Abstract

Background
CD33 is expressed on the surface of myeloblasts in 85 to 90% of patients with AML and represents a promising target regardless of age, risk factors, or underlying mutational heterogeneity. SGN-CD33A is an anti-CD33 engineered cysteine antibody conjugated to an average of 2 molecules of a pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) dimer, a highly potent DNA crosslinking agent. Upon binding to the cell surface, SGN-CD33A is internalized and transported to the lysosomes where PBD dimer is released within the cell through proteolytic cleavage of the linker, crosslinking DNA and leading to cell death.
Methods
This phase 1, open-label, 3+3 dose-escalation study (NCT01902329) is designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), and anti-leukemic activity of SGN-CD33A. Eligible patients (ECOG 0-1) must have CD33-positive AML, and have either relapsed disease following initial remission (CR) of > 3 months, or have declined conventional induction/consolidation. SGN-CD33A is administered outpatient IV every 3 weeks for up to 4 cycles (Part A), followed by optional maintenance treatment for patients achieving a CR/CRi (Part B). Investigator assessment of response is per IWG criteria (Cheson 2003).
Results
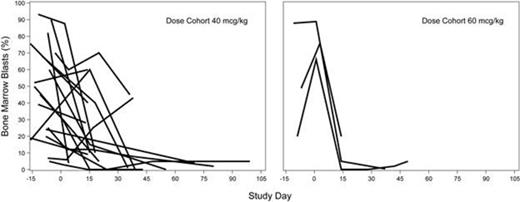
To date, 40 patients (48% female) with a median age of 75 years (range, 27-86) have been treated. Twenty patients had relapsed AML after 1st CR with intensive therapy (3 of these had intensive frontline therapy plus 1 additional line of low intensity therapy); 20 had declined conventional intensive therapy (13 of these patients had received 1-2 prior low intensity therapies, primarily hypomethylating agents). Of the patients enrolled, 45% had underlying myelodysplasia and most had disease with intermediate (70%) or adverse (18%) cytogenetic risk, 8% with mutated NPM1 (without FLT3 mutation) and 13% with mutated FLT3. Dose levels tested were 5 mcg/kg (n=3), 10 mcg/kg (n=3), 20 mcg/kg (n=13), 40 mcg/kg (n=18), and 60 mcg/kg (n=3). To date, a maximum of 4 cycles was received in Part A and 10 cycles in Part B (total median of 2 cycles on treatment; range, 1-13 cycles). Thirteen patients remain on treatment and enrollment is ongoing. Two dose-limiting toxicities have been reported, a Grade 3 pulmonary embolism (20 mcg/kg) and a Grade 4 hypocellular marrow (>28 days; 40 mcg/kg). The only Grade 3 or higher adverse event (AE) reported in >10% of patients was febrile neutropenia (55%). Other treatment-emergent AEs regardless of relationship to study treatment reported in ˃10% of patients were fatigue (48%), diarrhea (20%), constipation (18%), cough (18%), dyspnea (18%), epistaxis (18%), peripheral edema (18%), malaise (15%), hypokalemia (13%), and pleural effusion (13%). The 30-day mortality was 2.5%, with no treatment-related deaths occurring during that time; 1 elderly patient died from a traumatic fall unrelated to SGN-CD33A. Blast clearance in marrow was obtained in 16 of 38 efficacy evaluable patients (42%) across all dose levels. A dose-response relationship is evolving with rapid and marked decreases in bone marrow blasts at 40 and 60 mcg/kg in 19 of 21 patients (Figure 1). Of 17 efficacy evaluable patients treated at 40 mcg/kg, 8 experienced clearance of marrow blasts; these patients achieved a best clinical response of CR (2), CRi (3), and morphologic leukemia-free state (mLFS; 3) thus far. In addition, complete remissions were observed at 5 mcg/kg (1 CR), 10 mcg/kg (1 CRi), and 20 mcg/kg (2 CRis). Preliminary PK data demonstrated rapid clearance of ADC, suggesting target-mediated disposition. Plasma ADC exposure generally increased with increasing dose levels.
Conclusions
A MTD for SGN-CD33A is not yet identified and enrollment continues. AEs observed were generally manageable, often associated with underlying myelosuppression. To date, SGN-CD33A has demonstrated antileukemic activity with 47% achieving blast clearance at the 40 mcg/kg dose level. The observed low 30-day mortality (2.5%) and rapid clearance of marrow blasts in patients with poor risk factors (median age 75, predominantly intermediate and adverse cytogenetic risk, and 45% underlying myelodysplasia) with outpatient administration are encouraging. Enrollment is ongoing to further define optimal dose and schedule. In addition, combinations of SGN-CD33A with standard AML and MDS agents will be evaluated.
Bone Marrow Blasts Over Time
Stein:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding; Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Off Label Use: SGN-CD33A is an investigational agent being studied in patients with AML. SGN-CD33A is not approved for use. Stein:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding. Walter:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amphivena Therapeutics, Inc.: Consultancy; Amgen: Research Funding; Amphivena Therapeutics, Inc.: Consultancy; Amgen: Research Funding. Fathi:Exelixis: Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceuticals International Co.: Research Funding; Ariad: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding. Lancet:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding. Kovacsovics:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding. Advani:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding. DeAngelo:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding. O'Meara:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Zhao:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Kennedy:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Erba:Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract