Abstract
Introduction: ITP, characterized by a reduction in platelets leading to thrombocytopenia, which persists for >12 months is considered chronic (cITP). Eltrombopag is an oral thrombopoietin receptor agonist approved for treatment of patients with cITP aged ≥1 year refractory to other treatments (eg corticosteroids, immunoglobulins). The recently completed Phase III EXTEND (Eltrombopag eXTENded Dosing) study was a global, open-label, extension study of patients with cITP, who received eltrombopag or placebo in prior eltrombopag clinical studies. The primary objective of EXTEND was to describe the long-term safety and tolerability of eltrombopag treatment in these patients. Here, we examine the occurrence of hepatobiliary and thromboembolic events (TEEs) as adverse events (AEs) of special interest in this study.
Methods:Adult patients (≥18 years old) diagnosed with cITP according to ASH/BCSH guidelines were enrolled and received eltrombopag starting at 50 mg/day. Dose was titrated to 25-75 mg per day or less often as required, based on individual platelet count responses (targeted range ≥50-200x109/L). Patients who received 2 years of treatment and transitioned off eltrombopag due to commercial availability of eltrombopag were considered to have completed the study, whether or not they continued treatment with eltrombopag. The primary endpoint included detection and documentation of investigator-reported AEs, which included hepatobiliary AEs and TEEs. Analyses were conducted using the safety population, defined as all subjects who entered the study and had taken at least one dose of the study medication.
Results:302 patients were enrolled and received at least one dose of eltrombopag: 67% were female; 38% splenectomized; 49% aged 18-49 years. Median duration of exposure was 2.4 years (range, 2 days to 8.8 years) and mean average daily dose was 50.2 (range, 1-75) mg/day. Overall, 259/302 (86%) achieved platelet counts of ≥50×109/L at least once during the study and 126/248 (51%) patients maintained continuous platelet counts ≥50×109/L for at least 31 weeks. Incidence of bleeding symptoms (WHO grades 1-4) generally decreased over time in patients with available data, from 57% (n=171/302) at baseline to 16% at 1 year (n=13/80), and 21% (12/58) at 2 years.
45 (15%) patients experienced at least one hepatobiliary AE, with the highest incidence within the first year of treatment (Figure A). AEs of increased ALT or AST led to the discontinuation of five and three patients, respectively and four patients discontinued due to an AE of increased blood bilirubin. Nine patients experienced ALT and/or AST >3 x upper limit of normal (ULN) and total bilirubin >1.5xULN.
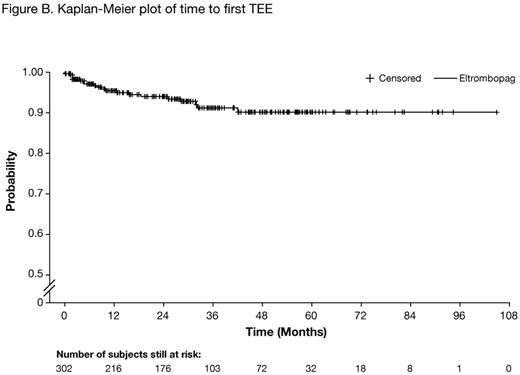
19 (6.3%) patients experienced a total of 23 TEEs. Most events occurred in the first year (Figure B), and none after year 4. TEEs included deep vein thrombosis (n=6), cerebral infarction (stroke) [n=3], myocardial infarction (n=4), transient ischemic attack (n=2), others (n=8, 1 occurrence of each). A clear association with elevated platelet counts was not observed. Platelets >200x109/L at the time of the TEE were recorded in 8/19 patients; 6/19 experienced the TEE at or shortly after achieving their maximum platelet count. In total, 10 patients discontinued because of TEEs.
Conclusions: Long-term treatment with eltrombopag in patients with cITP led to sustained platelet increases and reduced bleeding symptoms. The highest incidences of hepatobiliary AEs and TEEs occurred during the first year of treatment, though several events were recorded after 3 years of therapy. Long-term eltrombopag therapy was well-tolerated with a positive benefit-risk relationship in adults with cITP, with decreasing events after the first year of treatment.
Saleh:GSK: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Bussel:Amgen, Novartis & GSK: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Boehringer Ingleheim, Prophylix Pharma, Protalex, Rigel Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Momenta Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Prophylix Pharma, Protalex, Rigel Pharmaceutical: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; UptoDate: Patents & Royalties; Physicians Education Resource: Speakers Bureau. Wong:Bayer, Biogen-Idec and Novartis: Consultancy; Bayer, Biogen-Idec, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche: Research Funding; Biogen-Idec and Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. El-Ali:Novartis: Employment. Quebe-Fehling:Novartis: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.