9) |
Disease stage is based on International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry classification.
NC indicates nucleated cells.
Graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis, conditioning regimen, and supportive therapy
Prophylaxis for acute GVHD consisted of the standard combination of cyclosporine A (CSA) and methotrexate (MTX) in 100 (94%) patients. Conditioning for transplantation varied according to stage of disease at transplantation. Thirty-two (30%) patients underwent fractionated total body irradiation (TBI) (12 Gy in 6 fractions over 3 days), and 58 (54%) patients received busulfan and cyclophosphamide (BuCY) (Table1).
All patients were isolated in laminar airflow rooms. Irradiated and leukocyte-depleted blood products were used for all patients. Patients received transfusions of red blood cells (RBCs) or platelets when the hemoglobin level was lower than 8 g/dL and the platelet count was less than 20 × 109/L, respectively. Selective gut decontamination with oral antibiotics and viral/fungal/parasitic prophylaxis was performed according to local policy, which remained constant during the 6-year study period. Preemptive treatment with ganciclovir or foscarnet for CMV reactivation based on CMV antigenemia screening was used from January 1994. Beginning before day +7, prophylactic hematopoietic growth factors (HGFs) were administered in 11 (10%) patients because of their inclusion in a randomized clinical trial.
Graft collection, manipulation, and stem cell content
Bone marrow was harvested from both posterior iliac crests after the patient was administered general anesthesia. Marrow was aspirated with plastic syringes in aliquots of 2 to 10 mL and was diluted with heparinized tissue culture medium RPMI 1640 or acid-citrate dextrose (ACD). Automated cell counts and CD34+ cell quantification were performed before and after processing, but only the latter was taken into account in this study. CD34+ cell quantification was performed as previously described by fluorescence analysis.10
Gene polymorphism analysis
After informed consent was received, all donor and recipient genotypes were screened blind to the clinical outcome of each transplantation procedure. Peripheral blood leukocytes from patients and donors were stored in liquid nitrogen and were used as a source of DNA, which was extracted through the salting-out method.11
Previously published polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and restriction–digestion protocols were used to identify the −308G>A TNF-α and the +252A>G TNF-α polymorphisms,12 the MPO −463A>G polymorphism,8 and an 86-bp tandem repeat (VNTR) in intron 2 of IL-1Ra.13
We developed a method for PECAM-1 genotyping using the primers 5′-ACGGTGCAAAATGGGAAGAA-3′ and 5′-AGAGGGTGATGGGTGGAGAG-3′. PCR was performed at 94°C for 3 minutes followed by 35 cycles at 94°C for 30 seconds, 55°C for 30 seconds, and 72°C for 60 seconds, and a final extension at 72°C for 7 minutes. The 364-bp product was digested with AluI and was electrophoresed on 2.5% agarose. For the identification of the G>C polymorphism at −174 of theIL-6 gene, we used primers DF5 (5′-GTGGTTCTGCTTCTTAGC-3′) and a reverse of set 3 (5′-CTGATTGGAAACCTTATTAAG-3′) from Fishman et al.14 PCR was performed at 94°C for 3 minutes followed by 35 cycles at 94°C for 30 seconds, 65°C for 40 seconds, and 72°C for 40 seconds, and a final extension at 72°C for 7 minutes. The 119-bp product was digested with NlaIII and was electrophoresed on 3% agarose.14
Genotyping for FcγRIIa was performed by allele-specific restriction enzyme digestion, as described by Jiang et al,15 usingBstUI digestion for the identification of the G and the A alleles.15 The 559T>G polymorphism of the FcγRIIIa gene was evaluated by allele-specific PCR, as described by Wu et al.16 Controls for each genotype were obtained by cloning and sequencing a 162-bp segment of exon 4 that included the polymorphic site from one G homozygote, one T homozygote, and one heterozygote and using the sequence primers described by Wu et al.16 The HNA-1a (NA1) and HNA-1b (NA2) polymorphic forms of FcγRIIIb were determined by allele-specific PCR using primers and conditions described by Hessner et al.17 PCR products were visualized on a 3% agarose gel.
IL-10 A>G polymorphism at −1084 was evaluated by using primers 5′-AATCCAAGACAACACTACTA-3′ and 5′-CTCCAGCACATAGAATGAAA-3′. PCR was performed at 94°C for 3 minutes followed by 35 cycles at 94°C for 30 seconds, 50°C for 45 seconds, and 72°C for 60 seconds, and a final extension at 72°C for 7 to 10 minutes. The 227-bp product was digested with NlaIII and electrophoresed on 8% acrylamide.
The A>T ICAM-1 polymorphism was genotyped by amplification of a 130-bp segment using primers 5′-TGTCCCCCTCAAAAGTCATCCTG-3′ and 5′-TTCCCAGGCAGGAGCAACTCCTT-3′.18 PCR was performed at 94°C for 3 minutes followed by 35 cycles at 94°C for 40 seconds, 65°C for 40 seconds, and 72°C for 40 seconds, and a final extension at 72°C for 7 to 10 minutes. The product was digested withNlaIII and was electrophoresed on 20% acrylamide.
The 3 polymorphisms of exon 1 of MBL at positions 1045, 1052, and 1061 of GenBank sequence AF080508—which correspond to coding positions for amino acids 52, 54, and 57, respectively—were examined in a 246-bp segment amplified with primers 5′-CCTCTCCTTCTCCTGAGTAT-3′ and 5′-GGACATCAGTCTCCTCATAT-3′. PCR was performed at 94°C for 3 minutes followed by 35 cycles at 94°C for 30 seconds, 54°C for 30 seconds, and 72°C for 60 seconds, and a final extension at 72°C for 7 minutes. Digestion with MboI and with BanI identified haplotypes C and B, respectively. Identification of the nucleotide at position 1045 by direct sequencing of the PCR product using BigDye (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) chemistry on an ABI377 automatic sequencer (Applied Biosystems) distinguishes haplotypes A and D.
End point definitions
The dates of the first episodes of severe bacterial, viral, and invasive fungal infections of all patients were analyzed together (overall first infections) and separately.
Severe bacterial infections.
We considered severe bacterial infection to have developed when sepsis, pneumonia, or septic shock was diagnosed according to previously published criteria.19 Bacterial pneumonia was also diagnosed when clinical and radiologic signs of pneumonia improved after empiric antibacterial, but not antifungal, therapy in the absence of positive findings on blood culture or bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL).20
Viral infections and diseases.
CMV infection was defined by a positive antigenemia level (presence of 2 or more positive nuclei per 200 000 leukocytes). CMV was diagnosed according to previously published criteria.21 Herpes simplex virus (HSV) was defined as a respiratory, digestive, or neurologic disease with the isolation of the HSV virus in culture. Probable adenovirus disease was defined through biopsy as the presence of adenovirus in 2 or more sites regardless of technique, except immunohistochemistry. Definitive adenovirus disease required histochemistry evaluation of positive findings on biopsy specimen or culture (except gastrointestinal) or cerebrospinal fluid sample and blood. Other viral infections were considered severe when a virus was isolated from the site of disease and necessitated antiviral treatment.
Invasive fungal infections.
Candidemia was defined by one or more positive findings on blood culture for Candida spp. Disseminated candidosis was defined by clinical or radiologic signs of fungal infection with one or more positive blood cultures for Candida spp. Probable invasive aspergillosis was defined by histopathologic or cytopathologic evidence of Aspergillus spp from needle aspiration or biopsy, with evidence of associated damaged tissue or positive culture obtained by a sterile procedure with clinical or radiologic signs consistent with infection. We considered clinical and radiologic signs of invasive aspergillosis with positive antigenemia (but without microbiologic identification) as probable invasive aspergillosis. Definitive invasive aspergillosis was defined as a clinical illness and as isolation ofAspergillus spp from a sterile site, hyphae consistent withAspergillus spp on biopsy, or aspiration plus culture ofAspergillus spp from the same organ, radiologic pulmonary lesions not attributable to other factors, and BAL fluid culture findings positive for Aspergillus spp.22
Other outcomes
Neutrophil recovery was defined as having occurred on the first of 3 consecutive days when neutrophil levels were higher than 0.5 × 109/L within the first 42 days of transplantation. Platelet recovery was defined as having occurred on the first of 7 days when unsupported platelet levels were higher than 20 × 109/L within the first 180 days of transplantation. Acute and chronic GVHD were diagnosed and graded according to published criteria.23 24 All patients were considered evaluable for acute (aGVHD) at day +1 after transplantation. Chronic GVHD (cGVHD) was evaluated among patients who survived with sustained engraftment from day +100 after transplantation. Transplantation-related mortality (TRM) was calculated from the time of transplantation to death related to transplantation, not to relapse, until day 180. Survival was calculated from the time of transplantation to death from any cause.
Statistical analysis
The reference date was March 1, 2000. Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to identify independent risk factors for death and TRM by means of log-rank tests and Cox proportional hazards models, respectively. The predictive effects of recipient and donor gene polymorphisms were assessed by TNF-α, TNF-β, IL-1Ra, IL-6, IL-10, PECAM-1, FcγRIIa, IIIa, and IIIb, MBL, and MPO. Because of the low prevalence of ICAM-1 variant alleles in the group analyzed, this gene polymorphism was not included in the risk factors analysis. Other clinically related variables analyzed were recipient and donor ages, recipient and donor sexes, sex match, female donor to male recipient, recipient weight, recipient and donor CMV serology and match, ABO compatibility, ABO major incompatibility, diagnosis of chronic leukemia, diagnosis of acute leukemia, stage of disease, use of a radiation-based conditioning, use of BuCY, nucleated cell doses, and CD34+ marrow cell doses.
For assessment of prognostic factors of neutrophil and platelet recovery, acute GVHD (grades II-IV or grades III- IV), chronic GVHD, first episode of infection (all types), first viral infection, first bacterial infection, and first invasive fungal infection, a similar methodology was used in a competing-risks setting, with death treated as a competing event. Univariate and multivariate analyses were then performed using the proportional subdistribution hazard regression model of Fine and Gray.25 A stepwise backward procedure was used construct a set of independent predictors of each end point. All predictors achieving P < .15 were considered, and predictors were sequentially removed if, in the multiple model,P > .05. All tests were 2-sided, and the type 1 error rate was fixed at 0.05. Statistical analyses were performed using SAS 8.1 (SAS, Cary, NC) and Splus2000 (MathSoft, Seattle, WA) software packages.
Results
Frequency of donor and recipient gene polymorphisms and corresponding phenotypes
Results of donor and recipient gene polymorphisms, their prevalence, and their corresponding phenotypes are listed in Table2. According to the literature, the frequency of the different gene polymorphisms studied were similar to those reported in a white population.
Frequency of gene polymorphisms and association with genotype and phenotype in 107 donor-recipient pairs
| Gene (point mutation) . | Genotype . | Associated phenotype . | No. patients (%) . | No. donors (%) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α (−308) | ||||
| AA | Higher production* | 2 (1) | 2 (1) | |
| AG | — | 22 (21) | 23 (22) | |
| GG | Lower production | 83 (78) | 82 (77) | |
| TNF-β (−252) | ||||
| GG | Higher production* | 10 (9) | 10 (9) | |
| AG | — | 30 (28) | 31 (29) | |
| AA | Lower production | 67 (63) | 66 (62) | |
| IL-1RN (IL-1 Ra) (VNTR) | ||||
| A1/A1 | — | 60 (56) | 55 (51) | |
| A1/A2 (IL-1RN*2) | Higher production† | 38 (35) | 39 (36) | |
| A1/A3 | — | 3 (3) | 5 (5) | |
| A2/A2 (IL-1RN*2) | Higher production | 6 (6) | 8 (7) | |
| IL-6 (−174) | ||||
| GG | Higher production* | 49 (46) | 42 (39) | |
| GC | — | 44 (41) | 51 (48) | |
| CC | Lower production | 14 (13) | 14 (13) | |
| IL-10 (−1082) | ||||
| AA | Lower production* | 34 (32) | 34 (32) | |
| AG | — | 50 (47) | 47 (44) | |
| GG | Higher production | 23 (21) | 26 (24) | |
| PECAM-1 or CD31 | ||||
| L/L | Not applicable‡ | 27 (25) | 26 (24) | |
| V/L | Not applicable‡ | 55 (51) | 62 (58) | |
| V/V | Not applicable‡ | 25 (23) | 19 (18) | |
| ICAM-1 or CD54 | ||||
| AA | Not applicable‡ | 104 (97) | 103 (96) | |
| AT | Not applicable‡ | 2 (2) | 4 (4) | |
| TT | Not applicable‡ | 1 (<1) | — | |
| FcγRIIa or CD32 (−131) | ||||
| H/H | Higher affinity for human IgG2, IgG32-153 | 29 (27) | 24 (22) | |
| R/H | — | 61 (57) | 58 (54) | |
| R/R | — | 17 (16) | 25 (23) | |
| FcγRIIIa or CD16a (−559) | ||||
| G/G | Higher affinity for IgG1 and IgG32-153 | 22 (21) | 18 (17) | |
| G/T | — | 44 (41) | 51 (48) | |
| T/T | — | 40 (38) | 37 (35) | |
| FcγRIIIb or CD16b | ||||
| HNA-1a/1a (NA1/NA1) | Higher affinity for immune-complexed IgG3 and lower levels of sFCγRIIIb2-153 | 12 (11) | 13 (12) | |
| HNA-1a/1b (NA1/NA2) | — | 51 (49) | 42 (40) | |
| HNA-1b/1b (NA2/NA2) | — | 42 (40) | 50 (48) | |
| MBL | ||||
| AA | — | 80 (76) | 75 (73) | |
| AB, AC, AD | Decreased serum concentration2-155 | 24 (23) | 23 (23) | |
| Non-A | Undetectable in serum | 1 (<1) | 4 (4) | |
| MPO (−463) | ||||
| GG | — | 59 (55) | 64 (60) | |
| AG | Decreased intracellular concentration2-154 | 35 (33) | 37 (35) | |
| AA | Decreased intracellular concentration | 13 (12) | 6 (5) |
| Gene (point mutation) . | Genotype . | Associated phenotype . | No. patients (%) . | No. donors (%) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α (−308) | ||||
| AA | Higher production* | 2 (1) | 2 (1) | |
| AG | — | 22 (21) | 23 (22) | |
| GG | Lower production | 83 (78) | 82 (77) | |
| TNF-β (−252) | ||||
| GG | Higher production* | 10 (9) | 10 (9) | |
| AG | — | 30 (28) | 31 (29) | |
| AA | Lower production | 67 (63) | 66 (62) | |
| IL-1RN (IL-1 Ra) (VNTR) | ||||
| A1/A1 | — | 60 (56) | 55 (51) | |
| A1/A2 (IL-1RN*2) | Higher production† | 38 (35) | 39 (36) | |
| A1/A3 | — | 3 (3) | 5 (5) | |
| A2/A2 (IL-1RN*2) | Higher production | 6 (6) | 8 (7) | |
| IL-6 (−174) | ||||
| GG | Higher production* | 49 (46) | 42 (39) | |
| GC | — | 44 (41) | 51 (48) | |
| CC | Lower production | 14 (13) | 14 (13) | |
| IL-10 (−1082) | ||||
| AA | Lower production* | 34 (32) | 34 (32) | |
| AG | — | 50 (47) | 47 (44) | |
| GG | Higher production | 23 (21) | 26 (24) | |
| PECAM-1 or CD31 | ||||
| L/L | Not applicable‡ | 27 (25) | 26 (24) | |
| V/L | Not applicable‡ | 55 (51) | 62 (58) | |
| V/V | Not applicable‡ | 25 (23) | 19 (18) | |
| ICAM-1 or CD54 | ||||
| AA | Not applicable‡ | 104 (97) | 103 (96) | |
| AT | Not applicable‡ | 2 (2) | 4 (4) | |
| TT | Not applicable‡ | 1 (<1) | — | |
| FcγRIIa or CD32 (−131) | ||||
| H/H | Higher affinity for human IgG2, IgG32-153 | 29 (27) | 24 (22) | |
| R/H | — | 61 (57) | 58 (54) | |
| R/R | — | 17 (16) | 25 (23) | |
| FcγRIIIa or CD16a (−559) | ||||
| G/G | Higher affinity for IgG1 and IgG32-153 | 22 (21) | 18 (17) | |
| G/T | — | 44 (41) | 51 (48) | |
| T/T | — | 40 (38) | 37 (35) | |
| FcγRIIIb or CD16b | ||||
| HNA-1a/1a (NA1/NA1) | Higher affinity for immune-complexed IgG3 and lower levels of sFCγRIIIb2-153 | 12 (11) | 13 (12) | |
| HNA-1a/1b (NA1/NA2) | — | 51 (49) | 42 (40) | |
| HNA-1b/1b (NA2/NA2) | — | 42 (40) | 50 (48) | |
| MBL | ||||
| AA | — | 80 (76) | 75 (73) | |
| AB, AC, AD | Decreased serum concentration2-155 | 24 (23) | 23 (23) | |
| Non-A | Undetectable in serum | 1 (<1) | 4 (4) | |
| MPO (−463) | ||||
| GG | — | 59 (55) | 64 (60) | |
| AG | Decreased intracellular concentration2-154 | 35 (33) | 37 (35) | |
| AA | Decreased intracellular concentration | 13 (12) | 6 (5) |
sFcγR indicates soluble FcγR; H, histidine; R, arginine; L, leucine; and V, valine.
A, G, C, and T are DNA bases.
Polymorphisms within the genes of TNF-α (−308), TNF-β (−252), IL-6 (−174), and IL-10 (−1082) have been linked to various degrees of production of their respective proteins.14 26-28
The IL-1 gene cluster contains 3 related genes—IL-1A, IL-1B, and IL-1RN—that encode the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1α and IL-1β and their endogenous receptor antagonist IL-1Ra, respectively.29 The IL-1RN gene has an 86-bp tandem repeat (VNTR) in intron 2, of which the less common allele 2 (IL-1RN*2) is associated with a wide range of chronic inflammatory and autoimmune conditions and increased risk for gastric cancer.30 IL-1RN*2 is associated with enhanced IL-1β production in vitro,31 but its effects on IL-1Ra production are contradictory.32-34
Adhesion molecule (PECAM-1 and ICAM-1) gene polymorphisms are not associated with a specific phenotype. In some studies, PECAM-1 or CD31 gene polymorphisms have been associated with aGVHD35,36and those of ICAM-1 with susceptibility to malaria.37
Polymorphisms of Fcγ receptors (FcγR) FcγRIIa (CD32), FcγRIIIa (CD16a), and FcγRIIIb (CD16b) critically affect interaction with antibodies. Polymorphisms of FcγRIIa affect receptor affinity and specificity when a G>A point mutation results in an arginine (Arg) or a histidine (His) residue at position 131 in the membrane proximal immunoglobulinlike domain.38-40FcγRIII is expressed on macrophages and lymphoid cells as a transmembrane receptor (FcγRIIIa) and as a GPI-linked molecule (FcγRIIIb) on neutrophils. A G>T point mutation at nucleotide 559 (559G>T) within FcγRIIIa results in an amino acid substitution at position 158 (valine to phenylalanine, Val158Phe) in immunoglobulinlike domain 2, reflecting different affinities for IgG1 and IgG3. FcγRIIIb represents the most abundant FcR on neutrophils. The FcγRIIIb-HNA1a (or NA1) and HNA1b (or NA2) isoforms differ by 4 amino acids in the membrane distal immunoglobulinlike domain, resulting in different patterns of glycosylation41 and affecting ligand affinity. It has also been demonstrated that FcγRIIIb-HNA-1b homozygous donors contain higher levels of soluble FcγRIIIb (sFcγRIIIb) than do HNA-1a homozygous donors.42
Human deficiency of MBL is known to be predominantly caused by point mutations within exon 1 of the MBL gene at codon 52, 54, or 57 (termed D, B, and D variants, respectively) that result in amino acid substitutions that compromise assembly of functional oligomers.43 Patients heterozygous for these mutations have reduced concentrations of MBL in serum, whereas the protein is almost absent from the serum of homozygous and compound heterozygous patients.44
MPO is an enzyme found primarily in the lysosomes of neutrophils. A single-base substitution (G>A) in an Alu repeat in the promoter region of the MPO gene, 463 bases upstream from the MPOgene, decreases expression, apparently by destroying a binding site for the SPI transcription factor.45
Association of donor and recipient gene polymorphisms with the incidence of infections: univariate and multivariate analyses
Table 3 shows the cumulative incidence of severe overall infections and separate bacterial, viral, and fungal infections and of transplantation-related deaths within 180 days of HLA-identical BMT according to donor and recipient gene polymorphisms. Table 4 shows multivariate analysis results considering patient-, donor-, and transplantation-related factors for hematopoietic recovery, acute and chronic GVHD, infections, early TRM, and survival.
Cumulative incidence of first episode of severe infection (bacterial, viral, or fungal) and TRM at day 180 and association with gene polymorphism
| Gene polymorphism . | Phenotype or genotype . | Overall infection . | Bacterial infection . | Viral infection . | Fungal Infection . | TRM . | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI, % . | P . | CI, % . | P . | CI, % . | P . | CI, % . | P . | CI, % . | P . | ||
| Cumulative incidence | — | 56 | — | 28 | — | 39 | — | 12 | — | 22 | — |
| Donor TNF-α (−308) | |||||||||||
| Low producer (GG) | 54 | NS | 26 | NS | 39 | NS | 12 | NS | 23 | NS | |
| High producer (AG+AA) | 64 | — | 36 | — | 40 | — | 12 | — | 20 | — | |
| Recipient TNF-α (−308) | |||||||||||
| Low producer (GG) | 53 | NS | 25 | NS | 39 | NS | 12 | NS | 23 | NS | |
| High producer (AG+AA) | 67 | — | 38 | — | 42 | — | 13 | — | 21 | — | |
| Donor TNF-β (−252) | |||||||||||
| High producer(GG+AG) | 56 | NS | 32 | NS | 34 | NS | 7 | NS | 20 | NS | |
| Low producer (AA) | 56 | — | 26 | — | 42 | — | 15 | — | 24 | — | |
| Recipient TNF-β (−252) | |||||||||||
| High producer (GG+AG) | 56 | NS | 33 | NS | 35 | NS | 8 | NS | 20 | NS | |
| Low producer (AA) | 55 | — | 25 | — | 42 | — | 15 | — | 24 | — | |
| Donor IL-1Ra (VNTR) | |||||||||||
| Low producer | 58 | NS | 28 | NS | 40 | NS | 15 | NS | 20 | NS | |
| High producer (IL-1RN*2) | 53 | — | 28 | — | 38 | — | 9 | — | 26 | — | |
| Recipient IL-1Ra (VNTR) | |||||||||||
| Low producer | 57 | NS | 27 | NS | 41 | NS | 14 | NS | 24 | NS | |
| High producer (IL-1RN*2) | 55 | — | 30 | — | 36 | — | 10 | — | 20 | — | |
| Donor IL-6 (−174) | |||||||||||
| High producer (GG) | 52 | NS | 26 | NS | 45 | NS | 10 | NS | 26 | NS | |
| Low producer (GC+CC) | 58 | — | 29 | — | 35 | — | 14 | — | 20 | — | |
| Recipient IL-6 (−174) | |||||||||||
| High producer (GG) | 51 | NS | 29 | NS | 41 | NS | 10 | NS | 22 | NS | |
| Low producer (GC+CC) | 60 | — | 28 | — | 38 | — | 14 | — | 22 | — | |
| Donor IL-10 (−1082) | |||||||||||
| High producer (GG) | 50 | NS | 21 | NS | 35 | NS | 18 | NS | 21 | NS | |
| Low production (AG+AA) | 59 | — | 32 | — | 41 | — | 10 | — | 23 | — | |
| Recipient IL-10 (−1082) | |||||||||||
| High producer (GG) | 57 | NS | 26 | NS | 35 | NS | 17 | NS | 30 | NS | |
| Low production (AG+AA) | 56 | — | 29 | — | 40 | — | 11 | — | 20 | — | |
| Donor PECAM-1 (CD31) | |||||||||||
| L/L | 62 | NS | 38 | NS | 38 | NS | 12 | NS | 19 | NS | |
| L/V or V/V | 54 | — | 25 | — | 40 | — | 12 | — | 23 | — | |
| Recipient PECAM-1 (CD31) | |||||||||||
| L/L | 70 | .04 | 41 | .06 | 48 | NS | 7 | NS | 22 | NS | |
| L/V or V/V | 51 | — | 24 | — | 36 | — | 14 | — | 23 | — | |
| Donor FcγRIIa (−131) | |||||||||||
| H/H | 46 | NS | 29 | NS | 29 | NS | 13 | NS | 25 | NS | |
| R/H or R/R | 59 | — | 28 | — | 42 | — | 12 | — | 22 | — | |
| Recipient FcγRIIa (−131) | |||||||||||
| H/H | 41 | .07 | 21 | NS | 31 | NS | 10 | NS | 17 | NS | |
| R/H or R/R | 62 | — | 31 | — | 42 | — | 13 | — | 24 | — | |
| Donor FcγRIIIa | |||||||||||
| T/T | 49 | NS | 24 | NS | 27 | NS | 8 | NS | 16 | NS | |
| G/T or GG | 61 | — | 30 | — | 46 | — | 14 | — | 26 | — | |
| Recipient FcγRIIIa | |||||||||||
| T/T | 48 | NS | 23 | NS | 30 | NS | 13 | NS | 25 | NS | |
| G/T or G/G | 61 | — | 30 | — | 45 | — | 12 | — | 21 | — | |
| Donor FcγRIIIb | |||||||||||
| HNA-1a/HNA-1a | 46 | NS | 23 | NS | 23 | NS | 15 | NS | 38 | .06 | |
| HNA-1a/HNA-1b | 52 | — | 31 | — | 40 | — | 14 | — | 14 | — | |
| HNA-1b/HNA-1b | 62 | — | 28 | — | 42 | — | 10 | — | 26 | — | |
| Recipient FcγRIIIb | |||||||||||
| HNA-1a/HNA-1a | 58 | NS | 25 | NS | 42 | NS | 8 | NS | 33 | NS | |
| HNA-1a/HNA-1b | 57 | — | 33 | — | 39 | — | 12 | — | 25 | — | |
| HNA-1b/HNA-1b | 55 | — | 24 | — | 38 | — | 14 | — | 17 | — | |
| Donor MBL | |||||||||||
| AA | 59 | NS | 31 | NS | 39 | NS | 13 | NS | 23 | NS | |
| AX or XX | 50 | — | 25 | — | 39 | — | 11 | — | 21 | — | |
| Recipient MBL | |||||||||||
| AA | 55 | NS | 28 | NS | 39 | NS | 11 | NS | 21 | NS | |
| AX or XX | 64 | — | 32 | — | 44 | — | 16 | — | 28 | — | |
| Donor MPO (−463) | |||||||||||
| GG | 52 | NS | 20 | .03 | 39 | NS | 14 | NS | 25 | .004 | |
| AG | 62 | — | 38 | — | 41 | — | 11 | — | 11 | — | |
| AA | 67 | — | 50 | — | 33 | — | 0 | — | 67 | — | |
| Recipient MPO (−463) | |||||||||||
| GG | 54 | NS | 22 | .02 | 37 | NS | 15 | NS | 20 | NS | |
| AG | 57 | — | 26 | — | 49 | — | 9 | — | 20 | — | |
| AA | 62 | — | 62 | — | 23 | — | 8 | — | 38 | — | |
| Gene polymorphism . | Phenotype or genotype . | Overall infection . | Bacterial infection . | Viral infection . | Fungal Infection . | TRM . | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI, % . | P . | CI, % . | P . | CI, % . | P . | CI, % . | P . | CI, % . | P . | ||
| Cumulative incidence | — | 56 | — | 28 | — | 39 | — | 12 | — | 22 | — |
| Donor TNF-α (−308) | |||||||||||
| Low producer (GG) | 54 | NS | 26 | NS | 39 | NS | 12 | NS | 23 | NS | |
| High producer (AG+AA) | 64 | — | 36 | — | 40 | — | 12 | — | 20 | — | |
| Recipient TNF-α (−308) | |||||||||||
| Low producer (GG) | 53 | NS | 25 | NS | 39 | NS | 12 | NS | 23 | NS | |
| High producer (AG+AA) | 67 | — | 38 | — | 42 | — | 13 | — | 21 | — | |
| Donor TNF-β (−252) | |||||||||||
| High producer(GG+AG) | 56 | NS | 32 | NS | 34 | NS | 7 | NS | 20 | NS | |
| Low producer (AA) | 56 | — | 26 | — | 42 | — | 15 | — | 24 | — | |
| Recipient TNF-β (−252) | |||||||||||
| High producer (GG+AG) | 56 | NS | 33 | NS | 35 | NS | 8 | NS | 20 | NS | |
| Low producer (AA) | 55 | — | 25 | — | 42 | — | 15 | — | 24 | — | |
| Donor IL-1Ra (VNTR) | |||||||||||
| Low producer | 58 | NS | 28 | NS | 40 | NS | 15 | NS | 20 | NS | |
| High producer (IL-1RN*2) | 53 | — | 28 | — | 38 | — | 9 | — | 26 | — | |
| Recipient IL-1Ra (VNTR) | |||||||||||
| Low producer | 57 | NS | 27 | NS | 41 | NS | 14 | NS | 24 | NS | |
| High producer (IL-1RN*2) | 55 | — | 30 | — | 36 | — | 10 | — | 20 | — | |
| Donor IL-6 (−174) | |||||||||||
| High producer (GG) | 52 | NS | 26 | NS | 45 | NS | 10 | NS | 26 | NS | |
| Low producer (GC+CC) | 58 | — | 29 | — | 35 | — | 14 | — | 20 | — | |
| Recipient IL-6 (−174) | |||||||||||
| High producer (GG) | 51 | NS | 29 | NS | 41 | NS | 10 | NS | 22 | NS | |
| Low producer (GC+CC) | 60 | — | 28 | — | 38 | — | 14 | — | 22 | — | |
| Donor IL-10 (−1082) | |||||||||||
| High producer (GG) | 50 | NS | 21 | NS | 35 | NS | 18 | NS | 21 | NS | |
| Low production (AG+AA) | 59 | — | 32 | — | 41 | — | 10 | — | 23 | — | |
| Recipient IL-10 (−1082) | |||||||||||
| High producer (GG) | 57 | NS | 26 | NS | 35 | NS | 17 | NS | 30 | NS | |
| Low production (AG+AA) | 56 | — | 29 | — | 40 | — | 11 | — | 20 | — | |
| Donor PECAM-1 (CD31) | |||||||||||
| L/L | 62 | NS | 38 | NS | 38 | NS | 12 | NS | 19 | NS | |
| L/V or V/V | 54 | — | 25 | — | 40 | — | 12 | — | 23 | — | |
| Recipient PECAM-1 (CD31) | |||||||||||
| L/L | 70 | .04 | 41 | .06 | 48 | NS | 7 | NS | 22 | NS | |
| L/V or V/V | 51 | — | 24 | — | 36 | — | 14 | — | 23 | — | |
| Donor FcγRIIa (−131) | |||||||||||
| H/H | 46 | NS | 29 | NS | 29 | NS | 13 | NS | 25 | NS | |
| R/H or R/R | 59 | — | 28 | — | 42 | — | 12 | — | 22 | — | |
| Recipient FcγRIIa (−131) | |||||||||||
| H/H | 41 | .07 | 21 | NS | 31 | NS | 10 | NS | 17 | NS | |
| R/H or R/R | 62 | — | 31 | — | 42 | — | 13 | — | 24 | — | |
| Donor FcγRIIIa | |||||||||||
| T/T | 49 | NS | 24 | NS | 27 | NS | 8 | NS | 16 | NS | |
| G/T or GG | 61 | — | 30 | — | 46 | — | 14 | — | 26 | — | |
| Recipient FcγRIIIa | |||||||||||
| T/T | 48 | NS | 23 | NS | 30 | NS | 13 | NS | 25 | NS | |
| G/T or G/G | 61 | — | 30 | — | 45 | — | 12 | — | 21 | — | |
| Donor FcγRIIIb | |||||||||||
| HNA-1a/HNA-1a | 46 | NS | 23 | NS | 23 | NS | 15 | NS | 38 | .06 | |
| HNA-1a/HNA-1b | 52 | — | 31 | — | 40 | — | 14 | — | 14 | — | |
| HNA-1b/HNA-1b | 62 | — | 28 | — | 42 | — | 10 | — | 26 | — | |
| Recipient FcγRIIIb | |||||||||||
| HNA-1a/HNA-1a | 58 | NS | 25 | NS | 42 | NS | 8 | NS | 33 | NS | |
| HNA-1a/HNA-1b | 57 | — | 33 | — | 39 | — | 12 | — | 25 | — | |
| HNA-1b/HNA-1b | 55 | — | 24 | — | 38 | — | 14 | — | 17 | — | |
| Donor MBL | |||||||||||
| AA | 59 | NS | 31 | NS | 39 | NS | 13 | NS | 23 | NS | |
| AX or XX | 50 | — | 25 | — | 39 | — | 11 | — | 21 | — | |
| Recipient MBL | |||||||||||
| AA | 55 | NS | 28 | NS | 39 | NS | 11 | NS | 21 | NS | |
| AX or XX | 64 | — | 32 | — | 44 | — | 16 | — | 28 | — | |
| Donor MPO (−463) | |||||||||||
| GG | 52 | NS | 20 | .03 | 39 | NS | 14 | NS | 25 | .004 | |
| AG | 62 | — | 38 | — | 41 | — | 11 | — | 11 | — | |
| AA | 67 | — | 50 | — | 33 | — | 0 | — | 67 | — | |
| Recipient MPO (−463) | |||||||||||
| GG | 54 | NS | 22 | .02 | 37 | NS | 15 | NS | 20 | NS | |
| AG | 57 | — | 26 | — | 49 | — | 9 | — | 20 | — | |
| AA | 62 | — | 62 | — | 23 | — | 8 | — | 38 | — | |
CI indicates cumulative incidence; P, Fine and Gray P value; and NS, not significant ifP > .10. See Table 2 for genotype and phenotype abbreviations.
Cox multivariate analysis for outcomes after HLA-identical BMT for patients with leukemia
| Outcomes (no. events) . | Variables increasing risk for outcomes . | Hazard ratio (95% CI), P . |
|---|---|---|
| Neutrophil recovery at d 40, n = 104 | ||
| Early/intermediate stage of disease | 2.27 (1.22-4.21), .01 | |
| Absence of TBI | 1.83 (1.22-2.75), .003 | |
| ABO compatibility | 1.67 (1.03-2.73), .04 | |
| Donor FcγRIIIb HNA-1a/HNA-1b | 1.77 (1.24-2.52), .002 | |
| Platelet recovery at d 180, n = 92 | ||
| Chronic leukemia | 2.08 (1.38-3.14), <.0001 | |
| Early stage of disease at transplantation | 1.94 (1.12-3.35), .02 | |
| Cell dose | 1.48/108 per kg (1.30-1.70), <.0001 | |
| ABO compatibility | 2.15 (1.45-3.19), .0002 | |
| Acute GVHD (II-IV) at d 100, n = 45 | ||
| Female donor to male recipient | 1.91 (1.05-3.47), .02 | |
| Donor IL-1Ra (absence of IL-1RN*2) | 2.07 (1.10-3.92), .017 | |
| First overall infections at d 180, n = 60 | ||
| Recipient-positive CMV serology | 2.82 (1.61-4.97), .0005 | |
| Recipient FcγIIa R-131 (HR or RR) | 1.92 (1.02-3.61), .04 | |
| First viral infection at day 180, n = 44 | ||
| Recipient-positive CMV serology | 10.34 (4.30-24.85), <.0001 | |
| Advanced stage of disease at transplantation | 4.49 (2.02-10.00), <.0001 | |
| Adult patients | 5.41 (1.47-19.97), .01 | |
| Donor-positive CMV to recipient-negative CMV serology | 2.28 (1.21-4.29), .01 | |
| First bacterial infection at d 180, n = 30 | ||
| Conditioning other than BuCY | 2.15 (1.08-4.51), .04 | |
| Major ABO incompatibility | 2.43 (1.16-5.09), .02 | |
| Donor MPO genotype AA+AG | 2.16 (1.08-4.32), .03 | |
| First fungal infection at d 180, n = 13 | ||
| Advanced stage of disease at transplantation | 6.51 (1.71-24.75), .006 | |
| Low CD34 cell dose | 1.41/106 per kg (1.01-1.97), .04 | |
| Chronic GVHD at 2 years, n = 50 of 95 at risk | ||
| Recipient IL-10 (GG) | 2.77 (1.10-6.95), .03 | |
| Recipient IL-1Ra (absence of IL-1RN*2) | 1.96 (1.06-3.60), .03 | |
| Recipient age, y | 1.61/10 (1.42-1.82), <.0001 | |
| Female donor | 1.92 (1.09-3.77), .02 | |
| TRM at d 180, n = 24 deaths | ||
| Advanced stage of disease | 4.80 (1.37-16.90), .01 | |
| Recipient age, y | 1.64/10 (1.15-2.35), .006 | |
| Donor MPO (AA) | 5.14 (1.71-15.44), .004 | |
| Donor FcγRIIIb HNA-1a/HNA-1a or HNA-1b/HNA-1b | 2.57 (1.01-6.62), .05 | |
| Survival at 5 y, n = 44 deaths | ||
| ABO major incompatibility | 2.45 (1.23-4.86), .01 | |
| Conditioning other than BuCY | 2.52 (1.35-4.71), .004 | |
| Recipient age, y | 1.31/10 (1.04-1.63), .02 |
| Outcomes (no. events) . | Variables increasing risk for outcomes . | Hazard ratio (95% CI), P . |
|---|---|---|
| Neutrophil recovery at d 40, n = 104 | ||
| Early/intermediate stage of disease | 2.27 (1.22-4.21), .01 | |
| Absence of TBI | 1.83 (1.22-2.75), .003 | |
| ABO compatibility | 1.67 (1.03-2.73), .04 | |
| Donor FcγRIIIb HNA-1a/HNA-1b | 1.77 (1.24-2.52), .002 | |
| Platelet recovery at d 180, n = 92 | ||
| Chronic leukemia | 2.08 (1.38-3.14), <.0001 | |
| Early stage of disease at transplantation | 1.94 (1.12-3.35), .02 | |
| Cell dose | 1.48/108 per kg (1.30-1.70), <.0001 | |
| ABO compatibility | 2.15 (1.45-3.19), .0002 | |
| Acute GVHD (II-IV) at d 100, n = 45 | ||
| Female donor to male recipient | 1.91 (1.05-3.47), .02 | |
| Donor IL-1Ra (absence of IL-1RN*2) | 2.07 (1.10-3.92), .017 | |
| First overall infections at d 180, n = 60 | ||
| Recipient-positive CMV serology | 2.82 (1.61-4.97), .0005 | |
| Recipient FcγIIa R-131 (HR or RR) | 1.92 (1.02-3.61), .04 | |
| First viral infection at day 180, n = 44 | ||
| Recipient-positive CMV serology | 10.34 (4.30-24.85), <.0001 | |
| Advanced stage of disease at transplantation | 4.49 (2.02-10.00), <.0001 | |
| Adult patients | 5.41 (1.47-19.97), .01 | |
| Donor-positive CMV to recipient-negative CMV serology | 2.28 (1.21-4.29), .01 | |
| First bacterial infection at d 180, n = 30 | ||
| Conditioning other than BuCY | 2.15 (1.08-4.51), .04 | |
| Major ABO incompatibility | 2.43 (1.16-5.09), .02 | |
| Donor MPO genotype AA+AG | 2.16 (1.08-4.32), .03 | |
| First fungal infection at d 180, n = 13 | ||
| Advanced stage of disease at transplantation | 6.51 (1.71-24.75), .006 | |
| Low CD34 cell dose | 1.41/106 per kg (1.01-1.97), .04 | |
| Chronic GVHD at 2 years, n = 50 of 95 at risk | ||
| Recipient IL-10 (GG) | 2.77 (1.10-6.95), .03 | |
| Recipient IL-1Ra (absence of IL-1RN*2) | 1.96 (1.06-3.60), .03 | |
| Recipient age, y | 1.61/10 (1.42-1.82), <.0001 | |
| Female donor | 1.92 (1.09-3.77), .02 | |
| TRM at d 180, n = 24 deaths | ||
| Advanced stage of disease | 4.80 (1.37-16.90), .01 | |
| Recipient age, y | 1.64/10 (1.15-2.35), .006 | |
| Donor MPO (AA) | 5.14 (1.71-15.44), .004 | |
| Donor FcγRIIIb HNA-1a/HNA-1a or HNA-1b/HNA-1b | 2.57 (1.01-6.62), .05 | |
| Survival at 5 y, n = 44 deaths | ||
| ABO major incompatibility | 2.45 (1.23-4.86), .01 | |
| Conditioning other than BuCY | 2.52 (1.35-4.71), .004 | |
| Recipient age, y | 1.31/10 (1.04-1.63), .02 |
Overall first infection
At day 180 after transplantation, 60 patients had experienced at least one episode of microbiologically or clinically documented first severe bacterial (n = 22), first viral (n = 34), or first fungal infection (n = 4). Infection was directly responsible for 17 of 36 (47%) transplantation-related deaths in the whole period of follow-up. The cumulative incidence rate of any first infection by day 180 was 56%. In univariate analysis, recipient CD31 (L/L) (P = .04) and recipient FcγRIIa R-131 (P = .07) genotypes were associated with an increased incidence of severe infection (Table 3). In univariate analysis, other factors increasing the risk for severe infection were adult patients (P = .02), recipient positive CMV serology (P = .005), and advanced stage of disease at transplantation (P < 10−4). In multivariate analysis, recipient FcγRIIa R-131 (HR = 1.92; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.02-3.61; P = .04] and recipient-positive CMV serology (HR = 2.82; 95% CI = 1.61-4.97;P = .0005) statistically increased the risk for first infection (Table 4).
Bacterial infection
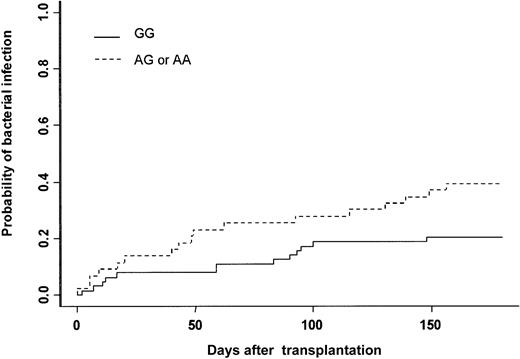
The cumulative incidence of at least one bacterial infection was 28% at day 180. Thirty patients experienced severe bacterial infection (16 sepsis, 9 pneumonia, and 5 septic shock). Gram-positive bacteria were isolated in 13 patients (Staphylococcus coagulase negative n = 10, Streptococcus pneumonian = 2, Enterococcus faecium n = 1), and gram-negative bacteria were isolated in 11 patients (Pseudomonas aeruginosan = 4, Klebsiella pneumonia n = 3,Enterobacter cloacae n = 1, Actinobacter sp n = 1, Bacterioidis fragilis n = 1,Stenotrophomonas maltophilia n = 1). In 6 patients no bacteria were isolated, but patients had clinical or radiologic signs of bacterial infection (see “End point definitions”). In univariate analysis, recipient and donor MPO genotypes were associated with the incidence of severe bacterial infection (Table 3). The cumulative incidence was 20% when the MPO donor genotype was GG, 38% when it was AG, and 50% when it was AA (Figure 1, Table 3). The type of clinical manifestation (pneumonia, sepsis, septic shock) or the etiology of bacterial infection (gram-positive or gram-negative) were not associated with GG or AG-AA donor genotype (data not shown). Among all other gene polymorphisms studied, there was a trend toward increased risk for bacterial infection when the recipient was CD31 (L/L), (P = .06) (Table 3). Other patient-, donor-, and transplantation-related factors increasing the risk for bacterial infection were intermediate or advanced status of leukemia (P = .04), conditioning other than BuCY (P = .04), and ABO major incompatibility (P = .01). In multivariate analysis adjusted for confounding variables, only 3 factors increased the risk for severe bacterial infection: (1) donor MPO genotype (AG-AA) (HR = 2.16; 95% CI = 1.08-4.32; P = .03); (2) conditioning regimen other than BuCY (HR = 2.15; 95% CI = 1.03-4.51; P = .04); and (3) ABO major incompatibility (HR = 2.43: 95% CI = 1.16-5.09;P = .02) (Table 4).
Severe bacterial infection.
Cumulative incidence of severe bacterial infection after HLA-identical BMT according to bone marrow donor MPO genotype.
Severe bacterial infection.
Cumulative incidence of severe bacterial infection after HLA-identical BMT according to bone marrow donor MPO genotype.
Viral infections and diseases
The cumulative incidence of patients who experienced at least one viral infection was 39% at day 180, with a total of 44 events (CMV infection, 41; CMV disease, 1; herpes simplex virus, 1; adenovirus, 1). Genetic factors were not associated with first viral infection. In univariate analysis, the following factors were associated with an increased risk for viral infection: positive recipient CMV serology (P < 10−4), advanced stage of disease at transplantation (P = .02), adult status (P = .02), and CMV-positive donor to a negative CMV patient (P = .03). In multivariate analysis, positive recipient CMV serology (HR = 10.34; 95% CI = 4.30-24.85;P = <10−4), positive donor CMV serology to negative recipient CMV serology (HR = 2.28; 95% CI = 1.21-4.29;P = .01), advanced stage of disease at transplantation (HR = 4.49; 95% CI = 2.02-10.00;P < 10−4), and adult status (HR = 5.41; 95% CI = 1.47-19.97; P = .01) were factors associated with a higher incidence of first viral infections and diseases.
Invasive fungal infections
The estimated probability for at least one invasive fungal infection (IFI) at 180 days was 12%. There were 8 invasive aspergillosis (Aspergillus spp, 3; Aspergillus fumigatus, 4; Aspergillus niger, 1), 2 candidemia (Candida spp, 1; Candida albicans, 1), 2 disseminated candidiasis, and 1 disseminated Malassesia furfur fungal infections. Gene polymorphisms were not associated with the incidence of IFI (Table 3). In univariate analysis, advanced stage of disease at transplantation (P = .05), lower nucleated cell dose (P = .03), and lower CD34 cell dose (P = .03) were associated with increased risk for IFI. In multivariate analysis, when adjusting for confounding variables, only advanced stage of disease at transplantation (HR = 6.51; 95% CI = 1.71-24.75; P = .006) and lower CD34 cell dose (HR = 1.41 per 106/kg; 95% CI = 1.01-1.97;P = .04) influenced the increased incidence of IFI.
Neutrophil and platelet recoveries
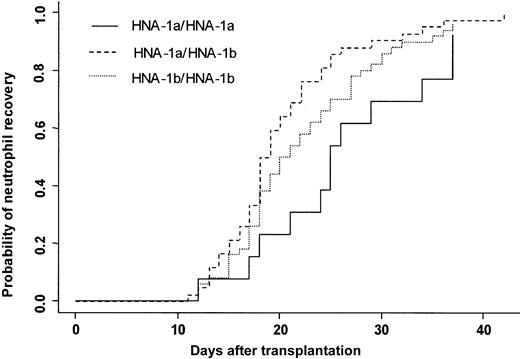
Three patients died in the first 28 days after transplantation without having achieved neutrophil recovery. One hundred four (97%) patients achieved an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) greater than 0.5 × 109/L at day 42. The cumulative incidence rate of recovery at day 42 was 96%. At day 20, 50% of the patients had achieved an ANC greater than 0.5 × 109/L. Two patients had late graft failure. Donor FcγRIIIb gene polymorphism influenced the time to neutrophil recovery. Bone marrow donor genotype HNA-1a/HNA-1a was associated with a delayed neutrophil recovery (25 days) compared with a neutrophil recovery of donor HNA-1a/HNA-1b (19 days) (P = .007) (Figure 2). In multivariate analysis, time to neutrophil recovery was shorter when the bone marrow donor was HNA-1a/HNA-1b, (HR = 1.77; 95% CI = 1.24-2.52; P = .002). Other factors associated with shorter time of recovery were early/intermediate stage of disease (HR = 2.27; 95% CI = 1.22-4.21; P = .01), absence of TBI (HR = 1.83; 95% CI = 1.22-2.75; P = .003), and ABO compatibility (HR = 1.67; 95% CI = 1.03-2.73;P = .04) (Table 4).
Neutrophil recovery.
Cumulative incidence of neutrophil recovery after HLA-identical BMT according to bone marrow donor FcγIIIb genotype.
Neutrophil recovery.
Cumulative incidence of neutrophil recovery after HLA-identical BMT according to bone marrow donor FcγIIIb genotype.
Recipient or donor gene polymorphism did not influence time to platelet recovery (data not shown). In multivariate analysis, the following factors were associated with shorter time to platelet recovery: chronic leukemia (HR = 2.08; 95% CI = 1.38-3.14;P < 10−4), early stage of disease (HR = 1.94; 95% CI = 1.12-3.35; P = .02), higher bone marrow cell dose (HR = 1.48/U; 95% CI = 1.30-1.70;P < 10−4), and ABO match (HR = 2.15; 95% CI = 1.45-3.19; P = .0002).
Acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease
Forty-five patients had aGVHD of grade II or more; the cumulative rate was 42% at day 100. Eighteen patients (17%) had aGVHD of grade III or IV; the estimated incidence was 17% at day 100. In univariate analysis, the following genotypes were associated with risk for aGVHD (grades II-IV): recipient TNF-β genotype (GG + AG = 30% vs AA = 49%) (P = .05) and donor IL-1Ra genotype (absence of IL-1RN*2 = 52% vs presence of IL-1RN*2 = 30%) (P = .03). Some other genotypes were statistically weakly associated with the risk for aGVHD, such as donor TNF-β genotype (GG + AG = 32% vs AA = 48%) (P = .08), recipient IL-1Ra genotype (absence of IL-1RN*2 = 49% vs IL-1RN*2 = 32%) (P = .07), recipient IL-10 genotype (GG = 57% vs AG + AA = 38%) (P = .08), and recipient MPO genotype (GG = 49% vs AG + AA = 33%) (P = .09). Other factors increasing the risk for aGVHD were female donor to male recipient (P = .04) and major ABO incompatibility (P = .04). The incidence of aGVHD grades III and IV was not associated with donor or recipient characteristics (data not shown). In multivariate analysis, only 2 factors were associated with the risk for aGVHD grades II to IV: female donor to male recipient (HR = 1.91; 95% CI = 1.05-3.47; P = .02) and donor IL-1Ra genotype (absence of IL-1RN*2) (HR = 2.07; 95% CI = 1.10-3.92; P = .017).
Chronic GVHD developed in 50 of 95 patients at risk. At 2 years, the cumulative incidence rate was 32%. In univariate analysis, recipient IL-10 genotype was associated with increased risk for cGVHD (GG = 58% vs AG+AA = 26%) (P = .04). There was a trend toward decreasing risk for cGVHD when recipient IL-1Ra had IL-1RN*2 than when it did not have IL-1RN*2 (26% vs 36%) (P = .07). In multivariate analysis, the following factors were associated with risk for cGVHD: recipient age (HR = 1.61 per 10 years; 95% CI = 1.42-1.82; P = .0001), recipient IL-10 (GG) (HR = 2.77; 95% CI = 1.10-6.95; P = .03), recipient IL-1Ra (HR = 1.96; 95% CI = 1.06-3.60;P = .03), and female donor to male recipient (HR = 1.92; 95% CI = 1.09-3.37; P = .02).
Early transplantation-related mortality
Twenty-four patients died of transplantation-related complications within the first 180 days of transplantation. At day 180, the cumulative incidence of nonleukemic death was 22%. The main causes of TRM were GVHD (n = 7, 29%), infections (n = 9, 37.5%), interstitial pneumonitis (n = 3, 12.5%), late graft failure and infection (n = 2, 8.5%), multiorgan failure (n = 2, 8.5%), and hemorrhage (n = 1, 4%). In univariate analysis, donor FcγIIIb HNA-1a/HNA-1a and donor MPO AA genotypes were associated with increased risk for nonleukemic death at day 180 (Table 3). In multivariate analysis, the risk for early death was increased for patients with advanced-stage disease (HR = 4.80; 95% CI = 1.37-16.90;P = .01), older age (HR = 1.64 per 10 years; 95% CI = 1.15-2.35; P = .006), donor MPO (AA) (HR = 5.14; 95% CI = 1.71-15.44; P = .003), and donor FcγRIIIb HNA-1a/HNA-1a or HNA- 1b/HNA-1b (HR = 2.57; 95% CI = 1.01-6.62;P = .05). Causes of death of patients according to donor FcγRIIIb and MPO gene polymorphism are listed in Table5.
Causes of nonleukemic deaths at day 180 according to donor FcγRIIIb and MPO genotype
| Causes . | Donor FcγR IIIb . | Donor MPO . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNA-1a/1a (n = 13) . | HNA-1a/1b (n = 42) . | HNA-1b/1b (n = 50) . | GG (n = 64) . | AG (n = 37) . | AA (n = 6) . | |
| GVHD | 2 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 3 | — |
| Infection | 1 | 2 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 1 |
| Graft failure or infection | 1 | — | 1 | 1 | — | 1 |
| Interstitial pneumonitis | — | 2 | 1 | 2 | — | 1 |
| Others | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | — | 1 |
| Total | 5 | 6 | 13 | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| Causes . | Donor FcγR IIIb . | Donor MPO . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNA-1a/1a (n = 13) . | HNA-1a/1b (n = 42) . | HNA-1b/1b (n = 50) . | GG (n = 64) . | AG (n = 37) . | AA (n = 6) . | |
| GVHD | 2 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 3 | — |
| Infection | 1 | 2 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 1 |
| Graft failure or infection | 1 | — | 1 | 1 | — | 1 |
| Interstitial pneumonitis | — | 2 | 1 | 2 | — | 1 |
| Others | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | — | 1 |
| Total | 5 | 6 | 13 | 16 | 4 | 4 |
Relapse and survival
Nine patients had hematologic relapses. Median time for relapse was 450 days (range, 91-1600 days). With a median follow-up of 52 months (range, 8-119 months), 63 (59%) patients were alive on March 1, 2000. The 5-year estimate of survival for the whole population was 54%. Forty-four (41%) patients died—6 after relapse, 36 of transplantation-related complications, and 2 of other causes. Donor and recipient gene polymorphism did not influence the overall risk for death. Multivariate analysis showed that ABO major incompatibility (HR = 2.45; 95% CI = 1.23-4.86; P = .01), increasing recipient age (HR = 1.3 per 10 years; 95% CI = 1.04-1.63;P = .02), and use of a conditioning regimen other than BuCY (HR = 2.52; 95% CI = 1.35-4.71; P = .004) increased the risk for death.
Discussion
The impressive volume of data emerging daily from genomics and high-throughput sequencing and gene expression analysis is generating unprecedented opportunities for defining the genetic basis of susceptibility to complex diseases.46 Allogeneic SCT is an established but complex therapy for patients with hematologic malignant and nonmalignant diseases. Unfortunately, complications such as GVHD and infections still cause significant morbidity and mortality after SCT. Genetic factors related to patients and donors, such as cytokine or adhesion molecule gene polymorphisms, have been reported to modify the incidence and severity of aGVHD.1,2,35,36 47 However, their influence on infections and other outcomes after BMT have not been described.
In search of donor and recipient genetic factors that could modify the incidence or the course of bacterial, viral, and fungal infections and other outcomes—namely, hematopoietic recovery, GVHD, TRM, and survival after BMT—we analyzed the frequency of variant alleles of 11 candidate inflammatory and host defense genes in a cohort of 107 HLA–geno-identical BM transplant recipients/donors. For each candidate gene, previous data suggested that the variant allele(s) biologically altered either the function of the gene product or the expression of the gene. It is possible that subtle changes (polymorphisms) in genes of immune function, which may have little or no effect in the general population, can assume greater significance in immunosuppressed transplant recipients.
In the present analysis, we associated donor and recipient genetic factors with first episodes of severe infections and with separate bacterial, viral, and fungal infections. Interestingly, we found that recipients with FcγRIIa-R131 had an increased incidence of first severe infection of any type. FcγRIIa (CD32) is a surface receptor of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes), macrophages, dendritic cells, platelets, T cells, and endothelial cells that reacts with the Fc region of immunoglobulin G2 (IgG2).48 It is polymorphic and has 2 codominant allelic forms that differ functionally as the result of a single amino acid substitution at position 131.40 The His131 allelic form has high affinity for the Fc of IgG2, and the R131 allelic form binds IgG2 poorly.38,40 Some studies have associated the FcγRIIa R-131 allotype with encapsulated bacterial infection (pneumococcal bacteremia and pneumonia4), meningococcal septic shock,39and periodontitis with anaerobic gram-negative bacteria.49Besides its antibacterial effect, some authors have shown that FcγRIIa might be relevant to viral infections (measles and dengue virus).50 51 In our study, in multivariate analysis, recipient FcγRIIa R-131 increased the incidence of overall infection. This recipient genotype is not statistically associated with increased risk for a specific infection etiology; however, the incidence of bacterial and viral infections in FcγRIIa R-131 increased 10% and 11%, respectively, compared with homozygous recipients with the FcγRIIa H-131 genotype. Unfortunately, the association of host defense and inflammatory gene polymorphisms with immune reconstitution was not analyzed.
In our study, a new and important finding is that donor MPO genotype may influence the incidence of severe bacterial infections when adjusting for other patient-, donor-, and transplantation-related factors. MPO is a lysosomal hemoprotein located in the azurophilic granules of polymorphonuclear (PMN) leukocytes and monocytes. It is part of the host defense system of human PMN leukocytes, responsible for microbicidal activity against a wide range of organisms. Phagocytes deficient in MPO express in vitro a mild-to-moderate defect in bacterial killing but a marked defect in fungal killing.52Moreover, MPO has been shown to alter the production or effect of nitric-oxide–derived inflammatory oxidants in activated neutrophils.53 In a recent epidemiologic study, a significantly higher occurrence of severe infections and chronic inflammatory processes was noted among a group of 100 patients with total and subtotal MPO deficiency compared with a healthy population.54 In addition, MPO-deficient mice showed severely reduced cytotoxicity to Candida albicans,Candida tropicalis, Trichospora asahii, andPseudomonas aeruginosa and a significantly delayed clearance of Aspergillus fumigatus and Klebsiellapneumonia.55 A single-base substitution (G>A) in the promoter region of the MPO gene (position −463) has been demonstrated to markedly reduce transcription of the protein in acute myelocytic leukemia cells.45 Reynolds et al56 showed differences in MPO mRNA and protein levels.56 Moreover, indirect evidence of MPO gene polymorphisms and MPO activity have been reported in epidemiologic studies. Recently, Meisel et al57 reported the association of MPO polymorphism and periodontal disease. They looked at more than 3000 subjects—1083 patients and the rest controls—and found that females with the GG genotype were 50% more susceptible to periodontal disease, apparently because MPO released by reactive neutrophils damages the cells. That is a large sample size, and it clearly indicates that the polymorphism is linked to risk for a neutrophil-induced disease state. It is also important to point out that the GG genotype has been linked to lung cancer risk.8 9 These studies provide strong evidence that the polymorphism does result in a difference in MPO activity that affects disease susceptibility. Therefore, MPO protects against microbial invasion, whereas in inflammatory disease states it unintentionally contributes to cell damage.
Importantly, we found that bone marrow donor MPO genotype AG or AA increased the risk for bacterial infection after BMT, probably reflecting the decreased bactericidal activity of MPO in engrafted neutrophils. In multivariate analysis, the AA genotype was also associated with risk for nonleukemic death 180 days after transplantation. However, because of the small number of patients, the main causes of death were not identified. This finding suggests that MPO polymorphisms may contribute to an understanding of the role of MPO in host defenses, and they should be evaluated in other clinical situations in which infections are a major issue—among them organ transplantation and immunodeficiency. Moreover, strategies for specific antibacterial prophylaxis and better surveillance of bacterial infections in recipients of donor A>G or AA MPO genotype should be further analyzed.
We expected to find associations between infections and inflammatory and MBL gene polymorphisms. Proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF, which act as powerful agents of innate immunity against infections, have attracted considerable interest as candidate susceptibility genes in a range of infectious disease.6 It is difficult to raise hypotheses about the absence of a correlation between cytokine gene polymorphisms, specifically TNF, and infections that are mainly viral.58 As discussed above, however, gene candidates associated with infections in the general population may be different in immunosuppressed transplant recipients. Recently, Mullighan et al59 reported the influence of MBL gene polymorphisms and infections after allogeneic SCT. Almost 90 patients undergoing BMT, peripheral blood SCT, and T-cell–depleted transplantation were analyzed. They found an association between infections and MBL gene polymorphisms only after neutrophil recovery using rough statistics (Fisher exact test). Our approach was different because we analyzed only HLA nonmanipulated BMT for leukemia. Using competing-risk analysis, MBL gene polymorphisms were not associated with time to first infections independently of neutrophil recovery. These points could explain the differences in the results of both studies.
In our study, one interesting and first-reported result is the influence of donor FcγRIIIb on neutrophil recovery. We found, through multivariate analysis, that patients who received bone marrow from FcγRIIIb HNA-1a/HNA-1a donors experience delayed neutrophil recovery compared with recipients of bone marrow from FcγRIIIb HNA-1a/HNA-1b donors. FcγRIIIb is expressed on polymorphonuclear leukocytes as a GPI-linked molecule. It is the most abundant FcR on neutrophils, and it bears the human neutrophil antigen (HNA) polymorphism implicated in alloimmune and autoimmune neutropenias.60,61 In allogeneic SCT, antibodies reacting with neutrophils (ARNs) have been associated with delayed neutrophil recovery.62,63 Klumpp et al63 reported that the median number of days for achieving neutrophil levels higher than 500/μL was 21 days in recipients of stem cell transplants with ARNs; it was 17 days in patients without ARNs. Based on these observations, we can speculate that HNA-1a/HNA-1a bone marrow donors are more prone to produce HNA-1a autoantibodies against engrafted neutrophils.
Moreover, soluble FcγRIIIb (sFcγRIIIb) is readily detected in plasma, and plasma from FcγRIIIb–HNA-1b homozygous donors was shown to contain higher levels of sFcγRIIIb than that from HNA-1a homozygous donors.42 Plasma concentrations of sFcγRIIIb have been found to correlate with the production of neutrophils and total body mass of neutrophils.64
Finally, we confirmed previous findings regarding the influence of donor IL-1Ra (IL-1RN*2) as a protective gene polymorphism in aGVHD.65,66 Other gene polymorphisms, such as TNF, IL-6, IL-10, and CD31, have been correlated with the risk for aGVHD.2,35,36,47,66 In our study their influence was only observed in univariate analysis. We also detected an influence of recipient IL-10 and recipient IL-1Ra genotype on the incidence of cGVHD not previously reported. The probable explanation for our results compared with those of others is that we analyzed a homogenous population of patients with leukemia with few variations in the conditioning regimen, including all the candidate genes that could influence the risk for GVHD. In addition, we used multivariate analysis taking competitive risk into account to study risk factors. This analysis considered death as a competitive risk for the other events, including GVHD, whereas most studies used rough statistics (Fisher exact test)1,67 or routine Cox proportional hazards regression models that treat death as censoring, which can produce biased estimates if the different risks in competition are not independent.2 65 One might consider, however, that even in a relatively homogenous population of patients, such as patients who undergo transplantation for leukemia, it is possible that an imbalance exists in the underlying patient population that could explain the statistically significant differences. Thus, the polymorphism might not have been a marker for outcomes after BMT but simply a chance association.
Finally, and most important, MPO and FcγRIIIb genotypes influenced the risk for early death after transplantation. It is interesting that genetic risk factors influencing neutrophil recovery and infections are also important risk factors for nonleukemic death. In fact, the most frequent causes of nonleukemic death after BMT are infections and GVHD. We analyzed the influence of GVHD on TRM as a time-dependent covariate (data not shown). As expected, in multivariate analysis for TRM, the presence of GVHD was an important risk factor for death, even though donor MPO AA and FcγRIIIb HNA-1a/1a or HNA-1b/1b remained pejorative factors (data not shown). The d3 allele of the dinucleotide (GA) microsatellite polymorphisms of TNF d3/d3 have been associated with early TRM after BMT in one study67 but were not confirmed in multivariate analysis in other.2 We have not looked at this specific polymorphism.
In conclusion, donor and recipient inflammatory and host defense genetic factors are associated with neutrophil recovery, infections (mainly bacterial), and acute and chronic GVHD after HLA-identical BMT. Most important, donor genetic risk factors influencing bacterial infections (MPO), speed of neutrophil recovery (FcγRIIIb), and aGVHD (IL-1Ra) influenced the risk for nonleukemic death after BMT. These findings are informative for understanding the mechanisms of host defenses, for choosing the donor and establishing new prophylactic and therapeutic strategies against infection, neutrophil engraftment, and GVHD, and, thus, for improving the final outcome of allogeneic BMT.
We thank M. H. Tavela and A. G. Araujo for technical assistance, Prof J. Bux for discussions concerning the FcγRIIIb genotypes, and Prof W. F. Reynolds for discussions concerning the MPO gene and MPO protein activity.
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, July 25, 2002; DOI 10.1182/blood-2002-04-1033.
Supported by Assistance Publique-Hopitaux de Paris, IFR Saint-Louis, Association pour la Recherche sur les Transplantations Médullaires, and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Brazil.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Vanderson Rocha, Service du Pr. E. Gluckman, Hôpital Saint Louis, 1 Av Claude Vellefaux, 75010 Paris, France; e-mail: vanderson.rocha@sls.ap-hop-paris.fr.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal