Abstract
Background and Objective: Treatment and triage decisions during influenza remain difficult due to lack of reliable severity of illness predictive score. Influenza A/H1N1 induces the expression and release of tissue-factor bearing microparticles (MP-TF), contributing to a prothrombic milieu. However, there are no studies reporting levels of circulating TF-expressing MPs during the course of human influenza. We sought to determine if MP-TF are an early predictor of mortality in critically ill patients with influenza A/H1N1.
Methods: This was a prospective, multicenter, case-cohort pilot study of three academic intensive care units. We prospectively studied 15 patients with primary influenza A/H1N1 that included 7 survivors and 8 non-survivors. For comparison, 27 healthy, medication-free, age- and gender-matched control subjects were also prospectively studied. Plasma was prepared from blood drawn upon ICU admission in influenza patients. MP-TF activity, thrombin-antithrombin complexes (TATc), and D-dimers were measured as markers of activation of coagulation. Plasma cytokine levels were measured on the same blood samples. Patients were followed for the primary outcome of 28-day mortality.
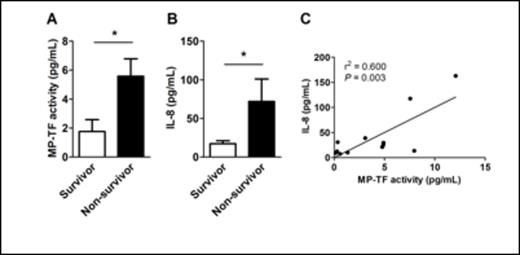
Results: The average admission APACHE II score of the influenza patients was 25.5±9.3, 60% of patients had shock, and the 28-day mortality rate was 53.3% (n=8/15). Compared to healthy controls, influenza patients had significantly higher plasma fibrinogen, C-reactive protein (CRP) MP-TF activity, TATc, D-dimer and a prolonged prothrombin time. However, of these procoagulant markers, only MP-TF activity predicted influenza related mortality (5.6±1.2 pg/ml in non-survivors vs. 1.8±0.8 pg/mL in survivors, p < 0.05; Table 1 and Fig. 1A). MP-TF activity, TATc levels, and D-dimer did not correlate with APACHE II score, platelet count, fibrinogen levels, CRP, or age or between patients with severe sepsis versus septic shock. Influenza non-survivors also had significantly higher plasma IL-8 levels compared with survivors (71.8±29.1 pg/ml vs. 17.3±3.7 pg/mL, p < 0.05; Figure 1B). MP-TF activity and IL-8 levels were significantly and positively correlated (r2 = 0.60, P =0.003; Figure 1C). Other cytokines, TATc, and D-dimer were not different between non-survivors and survivors.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that plasma IL-8 and MP-TF activity measured upon admission in patients with severe, primary influenza A/H1N1 infection is associated with subsequent mortality. Thus, these biomarkers may serve as very early prognostic markers for patients with influenza A/H1N1.
Characteristics of the influenza patients. Laboratory values, coagulation markers, and plasma cytokines were measured within 24 hours of ICU admission.
| . | All Influenza A/H1N1 Patients (n=15) . | Influenza Non-Survivors (n=8) . | Influenza Survivors (n=7) . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admission Characteristic | ||||
| Age, years | 43.3±11.0 | 45.8±4.6 | 40.4±15.5 | 0.37 |
| Male Gender, n (%) | 7 (47%) | 3 (38%) | 4 (57%) | 0.45 |
| Weight, kg | 95.5±25.2 | 86.6±20.9 | 105.7±27.4 | 0.15 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 33.3±7.2 | 31.5±5.0 | 35.4±9.1 | 0.31 |
| Obesity (BMI³30 kg/m2) | 10 (67%) | 5 (63%) | 5 (71%) | 0.71 |
| Tobacco Use, n (%) | 4 (27%) | 3 (38%) | 1 (14%) | 0.31 |
| APACHE II Score | 25.5±9.3 | 27.9±9.1 | 22.9±9.4 | 0.31 |
| Mechanically Ventilated, n (%) | 15 (100%) | 8 (100%) | 7 (100%) | -- |
| Shock, n (%) | 9 (60%) | 6 (75%) | 3 (43%) | 0.21 |
| P/F Ratio | 83±28 | 84±34 | 82±22 | 0.89 |
| Clinical Outcomes | ||||
| ICU Length of Stay, days | 21.9±7.7 | 23.0±7.9 | 20.7±7.8 | 0.58 |
| Duration of Ventilation, days | 8.2±1.0 | 8.5±0.9 | 7.6±0.9 | 0.11 |
| Secondary Bacterial Infection, n (%) | 5 (33%) | 4 (50%) | 1 (14%) | 0.28 |
| Overt DIC, n (%) | 15 (100%) | 8 (100%) | 7 (100%) | -- |
| Laboratory Values | ||||
| Platelets, 103/µL | 213±138 | 154±104 | 280±150 | 0.08 |
| White Blood Cells, K/µL | 7.3±4.4 | 8.5±4.9 | 5.9±3.5 | 0.28 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 11.7±1.9 | 11.5±2.0 | 12.0±1.8 | 0.66 |
| Serum Creatinine, mg/dL | 1.1±0.7 | 1.14±0.74 | 1.07±0.59 | 0.84 |
| Coagulation Markers | ||||
| Fibrinogen, mg/dL | 571±240 | 461±253 | 700±157 | 0.07 |
| C-reactive Protein, mg/L | 11.0±7.6 | 11.8±7.4 | 10.2±8.2 | 0.70 |
| PT, sec | 20±7.0 | 19.2±4.7 | 20.9±9.3 | 0.67 |
| aPTT, sec | 53.0±22.9 | 55.1±29.0 | 50.7±15.0 | 0.72 |
| MP-TF, pg/mL | 3.8±0.9 | 5.6±1.2 | 1.8±0.8 | < 0.05 |
| TATc, ng/mL | 11.8±2.7 | 14.3±3.5 | 9.1±4.1 | 0.35 |
| D-dimer, ng/mL | 2439±86 | 2568±98 | 2292±134 | 0.11 |
| . | All Influenza A/H1N1 Patients (n=15) . | Influenza Non-Survivors (n=8) . | Influenza Survivors (n=7) . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admission Characteristic | ||||
| Age, years | 43.3±11.0 | 45.8±4.6 | 40.4±15.5 | 0.37 |
| Male Gender, n (%) | 7 (47%) | 3 (38%) | 4 (57%) | 0.45 |
| Weight, kg | 95.5±25.2 | 86.6±20.9 | 105.7±27.4 | 0.15 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 33.3±7.2 | 31.5±5.0 | 35.4±9.1 | 0.31 |
| Obesity (BMI³30 kg/m2) | 10 (67%) | 5 (63%) | 5 (71%) | 0.71 |
| Tobacco Use, n (%) | 4 (27%) | 3 (38%) | 1 (14%) | 0.31 |
| APACHE II Score | 25.5±9.3 | 27.9±9.1 | 22.9±9.4 | 0.31 |
| Mechanically Ventilated, n (%) | 15 (100%) | 8 (100%) | 7 (100%) | -- |
| Shock, n (%) | 9 (60%) | 6 (75%) | 3 (43%) | 0.21 |
| P/F Ratio | 83±28 | 84±34 | 82±22 | 0.89 |
| Clinical Outcomes | ||||
| ICU Length of Stay, days | 21.9±7.7 | 23.0±7.9 | 20.7±7.8 | 0.58 |
| Duration of Ventilation, days | 8.2±1.0 | 8.5±0.9 | 7.6±0.9 | 0.11 |
| Secondary Bacterial Infection, n (%) | 5 (33%) | 4 (50%) | 1 (14%) | 0.28 |
| Overt DIC, n (%) | 15 (100%) | 8 (100%) | 7 (100%) | -- |
| Laboratory Values | ||||
| Platelets, 103/µL | 213±138 | 154±104 | 280±150 | 0.08 |
| White Blood Cells, K/µL | 7.3±4.4 | 8.5±4.9 | 5.9±3.5 | 0.28 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 11.7±1.9 | 11.5±2.0 | 12.0±1.8 | 0.66 |
| Serum Creatinine, mg/dL | 1.1±0.7 | 1.14±0.74 | 1.07±0.59 | 0.84 |
| Coagulation Markers | ||||
| Fibrinogen, mg/dL | 571±240 | 461±253 | 700±157 | 0.07 |
| C-reactive Protein, mg/L | 11.0±7.6 | 11.8±7.4 | 10.2±8.2 | 0.70 |
| PT, sec | 20±7.0 | 19.2±4.7 | 20.9±9.3 | 0.67 |
| aPTT, sec | 53.0±22.9 | 55.1±29.0 | 50.7±15.0 | 0.72 |
| MP-TF, pg/mL | 3.8±0.9 | 5.6±1.2 | 1.8±0.8 | < 0.05 |
| TATc, ng/mL | 11.8±2.7 | 14.3±3.5 | 9.1±4.1 | 0.35 |
| D-dimer, ng/mL | 2439±86 | 2568±98 | 2292±134 | 0.11 |
MP-TF activity and IL-8 predict mortality in patients with influenza A/H1N1.
(A) Plasma levels of MP-TF activity and (B) IL-8 levels in survivors and non-survivors. (C) Correlation between MP TF activity and IL-8 levelsin H1N1 influenza-infected patients (*P <0.05).
MP-TF activity and IL-8 predict mortality in patients with influenza A/H1N1.
(A) Plasma levels of MP-TF activity and (B) IL-8 levels in survivors and non-survivors. (C) Correlation between MP TF activity and IL-8 levelsin H1N1 influenza-infected patients (*P <0.05).
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.