Abstract
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is believed to be a stem-cell disorder involving cytopenia and dysplastic changes in three hematopoietic lineages. However, the involvement of pluripotent stem cells and progenitor cells has not been clarified conclusively. To address this issue, we used fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) of blood and bone marrow (BM) smears for mature cells and FISH of cells sorted by fluorescence-activated cell sorting for progenitor cells. Seven patients with MDS associated with trisomy 8 were studied. FISH showed +8 in granulocytes, monocytes, and erythroblasts, but not in lymphocytes. Sorted cells of T (CD3+), B (CD19+), and NK cells (CD3−CD56+) from peripheral blood did not contain +8, nor did CD34+ subpopulations from BM including B (CD34+CD19+), T/NK (CD34+CD7+) progenitors, and pluripotent stem cells (CD34+Thy1+). The +8 chromosome abnormality was identified in stem cells only at the level of colony-forming unit of granulocyte-erythrocyte-macrophage-megakaryocyte (CFU-GEMM; CD34+CD33+). It may thus be concluded that cells affected by trisomy 8 in the context of MDS are at the CFU-GEMM level and that cells of lymphoid lineage are not involved. These results provide new insights into the biology of MDS and suggest that intensive chemotherapy and autologous BM transplantation may become important therapeutic strategies.
© 1998 by The American Society of Hematology.
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROME (MDS) represents a group of acquired hematopoietic disorders. In 1982, the French-American-British (FAB) Cooperative Group proposed a morphological classification of these disorders into five categories: refractory anemia (RA), RA with ring sideroblasts (RARS), RA with an excess of blasts (RAEB), chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML), and RAEB in transformation (RAEB-T).1 MDS is characterized by cytopenia of more than two hematopoietic lineages with normal or hyperplastic marrow and dysplastic changes in three lineages. Because of the dysplastic changes, MDS has been thought to be a stem-cell disorder. Previous studies with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD),2 chromosome analysis,3restriction-length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis of phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK), and hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase (HPRT)4 support the hypothesis that MDS is a clonal disorder at a multipotent hematopoietic stem cell level. Our study yielded data consistent with involvement of the myeloid series but not of the lymphoid lineage.
From 60% to 73% of patients with MDS have nonrandom chromosome abnormalities. Trisomy 8, monosomy 7/7q-, monosomy 5/5q-, and 20q- are frequently found.5-7 The feasibility of chromosome analysis of every cell lineage is limited when standard cytogenetic techniques are used. A major disadvantage of G-6-PD isoenzyme analysis is the rarity of heterozygosity outside certain ethnic groups. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) studies require highly purified cell suspensions and are hampered by cell contaminants. In contrast, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) enabled us to identify chromosomal changes in nondividing cells of every lineage and to perform a cell by cell analysis in addition to analysis of metaphase spreads.8-13Furthermore, even a small-cell population can be collected by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) based on immunophenotype. The major disadvantage of flow cytometry is the lack of direct correlation between morphology and cell markers. For this reason, we used FISH of blood and bone marrow (BM) smears for mature cells and FISH of cells sorted by FACS for identification of stem cells in MDS patients with the typical chromosomal change of trisomy 8. Because this technique does not require cell culture or amplification, “sorter FISH” (FACS + FISH) can provide direct analysis of immature progenitor cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients.
Seven patients with MDS and carrying trisomy 8 chromosomes were selected for this study (Table 1). The diagnosis of MDS and determination of the subgroups were performed according to the FAB classification. The patients comprised three men and four women, whose age ranged from 35 to 73 years. MDS subgrouping yielded three patients with RA, one patient with RAEB, one patient with CMML, one patient with RAEB-T, and one patient whose disease changed from RAEB to acute myelocytic leukemia (M2). Patient 5 had a history of treatment for essential thrombocytosis (ET), and patient 7 had a history of treatment with melphalan and prednisolone for multiple myeloma from 1987 to 1991; in 1991, pancytopenia and chromosome abnormality der(1;7) were found and the diagnosis of treatment-related MDS (t-MDS) was made.
Peripheral blood (PB) specimens and BM were obtained from all patients after informed consent. BM mononuclear cells (BMMC) or PB mononuclear cells (PBMC) were isolated by Ficoll-Hypaque density-gradient centrifugation. After removal of the phagocytic cells from BMMC, the remaining nonphagocytic cells were used for the following study with FACS.
Chromosome analysis.
We used a standard technique for chromosome analysis. Aspirated BM (2 × 107 cells/mL) was cultured overnight, and the cells were exposed to Colcemid (GIBCO-BRL, Gaithersburg, MD) with 0.02μg/mL 2-hours before harvest. After 15 minutes of hypotonic treatment with 0.075 mol/L KCl, the cells were fixed with ethanol and acetic acid (3:1), and G-banded karyotype was analyzed and described according to the International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (ISCN 1995).14
FACS.
Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated CD7 (3A1-FITC, Coulter Immunology, Hialeah, FL), CD19 (B4-FITC; Coulter), CD33 (MY9-FITC; Coulter), CDw90 (Thy-1-FITC; Coulter), FITC CD3 (Leu4-FITC; Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA), and phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated CD34 (HPCA2-PE), CD56 (Leu19-PE) and CD3 (Leu4-PE; Becton Dickinson, Sunnyvale, CA) were used. Both FITC-conjugated and PE-conjugated nonspecific Ms IgG was obtained from Becton Dickinson.
Flow cytometry analysis and cell sorting were performed on an EPICS Elite (Coultronics, Merrgency, France). Between 1,000 to 30,000 cells per fraction were sorted and collected with FACS with a purity of 95%. These cells were then used to make cytospin preparations and were stained with May-Grünwald-Giemsa.
FISH.
The probes used in this study were commercially available chromosome-8–specific probes (D8Z2; Oncor, Inc, Gaithersburg, MD), which were labeled with Digoxigenin. For prehybridization, slides were immersed in 0.01N HCl/0.005% pepsin for 5 minutes, washed two times in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 3 minutes, and treated with 4% paraformaldehyde/PBS for 5 minutes. After two washes with PBS, the cells were dehydrated through 70%, 80%, and 100% ethanol. The hybridization protocol followed the manufacturer’s instructions. Signals were visualized by using 0.2 μg/μL antidigoxygenin-rhodamine (Boehringer Mannheim Biochemica, Mannheim, Germany)/1% block ace (Dainippon Pharmaceutical, Tokyo, Japan), which inhibits the nonspecific background. After counterstaining with 0.1 μg/mL 4′, 6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; Sigma, St Louis, MO), the signals were observed under a Nikon microscope (Tokyo, Japan) with a FITC/rhodamine dual-band filter, G2A, and a UV filter (Nikon). The preparations were evaluated by counting 100 nuclei per slide. The mean percentage of nuclei with a false-positive signal was calculated to arrive at a control PB from hematologically disease-free individuals. Although a previous study showed false-positive cells occurring at a frequency of about 2%, ours yielded a frequency of mean + 2SD:4.9% (cutoff).
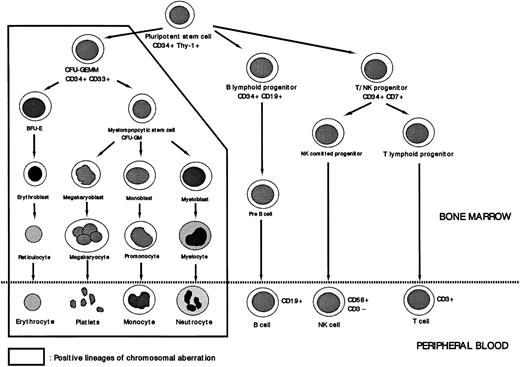
Stem cells were characterized by defining their subpopulations of CD34+ cells. Thy-1 is a marker expressed by fetal and adult BM stem cells. The Thy-1+ subset has multilineage differentiation capacity as shown by its ability to produce T cells, B cells, and myeloid cells.15,16 The CD34+CD10+CD19+ population represents exclusively B-lymphoid–committed progenitors.17 Cytoplasmic CD3+CD7+cells were considered to represent committed T-cell progenitors based on the fact that CD2, cyCD3, CD5, and CD7 are coexpressed on all mature T cells but not on all mature B cells.18 However, these antigens are also expressed on CD34+ natural-killer (NK) progenitors.19 In addition, CD7 is also present on B-cell and myeloid progenitors.20 These data suggest that CD34+CD7+ and CD5+/CD2+populations represent T-lymphoid–committed progenitors.18On the basis of these considerations, we considered CD34+Thy-1+ cells to be pluripotent stem cells, CD34+CD19+ to be B-progenitor cells, and CD34+CD7+ cells to be T/NK-progenitor cells.
RESULTS
Chromosome analysis.
The patients’ characteristics and karyotypes are listed in Table 1. Phytohemagglutinin (PHA)-stimulated culture of PB showed normal karyotypes for all patients.
Flow cytometry analysis.
The percentage of CD34+ BM cells increased from 1.5% for RA and 3.8% for CMML, to 10.6% for RAEB and 10.6% for RAEB-T, and notably 18.3% for transformed MDS (Table2).
Lineage involvement was identified by FISH analysis of blood and BM smears.
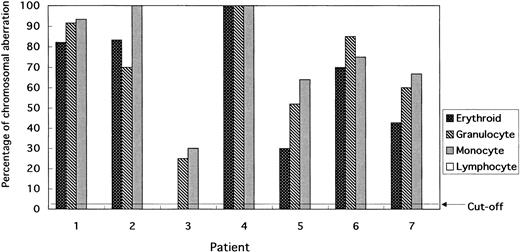
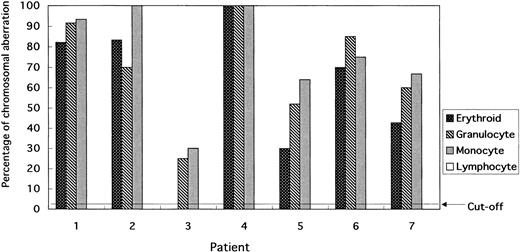
Cells collected by FACS tend to have reduced cytoplasm, but there is no difficulty in evaluating signals in the nuclei. Although the percentage of cells with the +8 chromosome aberration varied, the percentage in erythroid, granulocyte, and monocyte lineages was above the cutoff value. In contrast, lymphocytes did not show trisomy 8 in any of the patients, whereas erythroblasts tended to have a lower percentage of cells with the +8 chromosome abnormality (Figs 1 and 2). In particular, patient 5 had 20% fewer +8 cells than the other patients.
Percentage of cells bearing the +8 chromosomal aberration in erythroid, granulocytes, monocytes, and lymphocytes based on FISH analysis applied to blood and BM smears. No BM smear could be obtained from patient 3. No chromosomal aberrations were found in the lymphocytes of any patients.
Percentage of cells bearing the +8 chromosomal aberration in erythroid, granulocytes, monocytes, and lymphocytes based on FISH analysis applied to blood and BM smears. No BM smear could be obtained from patient 3. No chromosomal aberrations were found in the lymphocytes of any patients.
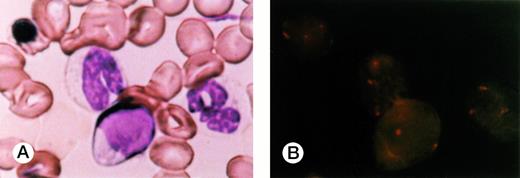
FISH of BM smear of patient 1. (A) An erythroblast, two neutrophils, and lymphocytes in May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain. (B) FISH results applied to the smear. Three signals were recognized in the erythroblast and neutrophils but none in the lymphocytes.
FISH of BM smear of patient 1. (A) An erythroblast, two neutrophils, and lymphocytes in May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain. (B) FISH results applied to the smear. Three signals were recognized in the erythroblast and neutrophils but none in the lymphocytes.
FISH analysis applied to sorted cells of B, T, and NK cells.
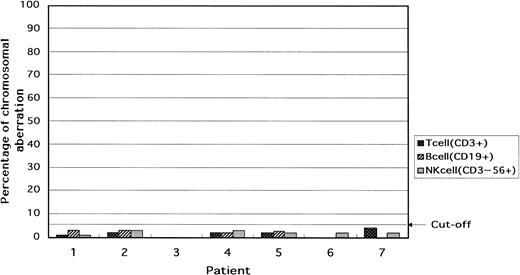
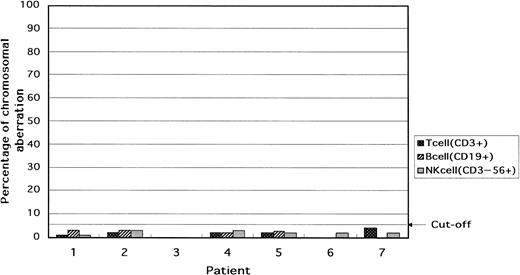
In the lymphoid cells of all patients, that is, B cells (CD19+), T cells (CD3+), and NK cells (CD3−56+), the percentage of cells with trisomy was below the cutoff value (Table 3and Fig 3).
Percentage of cells with the +8 chromosomal aberration in T (CD3+), B (CD19+), and NK (CD3−56+) cells in the blood. In all patients, the lymphocytes were intact with respect to chromosome 8.
Percentage of cells with the +8 chromosomal aberration in T (CD3+), B (CD19+), and NK (CD3−56+) cells in the blood. In all patients, the lymphocytes were intact with respect to chromosome 8.
FISH analysis of stem cells consisting of CD34+subpopulations.
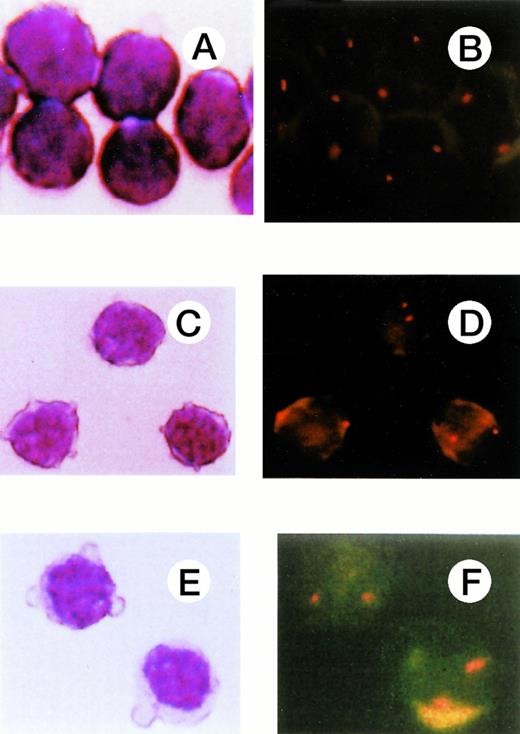
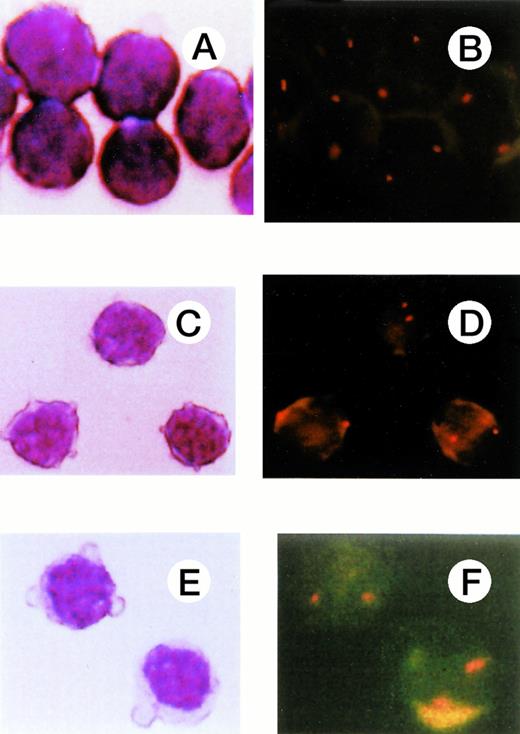
FISH of sorted cells based on immunophenotype. (A), (C), and (E) show T cells (CD3+), B cells (CD19+), and NK cells (CD3−56+), respectively, and (B), (D), (F), the FISH results for these cell populations. Two signals were observed in all these cell types.
FISH of sorted cells based on immunophenotype. (A), (C), and (E) show T cells (CD3+), B cells (CD19+), and NK cells (CD3−56+), respectively, and (B), (D), (F), the FISH results for these cell populations. Two signals were observed in all these cell types.
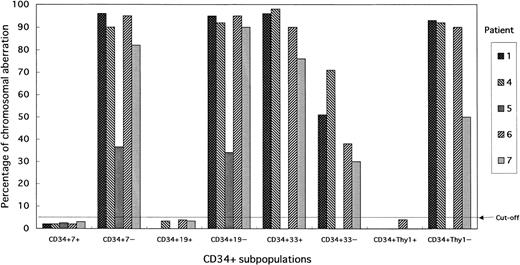
Percentage of cells with the +8 chromosome aberration in CD34+ subpopulations. The CD34+7+ (T/NK-progenitor cells), CD34+19+ (B-progenitor cells), and CD34+Thy-1+ (pluripotent-stem cells) of all patients showed an intact chromosome 8. Trisomy 8 was observed at a high frequency among CD34+33+ (CFU-GEMM) subpopulation cells.
Percentage of cells with the +8 chromosome aberration in CD34+ subpopulations. The CD34+7+ (T/NK-progenitor cells), CD34+19+ (B-progenitor cells), and CD34+Thy-1+ (pluripotent-stem cells) of all patients showed an intact chromosome 8. Trisomy 8 was observed at a high frequency among CD34+33+ (CFU-GEMM) subpopulation cells.
Analysis of CD34+ subpopulations. CD34+Thy1+ v CD34+Thy1− subpopulation.
We could collect enough CD34+Thy-1+ cells from only three patients (Fig 6A and B). The percentage of cells with the +8 chromosome abnormality in pluripotent stem cells (CD34+Thy1+) was below the cutoff value, in sharp contrast to that in CD34+Thy1− cells.
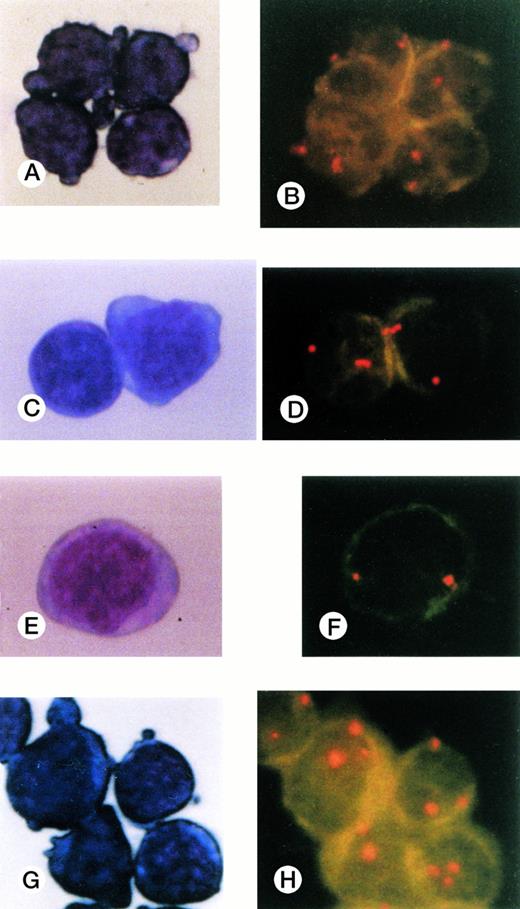
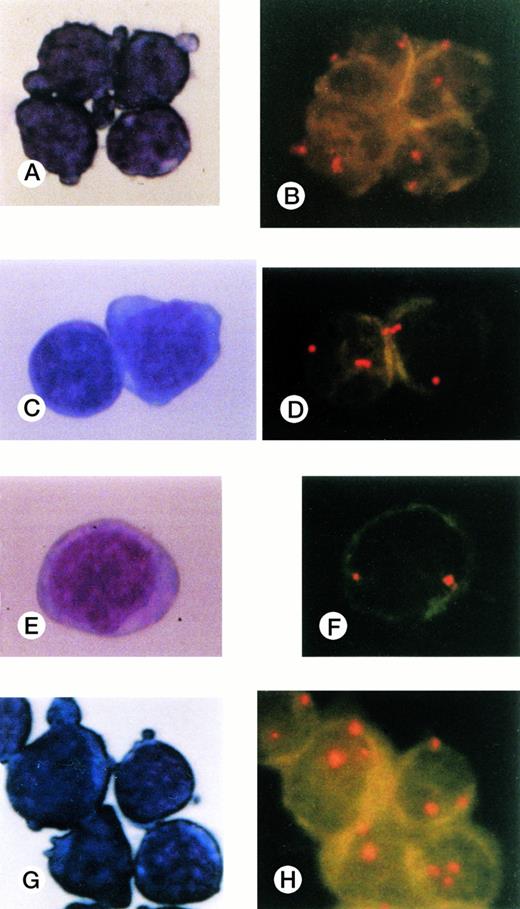
Cells collected by FACS and stained with May-Grünwald-Giemsa and FISH results for CD34+subpopulations. (A), (B) CD34+Thy-1+cells; (C),(D) CD34+CD19+ cells; (E),(F) CD34+7+ cells; (G),(H) CD34+CD33+ cells. Three signals were observed only in the CD34+CD33+subpopulation cells.
Cells collected by FACS and stained with May-Grünwald-Giemsa and FISH results for CD34+subpopulations. (A), (B) CD34+Thy-1+cells; (C),(D) CD34+CD19+ cells; (E),(F) CD34+7+ cells; (G),(H) CD34+CD33+ cells. Three signals were observed only in the CD34+CD33+subpopulation cells.
CD34+CD19+ v CD34+CD19− subpopulation.
In contrast with CD34+CD19− cells, the percentage of CD34+19+ cells with trisomy 8 was below the cutoff value in all patients (Fig 6C and D).
CD34+CD7+ v CD34+CD7− subpopulations.
The percentage of cells with trisomy 8 in the CD34+CD7+ subpopulation was clearly lower than that in the CD34+CD7− subpopulation (Fig 6E, 6F).
CD34+CD33+ v CD34+CD33− subpopulation.
In addition to the two patients from whom no cells could be collected, not enough cells could be obtained from patient 5. The incidence of trisomy 8 in CD34+CD33+ cells was similar to that in the CD34+Thy−, CD34+CD7−, and CD34+CD19− subpopulations. CD34+CD33− cells also contained the +8 chromosome abnormality, although the percentage was less than that of the CD34+CD33+ subpopulation (Fig 6G and H).
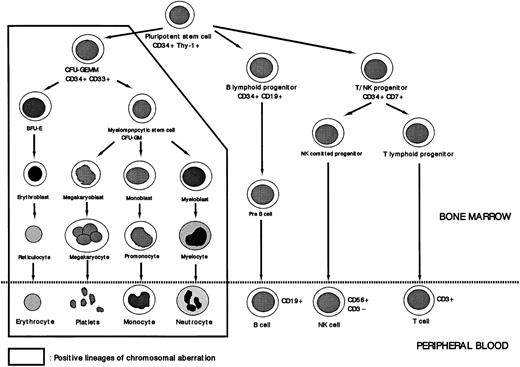
There was significant heterogeneity of +8 cells among the seven patients that is reflected to a certain extent in the percentage of +8 detected by FISH. Despite this heterogeneity, pluripotent stem cells (CD34+Thy1+), B-progenitor cells (CD34+CD19+), T/NK-progenitor cells (CD34+CD7+), all showed values below the cutoff value. CD34+CD33+ cells, compatible with the colony-forming unit of granulocyte-erythrocyte-macrophage-megakaryocyte (CFU-GEMM), had a higher percentage with the +8 chromosome abnormality than did CD34+CD33− cells, although no sharp differences were detected between the two cell types. The CD34+CD33− subpopulation included pluripotent stem cells, cells of the lymphoid lineage, and cells developmentally intermediate between pluripotent stem cells and CFU-GEMM. Because the first two subpopulations, pluripotent stem cells and the lymphoid progenitor cells, did not have the +8 chromosome abnormality, the cell population affected by trisomy 8 is assumed to consist of CD34+ cells that are more immature than CFU-GEMM (Fig 7).
Lineage involvement of abnormal clone of MDS. Trisomy 8 was not detected in cells of the lymphoid lineage or in CD34+Thy-1+ cells. The cells affected by the chromosomal aberration +8 are these assumed to be at the level of CFU-GEMM.
Lineage involvement of abnormal clone of MDS. Trisomy 8 was not detected in cells of the lymphoid lineage or in CD34+Thy-1+ cells. The cells affected by the chromosomal aberration +8 are these assumed to be at the level of CFU-GEMM.
DISCUSSION
MDS is believed to be a stem-cell disorder originating in dysplastic changes in multiple hematopoietic lineages. MDS only rarely develops into acute lymphoid leukemia, in sharp contrast to chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), a typical stem-cell disorder. CML develops into an acute phase involving myeloid, lymphoid, and other lineages. To investigate stem-cell involvement in MDS, we applied FISH to blood and BM smears for analysis of mature cells and to sorted cells for progenitors cells.
Cells affected by trisomy 8 in MDS were detected at the level of CFU-GEMM or an earlier cell population, but not in pluripotent stem cells. The lymphoid progenitor cells sorted by FACS did not show the +8 chromosome abnormality either. Data from standard chromosome analysis of PHA-stimulated cultures of PB also support these results. Furthermore, previous reports on other chromosomal abnormalities than +8 observed in MDS are consistent with our data.8-13 These data can explain why MDS patients rarely develop acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and also provide new insights into the biology of MDS and a rationale for standard remission-induction chemotherapy for MDS patients before the onset of disease progression. Autologous BM transplantation may represent a rational approach to treating MDS patients early after diagnosis if allogeneic BM transplantation can not be performed because HLA-matched donors are not available.
We conclude that the combination of FACS and FISH (“sorter FISH”) is an effective technique for identification of the lineage involvement of stem-cell disorders.
Address reprint request to Ikuo Miura, MD, Third Department of Internal Medicine, Akita University School of Medicine, 1-1-1 Hondo, Akita 010, Japan; e-mail: ikuo@med.akita-u.ac.jp.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be hereby marked "advertisement" is accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.