Case presentations
Case 1. Patient 1 is a 65-year-old plumber who presents with fatigue, headache, blurred vision, and intermittent nosebleeds for the past 3 months. Examination demonstrates mild generalized lymphadenopathy and a palpable spleen tip. The fundi show marked retinal vein engorgement with “sausaging.” Laboratory tests disclose mild anemia and a large monoclonal spike on serum protein electrophoresis. How should he be managed?
Elevated blood, plasma, or serum viscosity occurs in a number of hematologic disorders. Hyperviscosity syndrome (HVS) is a clinical feature in 10% to 30% of patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM), sometimes as its presenting manifestation.1 HVS also accompanies other conditions, such as multiple myeloma, rheumatoid disease, polycythemia, sickle cell disease, leukemia, and spherocytosis.2 The latter 4 cellular causes of HVS are beyond the scope of this discussion. The purpose of this paper is to discuss the characteristic features of HVS secondary to elevated plasma or serum viscosity and to evaluate evidence supporting various diagnostic and treatment approaches using the Grade system (Table 1).3,4
In searching the Medline database on hyperviscosity syndrome, 594 references were listed back to 1965. A limited number of older publications were also used. Only English-language articles were considered. Observational studies, systemic reviews, or case studies were included. No randomized trials on management of HVS were identified.
Methods to measure viscosity
Viscosity refers to resistance to flow or stickiness, from the Latin word “viscum alba” for mistletoe.5,6 (Mistletoe berries were once used to make a viscous glue.) Viscosity is classically measured in one of 2 ways: by determining the rate of fluid flow as a result of applying a predefined force or by measuring the amount of force required to achieve a predefined rate of fluid flow.
Although HVS is caused by hyperviscous blood, clinical laboratories generally only measure the serum or plasma component. Serum and plasma display Newtonian properties in that viscosity is independent of pressure drop or velocity gradient. Consequently, the method of measurement will not dramatically affect the test result. By contrast, whole blood viscosity is complex because of the suspension of red cells in plasma, resulting in non-Newtonian behavior. Different methods of measurement can yield various results.
In WM, serum or plasma viscosity measurements reflect the amount and properties of the IgM paraprotein. Monoclonal IgMs display a wide range of intrinsic viscosity values (0.106-0.162 dL/g), each protein having individual properties.7,8 However, relative viscosity values are highly reproducible for any individual protein. IgM is a star-shaped pentamer with a molecular size of 925 kDa (IgG is 150 kDa and albumin is 65 kDa). Thus, it is not surprising that this giant IgM molecule, which is 80% intravascular, exerts profound effects on blood flow and cells, especially when present in the high concentrations found in WM patients.
The methods used for the measurement of serum or plasma viscosity in patients have changed little since Waldenström's use of an Ostwald tube in 1944.9 College of American Pathologists (CAP) data for 2010 reveal that approximately 75% of clinical laboratories use a “capillary tube” (ie, Ostwald tube) viscometer.10 Viscosity is measured by the time required for a serum or plasma sample to flow through a tube under the influence of gravity. Viscous samples flow more slowly. Hence, viscosity is proportional to time.
The simplicity of these popular methods for viscosity measurement belies a lack of standardization and subtle risks for imprecision. Laboratories using the Ostwald and pipette methods report their data as ratios rather than in units of viscosity, such as centipoise (cp). The results are reported as the ratio of time for a patient sample to pass through the tube relative to the time for a reference fluid (eg, water). Consequently, commercial viscosity controls traceable to a National Institute of Standards and Technology standard, reported in centipoise, are not directly applicable. The Ostwald and pipette methods lack the kind of standardized commercial calibrators and controls that are commonplace for other hematology or chemistry assays.
Because the viscosity of water at 20°C approximates 1.0 cp, the viscosity ratio will be similar to the sample's viscosity in centipoise at this temperature. The accuracy of this generalization depends on the actual temperature at which the samples are measured. CAP data (2010) reveal that clinical laboratories measure viscosity at one of 2 temperatures: room temperature or 37°C.10 Temperature differences affect the measured viscosity because warmer fluids flow more easily.11 Despite normalization to water at the same temperature, CAP proficiency data indicate that warmed samples consistently yield slightly lower viscosity ratios.10
The Ostwald tube remains a simple, reliable method for measuring relative serum viscosity in patients. Of 499 serum viscosity determinations performed at Baylor Dallas, 297 (59.5%) were elevated.12 A total of 60% of these specimens contained monoclonal IgM. Results were reproducible to ± 5% and usually available within 3 hours.
A variety of automated viscometers are commercially available, the most common being the cone/plate type.13 CAP data reveal that only 7% of clinical laboratories use the cone/plate type of viscometer.10 Most validation studies linking HVS to a particular serum or plasma viscosity were performed using the Ostwald tube. Consequently, the viscosity ratios (normalized to water at 20°C) may not exactly match the viscosity measured by an automated method, expressed in centipoise.
Probably the most important consideration in selecting a method for viscosity measurement is precision (ie, reproducibility from day to day). For each WM patient, there is a viscosity threshold above which symptoms appear.1,12,14-18 This symptomatic threshold differs from patient to patient but is relatively consistent in the same WM patient.8,12,14-17 Whatever method is chosen, it is clinically important to obtain reproducible data. In this way, patient viscosities can be tracked over time and intervention initiated before HVS symptoms begin.
Recommendation (grade 2C)
In measuring serum or plasma viscosity, we suggest using the Ostwald method because of its simplicity, reproducibility, and clinical correlation. Other methods are acceptable, however, with proper initial validation.
Clinical presentation
HVS was described by Jan Waldenström in his original 1944 report of 2 patients with macroglobulinemia.9 Bleeding, usually skin and mucosal, is the most common manifestation of HVS. Blurred vision, headache, vertigo, dizziness, nystagmus, deafness, and ataxia also occur in HVS.1,8,12,14-18 Patients with severe HVS may have confusion, dementia, stroke, or coma. Heart failure and other cardiovascular signs are less common.1,14-18 Patients with WM have an increased blood volume because of an expanded plasma volume.17,18 Thus, a component of the anemia in WM is dilutional. Plasma volume expansion correlates with the rise in relative serum viscosity. HVS may be suspected because of abnormal results in antibody screening in the blood bank.19
Most patients with HVS have WM.1,16,17 Normal viscosity measured with an Ostwald tube is 1.4 to 1.8 relative to water.1,14-16 HVS is unlikely unless the serum viscosity is greater than 4.1,14,16-18 For patients with an IgG paraprotein, such as in multiple myeloma, the increase in serum viscosity is approximately proportional to the concentration of the paraprotein.14 For IgM paraproteins, relative viscosity can rise exponentially above a concentration of 3 g/dL.14
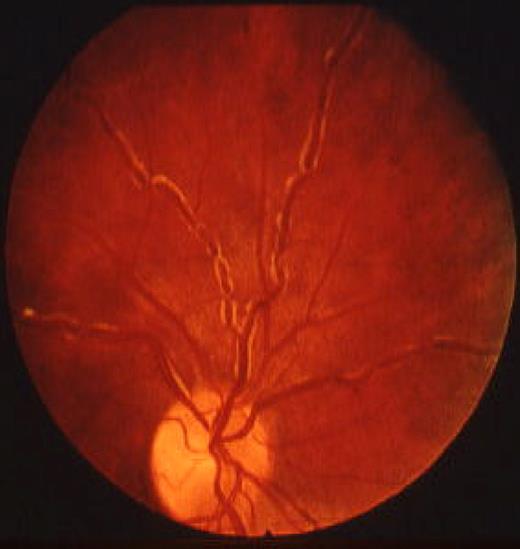
Viscosity levels in HVS vary significantly between patients. Such variation is the result, in part, of the previously mentioned wide range of intrinsic viscosity values noted in monoclonal macroglobulins.7,8 However, viscosity values correlate closely with signs and symptoms in the same patient (“symptomatic threshold”).1,12,14-18 The HVS can be diagnosed from the physical examination by the funduscopic finding of marked retinal venous engorgement resembling hot dogs on a string (ie, “sausaging”12,14-18,20 ; Figure 1). Hemorrhages, exudates, microaneurysms, papilledema, and an appearance indistinguishable from central retinal vein occlusion may be seen in later stages. Prompt diagnosis of HVS from the eye examination enables the institution of appropriate therapy (ie, plasmapheresis).1,12,14-18,20-22 In addition to raising plasma viscosity, macroglobulin coats red cells, leading to the characteristic stacking appearance (rouleaux) on peripheral blood smear in WM patients.12,14,16-18 Protein coating also contributes to a platelet functional defect that further accentuates the bleeding tendency.
Funduscopic appearance of patient with WM and mixed cryoglobulinemia. Note the marked retinal venous engorgement and “sausaging.” The white material at the edge of the veins may be cryoglobulin.12,20 Reprinted from Stone with permission.12
The presence of cryoglobulinemia can result in a strikingly temperature-dependent elevation of serum viscosity in WM patients.12,23-26 Most cryoglobulins are mixed monoclonal IgM-polyclonal IgG immune complexes with rheumatoid factor activity. These antigen-antibody complexes precipitate at lower concentrations than single component (type I) monoclonal cryoglobulins, in part because of their high thermal amplitude (temperature of precipitation).26,27
Treatment of HVS
Plasmapheresis, first carried out manually for macroglobulinemia in the late 1950s, was demonstrated to reverse retinopathy and other clinical manifestations in most patients with HVS.14,21,22 This procedure remains effective short-term treatment for HVS in WM because of the demonstrated correlation between IgM levels and serum viscosity and the 80% intravascular location of IgM. A relatively small reduction in IgM concentration has a significant effect on lowering serum viscosity. Because bleeding is the most common sign of HVS, urgent plasmapheresis using a cell separator should be carried out for patients experiencing visual symptoms to reduce the likelihood of blindness from retinal hemorrhages/retinal detachment.28 Plasmapheresis can reverse HVS-induced retinal changes promptly, including reducing retinal venous diameter and increased venous blood viscosity.29 Retinal examination findings correlate with symptomatic threshold for HVS in WM patients. Some WM patients can be managed predominately with plasmapheresis.1,12,16,30 However, plasma exchange does not affect the underlying disease process, and so chemotherapy is often begun concomitantly. Plasmapheresis can be carried out daily initially and then spaced out at longer intervals to keep the viscosity below the symptomatic threshold for that particular patient. Plasma exchange reduces plasma viscosity approximately 20% to 30% per session.31 Serial serum viscosity can be monitored daily to decide about further plasmapheresis. Generally, 1 to 1.5 plasma volumes are exchanged per session. Fluid replacement usually consists of albumin and saline in various proportions. Plasmapheresis is a safe and well-tolerated procedure.1,12,16-18,21,22,30,31 Various modifications of the apheresis procedure have been used for removal of paraprotein in patients with cryoglobulinemia. More data are necessary before these approaches can be recommended.
It is usually not necessary to plasmapherese patients down to normal viscosity to relieve symptoms. One potential exception is illustrated by a patient with documented WM who developed peripheral neuropathy associated with monoclonal IgM anti-myelin–associated glycoprotein antibody.12,27,32 Because her neurologic symptoms reproducibly recurred above a viscosity of 2.5 to 3, we sought to maintain the viscosity below 2.5 with frequent plasmapheresis. During a 23-year period, this patient underwent approximately 400 plasmapheresis procedures with little chemotherapy other than corticosteroids. Her prolonged course raises the possibility that patients with monoclonal IgM antibodies that produce neuropathy or other target organ dysfunction may benefit from a more aggressive effort to maintain serum viscosity near normal. Prospective clinical trials will be necessary to confirm this anecdotal observation.
Transient increases in IgM levels after single-agent rituximab therapy (“flares”) occur in 30% to 70% of WM patients.33-35 It has been recommended that plasmapheresis be carried out in advance of rituximab therapy if serum viscosity is more than 3.5 cp or IgM level is greater than 5 g/dL. The mechanism of the rituximab flare may involve release of IL-6 after stimulation of monocytes.36 The flare phenomenon may become somewhat less of a problem with the use of combination regimens that use chemotherapy before giving rituximab or omitting the rituximab for the first one or 2 cycles.
Plasmapheresis remains a valuable adjunct to the treatment of some patients with WM, although randomized trials of this procedure in HVS are lacking. It should be carried out as an emergency procedure in high-risk HVS patients.
HVS occurs uncommonly in myeloma. Patients with the unusual IgG3 subclass are more likely to develop HVS than other myeloma patients because of concentration-dependent aggregation.16,37 Although IgG is only 40% intravascular, plasmapheresis should be instituted in myeloma-associated HVS. HVS also occurs occasionally in IgA and light chain myeloma because of formation of polymers. Rheumatoid HVS is rare and may develop from aggregates of rheumatoid factor or intermediate IgG complexes.38
Recommendation (grade 2B)
Observational studies have consistently demonstrated that plasmapheresis can promptly reverse most clinical manifestations of serum HVS. Thus, early diagnosis is crucial. The concept of a symptomatic threshold in individual patients seems valid. Keeping serum viscosity below each patient's symptomatic threshold effectively prevents recurrent HVS. Plasmapheresis is sometimes necessary as an emergency procedure and is useful maintenance therapy in selected patients. Vigorous plasmapheresis in WM patients with autoreactive IgM antibodies requires further study.
Discussion
Although controlled trials for treatment of serum HVS are lacking, experience with management of patients by plasmapheresis has consistently demonstrated efficacy. Most signs and symptoms are reversible with prompt diagnosis and treatment. HVS is readily diagnosed on funduscopic examination, treatable with plasmapheresis, and monitored with serum or plasma viscosity measurements. Plasmapheresis is usually well tolerated and safe. When patients are maintained at a level below his or her symptomatic threshold, clinical manifestations of the syndrome are usually prevented. Whether patients having IgM proteins with autoantibody activity and consequent immune-mediated organ damage should be more aggressively pheresed is unknown, but this approach warrants a prospective therapeutic trial.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Shawn Guy-Pitts for providing excellent assistance with manuscript preparation.
This work was supported in part by the Edward and Ruth Wilkof Foundation.
Authorship
Contribution: M.J.S. and S.A.B. designed the review and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Marvin J. Stone, Baylor Sammons Cancer Center, 3410 Worth St, Ste 580, Rm 5117, Dallas, TX 75246; e-mail: marvins@baylorhealth.edu.