INTRODUCTION: Acute Graft-versus-Host-Disease (aGVHD) is a frequent complication where the endothelium may play a pivotal role. We recently investigated the potential role of extracellular vesicles (EVs) as novel biomarkers of aGVHD (Lia G. et al. Leukemia 2018). In this study we further investigated the correlation of plasma EVs and their content in miRNAs with the risk of developing aGVHD in the setting of post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCY) haploidentical-stem cell transplantation (Haplo-SCT).
METHODS: Thirty-two patients who underwent a Haplo-SCT were included. Plasma samples were collected from peripheral blood at given time-points (pre-transplant, on day 0, 3, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 45, 60, 75 and 90 after transplant). EVs were extracted by a protamine-based precipitation method and were characterized by Nano-tracking Particle Analysis (Nanosight). EVs were then analyzed by flow-cytometry (Guava EasyCyte Flow Cytometer) with a panel of 14 antibodies (CD44, CD138, CD146, KRT18, CD120a, CD8, CD30, CD106, CD25, CD26, CD31, CD144, CD86, and CD140a). MiRNAs were extracted from EVs by miRNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen) and retrotranscribed by miScript II RT Kit (Qiagen). Three miRNAs (miR100, miR194, miR155) were studied and quantified by qRT‐PCR using the miScript SYBR Green PCR Kit (Qiagen). Concomitant plasma concentrations of human Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor I (TNFR1) and human ST2 were also evaluated using a commercially available sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (DualSET® ELISA R&D Systems). The risk of aGVHD was evaluated by logistic regression models and Odds Ratios (ORs) were estimated as absolute levels and as proportional changes compared with pre-transplant baseline levels of each marker. Moreover, among biomarkers significantly associated with a higher risk of aGVHD, a multivariable logistic regression model using Akaike's information criteria (AIC) was estimated to define a biomarker combination. Ors were reported for 1-unit increase of standardized variables.
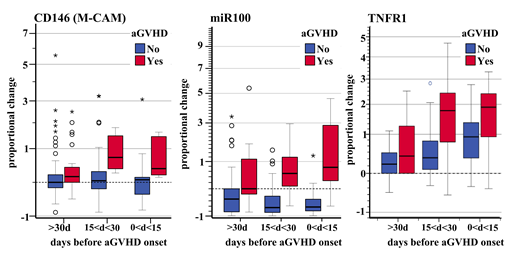
RESULTS: AGVHD (grade II-IV) was observed in 7/32 patients (22%) at a median of 41 (range 33-90) days after transplant. Logistic regression models showed that CD146 fluorescence was associated with a significantly increased risk of acute GVHD (OR 2.93 p<0.001) as well as expression changes in miR100, miR155 and miR194 (OR 3.90 p<0.001; OR 1.84 p=0.008; OR 2.68 p<0.001, respectively). Concentrations of plasmatic hTNFR1 and ST2 were also confirmed to be associated with increased risk of aGVHD (OR 1.47 p=0.04; OR 1.55 p=0.05, respectively) as previously described. Of note, all biomarkers associated with risk of aGVHD showed a consensual change in signal levels before the onset of aGVHD (Figure 1). By applying a backward selection on a multivariable logistic model using the AICapproach, we found that the combination of CD146-miR100-TNFR1 with an individual AUROC of 0.858, 0.923, and 0.794, respectively, increased their discrimination ability to predict aGVHD (multivariable AUROC = 0.987).
CONCLUSIONS: This study, in the setting of haplo-transplant, confirms the association of CD146, a cell adhesion molecule, and the risk of aGVHD suggesting an important role of endothelium damage in the pathogenesis of aGVHD. The association of miRNA100, miRNA155 and miRNA194, carried by EVs, and aGVHD was also significant. Interestingly, MiRNA100 was reported to regulate inflammatory neovascularization during GvHD while miR-155 plays a role in donor T cell expansion. We have also found that using three markers in combination (CD146-miR100-TNFR1) could greatly improve aGVHD predictivity. To translate our results into an in vivo model, we have recently designed preclinical mouse models to evaluate if a) antagomir (against miRNA100 and/or miRNA155) injections or b) pre-emptive treatments with endothelium protective agents such as defibrinotide or OMS721 (Anti-Masp2) may reduce the risk of aGVHD.
Figure1a) Signal variation from baseline level (preTx) of CD146 fluorescence, miR100 expression, and TNFR1 concentration before aGVHD onset.
Boccadoro:Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria; Mundipharma: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.