Abstract
Factor XI deficiency is associated with a bleeding diathesis, but factor XII deficiency is not, indicating that, in normal hemostasis, factor XI must be activated in vivo by a protease other than factor XIIa. Several groups have identified thrombin as the most likely activator of factor XI, although this reaction is slow in solution. Although certain nonphysiologic anionic polymers and surfaces have been shown to enhance factor XI activation by thrombin, the physiologic cofactor for this reaction is uncertain. Activated platelets secrete the highly anionic polymer polyphosphate, and our previous studies have shown that polyphosphate has potent procoagulant activity. We now report that polyphosphate potently accelerates factor XI activation by α-thrombin, β-thrombin, and factor XIa and that these reactions are supported by polyphosphate polymers of the size secreted by activated human platelets. We therefore propose that polyphosphate is a natural cofactor for factor XI activation in plasma that may help explain the role of factor XI in hemostasis and thrombosis.
Introduction
In the original cascade or waterfall model of coagulation,1 factor XI (FXI) is activated by factor XIIa (FXIIa), a member of the contact pathway of blood clotting. Patients with severe FXI deficiency may exhibit bleeding tendencies,2,3 especially postoperative or posttraumatic bleeding in tissues with robust fibrinolytic activity.4-6 Conversely, individuals with severe deficiencies in FXII, high-molecular-weight kininogen, or prekallikrein do not exhibit bleeding diatheses at all, indicating that the proteins responsible for triggering the classic contact pathway of blood clotting are completely dispensable for hemostasis.7 Thus, in normal hemostasis, FXI must be activated in vivo by a protease other than FXIIa. A solution to this conundrum was proposed in 1991 by Naito and Fujikawa8 and by Gailani and Broze,9 who reported that thrombin up-regulates its own generation by feeding back to activate FXI, leading to a “revised model of coagulation.”9-11 More recently, Matafonov et al identified that β-thrombin and γ-thrombin, proteolyzed derivatives of α-thrombin, also can activate FXI in plasma.12
The proposal that FXI activation by thrombin plays a significant role in blood clotting in vivo is somewhat controversial.13-15 In solution, the rates both of FXI activation by thrombin and of FXI autoactivation are slow but are markedly enhanced in the presence of polyanions,8,9,16,17 although most studies have used nonphysiologic cofactors such as dextran sulfate or high concentrations of sulfatides. The relevant physiologic cofactors for FXI activation by thrombin in plasma, if any, have yet to be definitely determined.
Polyphosphate (polyP), a linear polymer of inorganic phosphate residues, accumulates in a variety of microorganisms18 and is secreted by activated human platelets.19 We recently showed that polyP is a potent modulator of the human blood clotting system, acting at 3 points in the clotting cascade: It initiates the contact pathway of blood clotting in an FXII-dependent manner (requiring very long polyP polymers for optimal activity),20-22 it accelerates the activation of factor V (FV) by thrombin and factor Xa (FXa),20 and it enhances the thickness of fibrin fibrils.23
Here, we demonstrate that polyP potently accelerates FXI activation by α-thrombin, β-thrombin, and FXIa. Using carefully defined polymer lengths, we report that polyP polymers of the size secreted by activated human platelets are very active in stimulating FXI activation by thrombin in both a purified system and in plasma. We further report that activated platelets and platelet releasates promote FXI activation by thrombin. Together, these findings indicate that polyP is a potent natural cofactor for FXI activation by thrombin that may help explain the role of FXI in normal hemostasis.
Methods
Materials
PolyP preparations of narrow size distribution were prepared as described previously,21 and are indicated in this study by their polymer length followed by “mer” (eg, 167mer). A heterogeneous polyP preparation comprising 20 to 300mers was biotinylated on terminal phosphates using amine-PEG2-biotin from Pierce Chemical as described previously.24 Note that all polyP concentrations are reported in this study in terms of phosphate monomer concentration (monomer formula, NaPO3), except for Figure 3D that reports polyP polymer concentrations.
Purified FXI, FXIa, FVa, β-thrombin, corn trypsin inhibitor (CTI), mouse anti-human FXI monoclonal antibody, and FXI- or FXII-deficient plasmas were from Haematologic Technologies. α-Thrombin was from Enzyme Research Laboratories. Dextran sulfate with an average Mr 500 000 and protease-free BSA were from Calbiochem. L-Pyr-Pro-Arg-p-nitroanilide (L-2145) was from Bachem California. We made liposomes (20% phosphatidylserine, 40% phosphatidylcholine, 40% phosphatidylethanolamine [PCPSPE]; Avanti Polar Lipids) by sonication. Polybrene, benzamidine, 4-(2-aminoethyl) benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride, phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), streptavidin, theophylline, prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), thrombin receptor agonist peptide (SFLLRN-NH2), and hirudin were from Sigma-Aldrich. Biacore CM5 sensorchips were from GE Healthcare. EcPPXc, the recombinant polyP-binding domain of Escherichia coli exopolyphosphatase fused to maltose-binding protein and a His6 tag, was produced as described previously.25 Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae exopolyphosphatase fused to a His6 tag (rPPX1) was produced as described previously.26
Preparation of stimulated platelet suspensions and platelet releasates
Activated platelets and platelet releasates were prepared as follows. Fresh whole blood from normal, nonsmoking donors not on medication was collected into 0.32% sodium citrate, 2μM PGE1, and 1mM theophylline via atraumatic venipuncture. (All volunteer blood donors gave written informed consent, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, under a blood-drawing protocol approved by the University of Illinois Institutional Review Board.) Platelet-rich plasma was collected after centrifugation of blood at 37°C at 200g, after which the plasma was recentrifuged at 1500g to collect the platelets. Pelleted platelets were washed by centrifugation once with Tyrode's buffer (1 g/L d-glucose, 0.2 g/L CaCl2, 0.1 g/L MgCl2, 0.2 g/L KCl, 8 g/L NaCl, 0.05 g/L NaH2PO4, and 1 g/L NaHCO3) containing 0.32% citrate, 2μM PGE1, and 1mM theophylline, once with Tyrode's buffer containing 2μM PGE1 and 1mM theophylline, and once in Tyrode's buffer without additives. The resulting platelet pellets were resuspended at 5.3 × 106/μL (∼17-fold their concentration in whole blood) or 1.6 × 107/μL (∼ 50-fold whole blood concentration) in Tyrode's buffer and stimulated with 4μM thrombin receptor agonist peptide for 10 minutes at 37°C with agitation. In some experiments, FXI activation was analyzed in the suspension of activated platelets, whereas in other experiments FXI activation was analyzed using platelet releasates. To obtain cell-free releasate, activated platelets were pelleted by centrifugation at 2000g for 10 minutes, after which the supernatant was collected and recentrifuged at 13 000g for 10 minutes to deplete residual platelets and particles. The resulting platelet releasates were stored frozen until use. Some platelet releasate samples were boiled for 30 minutes to denature proteins before being used in FXI activation assays.
Activation of FXI
We incubated 30nM FXI and 5nM α-thrombin with either polyP, stimulated platelet suspension, platelet releasate, or dextran sulfate at 37°C in 30mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 50mM NaCl, and 0.1% BSA. In some reactions, activated platelets or platelet releasates were treated with 70 μg/mL rPPX1 for 1 hour at 37°C or preincubated with 250 μg/mL EcPPXc immediately before FXI activation assays. Timed samples (0-20 minutes) were removed and quenched by addition of polybrene (6 μg/mL final) to neutralize polyP and hirudin (0.14-0.5 U/mL final) to inactivate thrombin, after which the generated FXIa was quantified by measuring rates of L-2145 hydrolysis using a SpectraMax microplate reader (Molecular Devices). At the concentrations used, neither polyP nor polybrene affected L-2145 hydrolysis by FXIa.
FXI autoactivation reactions incubated with polyP or dextran sulfate and either 30 or 60nM FXI were conducted similarly except that they lacked α-thrombin, and only polybrene (6 μg/mL final) was used to quench the timed samples. Rates of L-2145 hydrolysis were converted to FXIa concentrations using a standard curve. Second-order rate constants (k2) for FXI autoactivation were calculated as described previously.27
For SDS-PAGE analyses of FXI autoactivation, 60nM FXI was incubated with polyP or dextran sulfate in 30mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 50mM NaCl, and 0.1% polyethylene glycol (Mr 8000). At various time points, aliquots were removed into reducing SDS sample buffer and resolved by SDS-PAGE (Bio-Rad Laboratories); proteins were visualized by silver staining.28
FXIa autolysis
We incubated 6nM FXIa with polyP preparations of varying polymer lengths (whose concentrations were adjusted to yield 3nM polymer) at 37°C in 30mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 50mM NaCl, and 0.1% BSA. Timed samples (0-2 minutes) were diluted and quenched with polybrene (6 μg/mL final), and the residual FXIa concentration was determined by quantifying the rate of L-2145 hydrolysis compared with a standard curve.
SPR analyses
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) binding studies were performed at 25°C using a Biacore 3000 instrument (Biacore). Streptavidin was bound to CM5 sensorchips by standard amine coupling; after blocking and washing, biotinylated polyP was captured on the surface. Varying concentrations of α-thrombin, β-thrombin, FXI, or FXIa in 50mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 50mM NaCl, and 0.005% surfactant P20 were flowed over the surface at 50 μL/min using a 2-minute association phase and 5-minute dissociation phase, with background subtraction using a streptavidin-coated reference cell without polyP. The running buffer for α- or β-thrombin contained 5mM benzamidine, whereas FXI and FXIa were pretreated with 4mM 4-(2-aminoethyl) benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride for 30 minutes before use to block the active sites of FXIa. Sensorchips were regenerated by washing with 1M NaCl between runs. Binding kinetics were analyzed according to the 1:1 Langmuir binding model. Kd values were calculated from the quotient of the derived dissociation (kdiss) and association (kass) rate constants.
Plasma clotting assay
Clotting times of citrated human plasma were quantified at 37°C using a STart4 coagulometer (Diagnostica Stago). Prewarmed polyP in 25mM HEPES, pH 7.4, and 1% BSA (HBA) was mixed in coagulometer cuvettes with prewarmed FXI- or FXII-deficient plasma to which CTI (100 μg/mL) and PCPSPE (60μM) had previously been added. β-thrombin in HBA was then immediately added, and the mixture was incubated for 1 minute at 37°C, after which clotting was initiated with addition of CaCl2. Final concentrations were 33% plasma, 20μM PCPSPE, 33 μg/mL CTI, 0 to 5μM polyP, 8.33mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 0.3% BSA, 12nM β-thrombin, and 8.33mM CaCl2.
Thrombin generation assay
Thrombin generation in human plasma was quantified at 37°C using a calibrated automated thrombogram (CAT) system with Thrombinoscope software (Diagnostica Stago). Prewarmed polyP in HBA in microplate wells was mixed with prewarmed FXI- or FXII-deficient plasma to which CTI (100 μg/mL), FVa (20nM), and PCPSPE (30μM) had previously been added. The FluCa reagent (containing CaCl2 and the thrombin fluorogenic substrate) was then added, and thrombin generation profiles were collected. Final concentrations included 67% plasma, 20μM PCPSPE, 13nM FVa, 67 μg/mL CTI, 0 to 50μM polyP, 8.33mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 0.17% BSA, and 20nM β-thrombin. For some control experiments, anti-FXI antibody (1 μg/mL) was preincubated with FXII-deficient plasma at 37°C for 30 minutes before use. For others, 5 μg/mL FXI was added to FXI-deficient plasma immediately after the FXI had been preincubated (at 500 μg/mL FXI in 25mM HEPES, pH 7.5) for 30 minutes with 0.5mM PMSF to abolish any contaminating FXIa activity. As an additional control, 50pM FXIa was added to FXI-deficient plasma, and the rate of thrombin generation was measured. In some samples, polyP was digested with 40 μg/mL rPPX1 for 1 hour at 37°C or preincubated with 250 μg/mL EcPPXc, before thrombin generation assays.
Results
polyP enhances FXI activation by thrombin
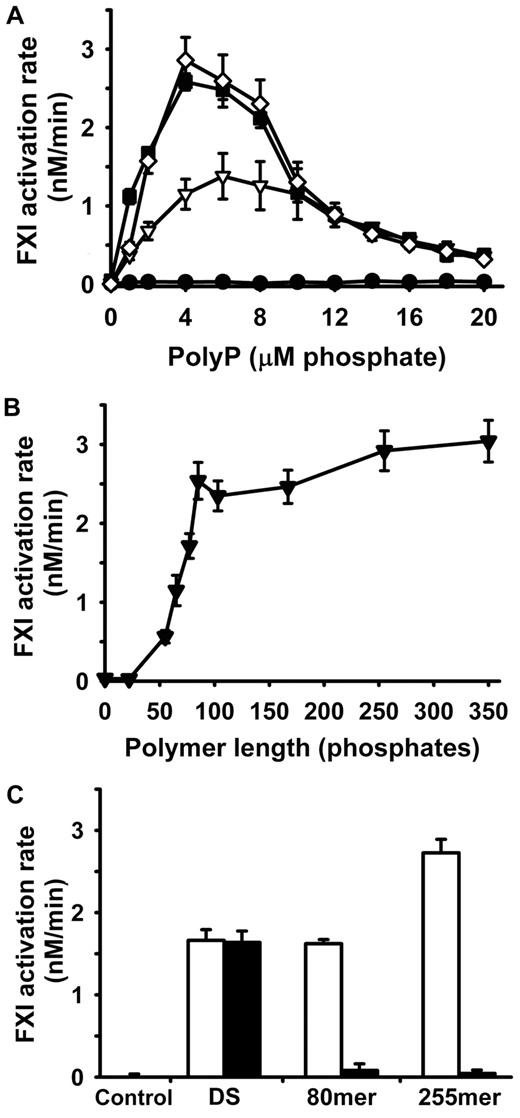
Previous studies have shown that FXI activation by thrombin is greatly accelerated in the presence of nonphysiologic polyanions such as dextran sulfate.8,9 We hypothesized that the highly anionic polymer polyP may serve as a physiologic cofactor for this reaction. Accordingly, we examined the rate of activation of 30nM FXI by 5nM α-thrombin over 20-minute time courses in the presence of varying concentrations of polyP of varying polymer lengths (Figure 1). In the absence of polyP, we observed very low rates of FXI activation, consistent with previous reports in the absence of polyanions (Figure 1A). Short-chain polyP (22mer) did not measurably stimulate FXI activation by α-thrombin at any tested polyP concentration, but longer polyP polymers (65mer, 167mer, and 350mer) strongly enhanced FXI activation in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 1A). The bell-shaped dose–response curve for polyP suggests a template mechanism in which both thrombin and FXI, or FXI and FXIa, assemble on the same polyP molecule.
polyP enhances FXI activation by α-thrombin. In all panels, initial rates of FXI activation were quantified at 37°C in reactions containing 30nM FXI, 5nM α-thrombin, and polyP or dextran sulfate. Data are mean ± SE (n = 4). (A) Concentration dependence of polyP-mediated enhancement of FXI activation by α-thrombin, tested with 4 different polyP polymer lengths: 22mer (●), 65mer (▿), 167mer (■), and 350mer (◊). (B) PolyP polymer length dependence of the enhancement of FXI activation by α-thrombin, using size-fractionated polyP preparations at 4μM phosphate (0 indicates no polyP). (C) EcPPXc abrogates the ability of polyP, but not dextran sulfate, to enhance FXI activation by α-thrombin. Rates of FXI activation were quantified in the absence (open bars) or presence (solid bars) of EcPPXc. Reaction conditions included no polyanion (control), with 1 μg/mL dextran sulfate (DS) or with 4μM polyP (80mer or 255mer, as indicated).
polyP enhances FXI activation by α-thrombin. In all panels, initial rates of FXI activation were quantified at 37°C in reactions containing 30nM FXI, 5nM α-thrombin, and polyP or dextran sulfate. Data are mean ± SE (n = 4). (A) Concentration dependence of polyP-mediated enhancement of FXI activation by α-thrombin, tested with 4 different polyP polymer lengths: 22mer (●), 65mer (▿), 167mer (■), and 350mer (◊). (B) PolyP polymer length dependence of the enhancement of FXI activation by α-thrombin, using size-fractionated polyP preparations at 4μM phosphate (0 indicates no polyP). (C) EcPPXc abrogates the ability of polyP, but not dextran sulfate, to enhance FXI activation by α-thrombin. Rates of FXI activation were quantified in the absence (open bars) or presence (solid bars) of EcPPXc. Reaction conditions included no polyanion (control), with 1 μg/mL dextran sulfate (DS) or with 4μM polyP (80mer or 255mer, as indicated).
Optimal enhancement of FXI activation occurred at 4μM polyP for the 167mer and 350mer preparations, so this polyP concentration was used to examine the relationship between polyP polymer length and enhancement of FXI activation by α-thrombin. The results (Figure 1B) show that polyP preparations with polymer lengths of more than 50 phosphate units significantly enhanced FXI activation by thrombin, with optimal rates observed with polymers that were 100mers or longer. We then compared the cofactor activity of polyP versus dextran sulfate and found that FXI activation by α-thrombin in the presence of 4μM polyP (255mer) was significantly greater than that obtained in the presence of 1 μg/mL dextran sulfate (Figure 1C). The isolated polyP-binding domain of EcPPXc has been used previously as a specific probe for localizing polyP in yeast cell walls,25,29 so we examined its ability to specifically inhibit the cofactor function of polyP. The inclusion of 30 μg/mL EcPPXc profoundly inhibited FXI activation by α-thrombin in the presence of polyP, but had no effect on FXI activation by α-thrombin in the presence of dextran sulfate (Figure 1C).
Activated platelets and platelet releasates enhance FXI activation
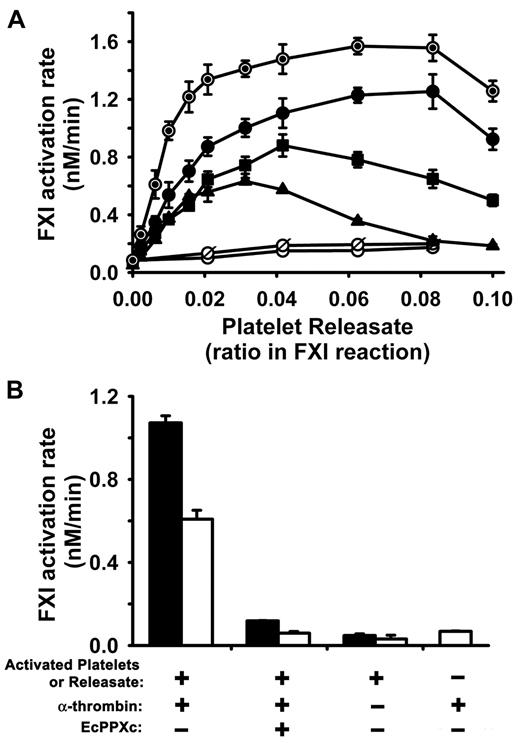
Activated human platelets secrete polyP with polymer lengths ∼ 60 to 100 phosphates,19,22 phosphate numbers that are in the size range that we found in Figure 1B would enhance FXI activation by α-thrombin. We therefore hypothesized that polyP secreted from activated platelets should serve as a cofactor for FXI activation by thrombin. Releasates from activated platelets markedly accelerated the rate of FXI activation in the presence of 5, 10, or 20nM α-thrombin (Figure 2A). In addition to polyP, activated platelets release a host of granule contents including many proteins, so we sought to determine the contribution of polyP to the ability of the platelet releasate to accelerate thrombin-mediated FXI activation. Boiling will denature almost all proteins, whereas purified polyP's cofactor activity is unaffected by boiling (data not shown), so we examined whether this cofactor effect in platelet releasates survived boiling. Figure 2A shows that boiled platelet releasates augmented thrombin-mediated FXI activation slightly better than nonboiled releasates. This increase in cofactor function may be because boiling denatures proteins in platelet releasates that might compete with thrombin and FXI for binding to polyP. In contrast, treatment of platelet releasates with EcPPXc, or digestion of releasates with rPPX1, abolished their ability to enhance FXI activation (Figure 2A), consistent with the idea that polyP secreted from activated platelets is the augmenting cofactor for FXI activation by α-thrombin.
Activated platelets and platelet releasates enhance the rate of FXI activation by α-thrombin. In all panels, initial rates of FXI activation were quantified at 37°C in reactions containing 30nM FXI, 5 to 20nM α-thrombin, and activated platelets or platelet releasate. (A) Dose response for platelet releasates from donor A in supporting FXI activation by 5nM (▴), 10nM (■), or 20nM (●) α-thrombin. Controls included boiled releasate (⊙) incubated with FXI and 20nM α-thrombin; and releasate preincubated with 250 μg/mL EcPPXc (○) or predigested with 70 μg/mL rPPX1 (ø) and then allowed to react with FXI and 20nM α-thrombin. (B) Activated platelets and releasates enhance FXI activation by thrombin. Initial rates of FXI activation by 20nM α-thrombin were quantified in the presence of 10-fold diluted platelet releasate (solid bars) or the same dilution of activated platelets plus releasate (open bars) from donor B, with or without preincubation with 250 μg/mL EcPPXc. Controls include FXI incubated with activated platelets (or releasate) from donor B but without α-thrombin, and FXI incubated with α-thrombin but without platelets or releasate. Data are mean ± SE (n = 3–4) from 2 separate donors. Platelets from donor A were activated at a concentration of 1.6 × 107/μL, whereas platelets from donor B were activated at a concentration of 5.3 × 106/μL.
Activated platelets and platelet releasates enhance the rate of FXI activation by α-thrombin. In all panels, initial rates of FXI activation were quantified at 37°C in reactions containing 30nM FXI, 5 to 20nM α-thrombin, and activated platelets or platelet releasate. (A) Dose response for platelet releasates from donor A in supporting FXI activation by 5nM (▴), 10nM (■), or 20nM (●) α-thrombin. Controls included boiled releasate (⊙) incubated with FXI and 20nM α-thrombin; and releasate preincubated with 250 μg/mL EcPPXc (○) or predigested with 70 μg/mL rPPX1 (ø) and then allowed to react with FXI and 20nM α-thrombin. (B) Activated platelets and releasates enhance FXI activation by thrombin. Initial rates of FXI activation by 20nM α-thrombin were quantified in the presence of 10-fold diluted platelet releasate (solid bars) or the same dilution of activated platelets plus releasate (open bars) from donor B, with or without preincubation with 250 μg/mL EcPPXc. Controls include FXI incubated with activated platelets (or releasate) from donor B but without α-thrombin, and FXI incubated with α-thrombin but without platelets or releasate. Data are mean ± SE (n = 3–4) from 2 separate donors. Platelets from donor A were activated at a concentration of 1.6 × 107/μL, whereas platelets from donor B were activated at a concentration of 5.3 × 106/μL.
We also investigated the effect of whole stimulated platelets (ie, activated platelets plus their releasate) in supporting FXI activation by 20nM α-thrombin. We found that whole activated platelets in suspension also strongly enhanced FXI activation by α-thrombin, although not quite as strongly as platelet releasate alone (Figure 2B). This reduction in FXI activation rate might be explained by thrombin, FXI, or FXIa binding, or a combination, to the surface of activated platelets and therefore being less available for interaction with polyP.30 Nevertheless, our results demonstrate that suspensions of stimulated whole platelets efficiently promote FXI activation by thrombin. In a control experiment, incubating EcPPXc with activated platelets or releasate decreased the rate of thrombin-mediated FXI activation to approximately the same baseline rate of FXI activation seen with thrombin but without platelets or releasate (Figure 2B). Furthermore, without added thrombin, very low rates of FXI activation were observed in the presence of platelets or releasates (Figure 2B).
polyP accelerates FXI autoactivation and FXIa autolysis
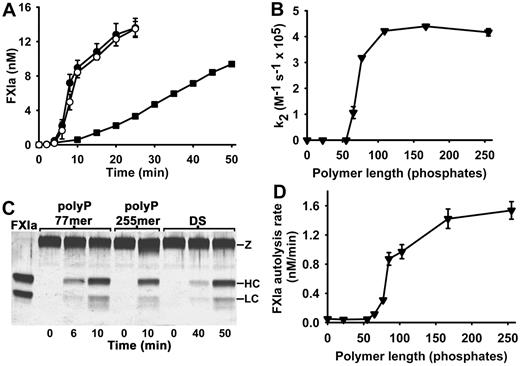
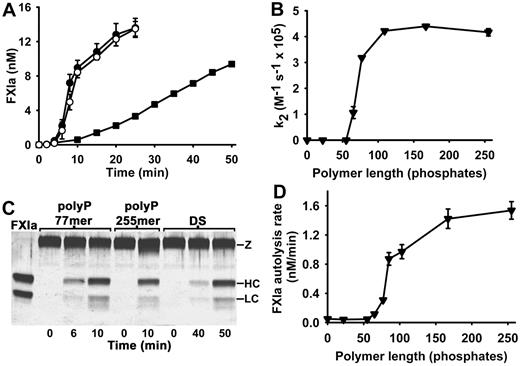
In the experiments in Figure 1, we observed essentially linear initial rates of FXI activation in the presence of polyP when we included 5nM α-thrombin as the FXI activator; however, in the absence of thrombin but in the presence of polyP, we observed sigmoidal progress curves for FXIa generation, with a substantial lag phase before FXIa was detectable (Figure 3A). This behavior is typical of FXI autoactivation (ie, FXIa-mediated FXI activation) that has been observed when purified FXI is incubated at appropriate concentrations with a variety of (typically nonphysiologic) anionic polymers.8,9,17 The experiment in Figure 3A shows that polyP (77mer or 255mer) supported more robust autoactivation of 60nM FXI than did an optimal concentration of dextran sulfate.
polyP accelerates FXI autoactivation and FXIa autolysis. (A) Progress curves of FXI autoactivation in which 60nM FXI was incubated with 4μM polyP 77mer (○), 4μM polyP 255mer (●), or 2 μg/mL dextran sulfate (■). (B) PolyP polymer length dependence of the enhancement of FXI autoactivation. Second-order rate constants for FXI autoactivation (k2) were determined in reactions containing 30nM FXI and 4μM polyP of the indicated polymer lengths (0 indicates the absence of polyP). (C) SDS-PAGE analyses of FXI autoactivation in the presence of polyP (77mer or 225mer) or DS. Parallel timed samples from the experiment in panel B were resolved on reducing SDS-PAGE and silver stained. The position of FXI (Z) and the FXIa heavy chain (HC) and light chain (LC) are indicated. The lane labeled FXIa contained purified FXIa. (D) PolyP polymer length dependence of the enhancement of FXIa autolysis. Initial rates of loss of FXIa enzymatic activity were quantified in reactions containing 6nM FXIa and polyP preparations of varying polymer lengths, whose concentrations were adjusted to yield 3nM polymer (0 indicates the absence of polyP). Data in panels A, B, and D are mean ± SE (n = 3).
polyP accelerates FXI autoactivation and FXIa autolysis. (A) Progress curves of FXI autoactivation in which 60nM FXI was incubated with 4μM polyP 77mer (○), 4μM polyP 255mer (●), or 2 μg/mL dextran sulfate (■). (B) PolyP polymer length dependence of the enhancement of FXI autoactivation. Second-order rate constants for FXI autoactivation (k2) were determined in reactions containing 30nM FXI and 4μM polyP of the indicated polymer lengths (0 indicates the absence of polyP). (C) SDS-PAGE analyses of FXI autoactivation in the presence of polyP (77mer or 225mer) or DS. Parallel timed samples from the experiment in panel B were resolved on reducing SDS-PAGE and silver stained. The position of FXI (Z) and the FXIa heavy chain (HC) and light chain (LC) are indicated. The lane labeled FXIa contained purified FXIa. (D) PolyP polymer length dependence of the enhancement of FXIa autolysis. Initial rates of loss of FXIa enzymatic activity were quantified in reactions containing 6nM FXIa and polyP preparations of varying polymer lengths, whose concentrations were adjusted to yield 3nM polymer (0 indicates the absence of polyP). Data in panels A, B, and D are mean ± SE (n = 3).
It is possible that FXI activation by thrombin in the presence of polyP actually consists of direct FXI activation by thrombin, plus FXI autoactivation once significant amounts of FXIa are generated. Therefore, we systematically examined the ability of polyP to enhance the rate of FXI autoactivation (ie, FXI activation without thrombin), and we determined the second-order rate constants for this reaction as a function of polyP polymer length. The results (Figure 3B) show that polyP polymers longer than 100mers maximally enhanced FXI autoactivation, whereas polymers in the range of 60 to 100 phosphate units in length supported FXI autoactivation but at a slower rate. FXI autoactivation was not detectable with polyP polymers shorter than 60mers or in the absence of polyP.
Parallel samples from the FXI autoactivation reaction in Figure 3A were visualized on silver-stained SDS-PAGE (Figure 3C), showing that the 80-kDa FXI zymogen was converted to the 50- and 30-kDa heavy and light chains of FXIa, as expected.8,9,16 This experiment underscores that polyP (77mer or 255mer) supported much more rapid FXI autoactivation than did dextran sulfate (Figure 3C). (When 60nM FXI was incubated in the absence of polyanions for 50 minutes, no FXIa was detectable by SDS-PAGE; data not shown.)
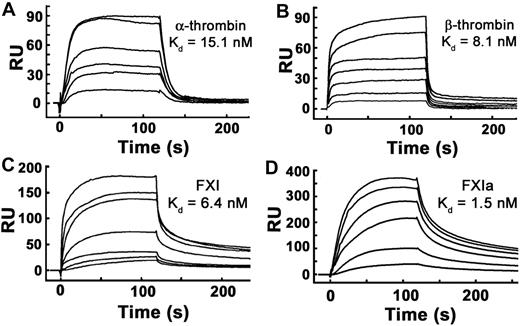
Thrombin, FXI, and FXIa bind with high affinity to immobilized polyP
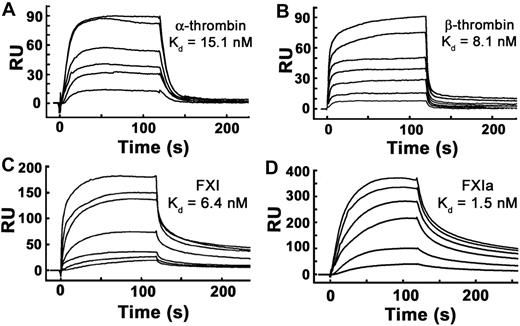
We reported previously that polyP binds α-thrombin with high affinity (Kd ∼ 5nM) when measured using SPR experiments in which thrombin was bound to the sensorchip and polyP was flowed over the surface.31 Using polyP bound to microplates, we also have reported high affinity polyP binding for α-thrombin (Kd ∼ 66 nM) and FXIa (Kd ∼ 6 nM).24 In this study, we further evaluated the binding interaction between polyP and thrombin, FXI, and FXIa using SPR in which biotinylated polyP was immobilized on sensorchips, and the proteins were flowed over the surface. FXI, FXIa, α-thrombin, and β-thrombin all bound tightly to immobilized polyP (Figure 4), yielding the following kass and kdiss rate constants and Kd values: α-thrombin, kass = 5.12 × 106 M−1 second−1, kdiss = 7.71 × 10−2 second−1, Kd = 15.1nM; β-thrombin, kass = 3.85 × 106 M−1 second−1, kdiss = 3.12 × 10−2 second−1, Kd = 8.1nM; FXI, kass = 1.64 × 106 M−1 second−1, kdiss = 1.05 × 10−2 second−1, Kd = 6.4nM; and FXIa, kass = 1.92 × 106 M−1 second−1, kdiss = 2.91 × 10−3 second−1, Kd = 1.5nM.
α-thrombin, β-thrombin, FXI, and FXIa bind with high affinity to immobilized polyP. Binding of α-thrombin, β-thrombin, FXI, or active site–inhibited FXIa to polyP was quantified using SPR, with biotinylated polyP bound to streptavidin sensorchips, over which varying protein concentrations were flowed. Panels are representative sensorgrams for 2.5 to 20nM α-thrombin (A), 5 to 80nM β-thrombin (B), 1.25 to 40nM FXI (C), and 2.5 to 20nM active site–inhibited FXIa (D). Kd values were derived as described under “Methods.”
α-thrombin, β-thrombin, FXI, and FXIa bind with high affinity to immobilized polyP. Binding of α-thrombin, β-thrombin, FXI, or active site–inhibited FXIa to polyP was quantified using SPR, with biotinylated polyP bound to streptavidin sensorchips, over which varying protein concentrations were flowed. Panels are representative sensorgrams for 2.5 to 20nM α-thrombin (A), 5 to 80nM β-thrombin (B), 1.25 to 40nM FXI (C), and 2.5 to 20nM active site–inhibited FXIa (D). Kd values were derived as described under “Methods.”
polyP can accelerate clotting of plasma and enhance thrombin generation in plasma, in a thrombin- and FXI-dependent manner
Although multiple studies have reported the activation of FXI by thrombin using purified proteins,8-12 some have questioned whether this reaction can proceed to any significant extent in plasma.13-15 We therefore examined whether polyP could accelerate the clotting of plasma in a thrombin- and factor XI-dependent manner. To eliminate interference from the activation of FXI by FXIIa, we used FXII-deficient plasma and also added CTI to inhibit any remaining traces of FXIIa that might be generated. Also, because our previous studies had shown that polyP accelerates the conversion of FV to FVa, which itself can alter the kinetics of thrombin generation,20 we supplemented the FXII-deficient plasma with 20nM FVa, to eliminate any contribution of polyP-mediated FV activation to thrombin generation. (FVa was not added to clotting assays performed with a mechanical coagulometer, because pilot studies indicated no impact of added FVa on clot times; data not shown.) And finally, because α-thrombin will promptly clot fibrinogen on its own (obfuscating any effects on FXI activation), we added β-thrombin to the FXII-deficient plasma, because β-thrombin has greatly diminished ability to clot fibrinogen but retains the ability to activate FXI.12
We performed clotting assays (in a coagulometer) using citrated FXII-deficient plasma containing CTI, to which we added β-thrombin and polyP, and then measured the time to clot formation after addition of CaCl2. Figure 5A shows that adding 22mer polyP preparations to such clotting assays does not alter the clotting time, whereas adding longer polyP polymers (65mer, 101mer, 211mer, or 445mer) shortened the clotting times in a concentration-dependent manner. (In control experiments without β-thrombin, the clotting times were all > 500 seconds; data not shown.) FXI-deficient plasma (also containing CTI) exhibited prolonged clotting times in this assay, and the clotting times were essentially unaffected by the presence of polyP 445mer (Figure 5A). These results show that polyP shortens the β-thrombin clotting time of plasma in a manner that is dependent on FXI but independent of FXII. This is consistent with the notion that thrombin activates FXI in plasma in a polyP-mediated manner.
PolyP plus β-thrombin accelerates plasma clotting and enhances thrombin generation. (A) PolyP shortens plasma clotting times triggered by β-thrombin (measured using a mechanical coagulometer). Citrated FXII- or FXI-deficient plasmas containing 100 μg/mL corn trypsin inhibitor and 20μM PCPSPE were incubated for 1 minute at 37°C with 12nM β-thrombin and varying polyP concentrations, after which CaCl2 was added and the time to clot formation was measured. PolyP tested with FXII-deficient plasma included 22mer (●), 65mer (▿), 101mer (♦), 211mer (○), or 445mer (▴). FXI-deficient plasma was tested with 445mer polyP (▵). Data are mean ± SE (n = 5). Panels B and C are mean thrombin generation (CAT) curves for FXII-deficient plasmas containing 100 μg/mL corn trypsin inhibitor, 20μM PCPSPE, and 20nM FVa (4 experiments of triplicate wells). (B) Concentration dependence of polyP's ability to enhance thrombin generation in the presence of 20nM β-thrombin and varying polyP (101mer at 0-50μM phosphate). (C) Effect of polyP polymer length on thrombin generation in the presence of 20nM β-thrombin and with or without 50μM polyP (65mer, 101mer, or 445mer). (D-H) Mean peak thrombin levels from experiments represented in panels B and C (± SE; n = 4) obtained with 20nM β-thrombin and varying polyP. (D) Peak thrombin levels in FXII-deficient plasma at the indicated concentrations of polyP 65mer (▿), 101mer (♦), or 445mer (▵). In control experiments, polyP 445mer was preincubated with 250 μg/mL EcPPXc (◊) or predigested with 40 μg/mL rPPX1 (□). (E) Peak thrombin levels in FXII-deficient plasma preincubated with anti-FXI antibody ± 50μM polyP 101mer. (F) Peak thrombin levels in FXI-deficient plasma ± 50μM polyP 101mer. (G) Peak thrombin levels in FXI-deficient plasma to which 4 μg/mL FXI had been added ± 50μM polyP 101mer. (H) Peak thrombin levels in FXI-deficient plasma to which 50pM FXIa had been added ± 50μM polyP 101mer.
PolyP plus β-thrombin accelerates plasma clotting and enhances thrombin generation. (A) PolyP shortens plasma clotting times triggered by β-thrombin (measured using a mechanical coagulometer). Citrated FXII- or FXI-deficient plasmas containing 100 μg/mL corn trypsin inhibitor and 20μM PCPSPE were incubated for 1 minute at 37°C with 12nM β-thrombin and varying polyP concentrations, after which CaCl2 was added and the time to clot formation was measured. PolyP tested with FXII-deficient plasma included 22mer (●), 65mer (▿), 101mer (♦), 211mer (○), or 445mer (▴). FXI-deficient plasma was tested with 445mer polyP (▵). Data are mean ± SE (n = 5). Panels B and C are mean thrombin generation (CAT) curves for FXII-deficient plasmas containing 100 μg/mL corn trypsin inhibitor, 20μM PCPSPE, and 20nM FVa (4 experiments of triplicate wells). (B) Concentration dependence of polyP's ability to enhance thrombin generation in the presence of 20nM β-thrombin and varying polyP (101mer at 0-50μM phosphate). (C) Effect of polyP polymer length on thrombin generation in the presence of 20nM β-thrombin and with or without 50μM polyP (65mer, 101mer, or 445mer). (D-H) Mean peak thrombin levels from experiments represented in panels B and C (± SE; n = 4) obtained with 20nM β-thrombin and varying polyP. (D) Peak thrombin levels in FXII-deficient plasma at the indicated concentrations of polyP 65mer (▿), 101mer (♦), or 445mer (▵). In control experiments, polyP 445mer was preincubated with 250 μg/mL EcPPXc (◊) or predigested with 40 μg/mL rPPX1 (□). (E) Peak thrombin levels in FXII-deficient plasma preincubated with anti-FXI antibody ± 50μM polyP 101mer. (F) Peak thrombin levels in FXI-deficient plasma ± 50μM polyP 101mer. (G) Peak thrombin levels in FXI-deficient plasma to which 4 μg/mL FXI had been added ± 50μM polyP 101mer. (H) Peak thrombin levels in FXI-deficient plasma to which 50pM FXIa had been added ± 50μM polyP 101mer.
We also used the CAT system to examine the ability of polyP to enhance thrombin-mediated thrombin generation in plasma. Figure 5B shows mean thrombin generation profiles in FXII-deficient plasma to which 20nM β-thrombin was added together with polyP (101mer). Increasing concentrations of polyP (up to 50μM) yielded increased thrombin bursts, whereas essentially no thrombin generation was observed in the presence of polyP but in the absence of β-thrombin (data not shown). In Figure 5C, we examined the ability of 50μM polyP of varying polymer lengths to enhance thrombin generation, and we found that polyP caused increased thrombin generation in a polymer size–dependent manner. Figure 5D summarizes the mean peak thrombin levels generated in experiments described in Figure 5B and C, showing that peak thrombin levels increased with polyP concentration (for the 101mer) and also showing the peak thrombin levels at 50μM polyP for the 65mer and 445mer polymers. Furthermore, treatment of polyP 445mer with either EcPPXc or rPPX1 abrogated thrombin generation (Figure 5D). Figure 5E shows that adding a blocking antibody to FXI abolished polyP-mediated thrombin generation in FXII-deficient plasma. Also, there was no observable polyP-mediated thrombin generation in FXI-deficient plasma (Figure 5F), although this was restored when purified FXI was added back to the FXI-deficient plasma (Figure 5G). Lastly, polyP did not enhance thrombin generation in FXI-deficient plasma to which FXIa was added (Figure 5H).
Discussion
Deficiencies of FXII, prekallikrein, or high-molecular-weight kininogen are not associated with bleeding tendencies, whereas individuals with severe FXI deficiency can exhibit mild-to-moderate bleeding diatheses, most particularly injury-induced bleeding in tissues with high fibrinolytic activity. This has led to the proposal that the primary role of FXI is not to participate in the initiation of blood coagulation, but to further thrombin generation, possibly for activation of thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor to protect and consolidate the clot.32-34 A body of work supports a model in which FXI is activated by thrombin, a process that is accelerated by anionic molecules and surfaces. Furthermore, previous studies have shown that FXI activation by thrombin is enhanced in the presence of activated platelets.35-37 We recently showed that polyP of the size secreted by human platelets accelerates blood clotting reactions20,21 and binds with high affinity to α-thrombin and FXIa.24,31 Taken together, these findings led us to formulate and test the hypothesis that polyP, a natural polyanion secreted by activated platelets,19,22 mediates FXI activation by α-thrombin.
Using purified proteins, we found that polyP polymers of the sizes secreted by platelets (60-100mers)—and larger—potently accelerated FXI activation by α-thrombin, possibly by a template mechanism, with polyP being more active than the nonphysiologic polyanion dextran sulfate. We also showed that polyP-mediated FXI activation by α-thrombin was specifically abrogated by EcPPXc, the isolated polyP-binding domain of E coli exopolyphosphatase, indicating that this recombinant protein may be used to interrupt the procoagulant activity of polyP. Consistent with reports of anionic polymers accelerating FXI autoactivation8,17 and autolysis,9 we found that polyP polymers more than 50 phosphate units long strongly enhanced FXI autoactivation. These results suggest that the combination of thrombin and polyP in plasma could result in the generation of additional thrombin through a combination of polyP-mediated FXI activation by thrombin and polyP-mediated FXI autoactivation.
Oliver et al demonstrated that FXII-independent activation of FXI by thrombin was augmented in the presence of activated platelets,37 whereas Wielders et al showed that thrombin initiates and augments FXI-dependent thrombin generation in platelet-rich plasma.36 To date, however, the platelet-derived cofactor for FXI activation by thrombin, and the underlying mechanism, has not been well defined. In this study, we showed that platelet releasates enhanced FXI activation by α-thrombin, an activity that was not diminished by boiling (to denature potentially confounding proteins, including platelet-derived FXI35 ), but that was abrogated by EcPPXc treatment or rPPX1 digestion. Furthermore, suspensions of activated platelets also strongly enhanced thrombin-mediated FXI activation, albeit at a rate ∼ 2-fold lower than that of platelet releasates. It is possible that binding of some of the thrombin, FXI, FXIa, or a combination, to the surface-activated platelets30 could therefore reduce their interaction with polyP and that this might explain the somewhat reduced rate of FXI activation in the presence of platelets compared with the same concentration of platelet releasate. Taken together, our findings indicate that platelet polyP may be a natural, physiologic cofactor for the activation of FXI by thrombin.
The physiologic relevance of FXI activation by thrombin in a plasma environment has been questioned.13,14,38 Some criticisms include excessively diluting the plasma in FXI-dependent clotting assays and inadvertent FXI activation by the contact system during blood drawing and isolation of plasma. We addressed these issues by using FXII-deficient plasma supplemented with CTI to greatly reduce the possibility of FXI activation by FXIIa. Thrombin generation using CAT assays in minimally diluted FXII-deficient plasma demonstrated substantial thrombin-mediated thrombin generation in the presence of polyP. This thrombin generation required FXI but not FXII.
A recent report suggests that FVa can promote FXI activation by α-thrombin.10 We did not address this question directly in the present study, but we did find that adding 20nM FVa to FXII-deficient plasma in clotting assays initiated with β-thrombin in the presence of polyP resulted in no further shortening of clotting time compared with FXII-deficient plasma not spiked with FVa (data not shown). In further studies, it will be interesting to examine whether polyP can synergize with FV or FVa to accelerate thrombin-mediated FXI activation.
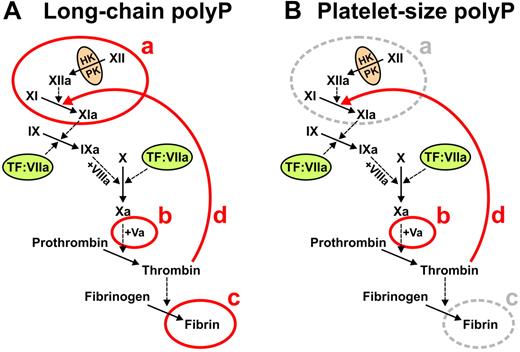
Our previous studies established that polyP acts at 3 points in the blood clotting cascade, whereas the present study adds a fourth point of action (summarized in Figure 6). Using carefully size-fractionated polyP preparations,21 we established previously that polyP of the size range that accumulates in many infectious microorganisms (ie, hundreds to thousands of phosphate units long) potently triggers the contact pathway, accelerates FV activation, and enhances fibrin polymerization (Figure 6A). In contrast, shorter polyP polymers, of the size secreted by activated human platelets (ie, 60-100mers) were far less potent than long-chain polyP in triggering contact activation or in enhancing fibrin polymerization, while retaining full ability to promote FV activation (Figure 6B).21 The present study now shows that polyP preparations of the size secreted by human platelets—as well as longer polymers—potently stimulate the activation of FXI by thrombin as well as FXI autoactivation (Figure 6B). Taken together, these findings support the notion that platelet polyP primarily functions to accelerate and enhance thrombin generation but not to trigger it. Alternatively, microbial polyP can potently trigger the blood clotting cascade via the contact pathway, together with enhancing thrombin generation and fibrin polymerization, possibly as part of the host response to pathogens.
Summary of roles of polyP in blood clotting. (A) Long-chain polyP (hundreds to thousands of phosphate units long) acts at 4 points in the clotting cascade, indicated in red: a, initiates the contact pathway of blood clotting20,21 ; b, accelerates FV activation20,21 ; c, enhances fibrin polymerization21,23 ; and d, accelerates FXI activation by thrombin (this study). (B) Platelet-size polyP (60-100mers) acts most potently at 2 points in the clotting cascade, indicated in red: b, accelerates FV activation21 ; and d, accelerates FXI activation by thrombin (this study).
Summary of roles of polyP in blood clotting. (A) Long-chain polyP (hundreds to thousands of phosphate units long) acts at 4 points in the clotting cascade, indicated in red: a, initiates the contact pathway of blood clotting20,21 ; b, accelerates FV activation20,21 ; c, enhances fibrin polymerization21,23 ; and d, accelerates FXI activation by thrombin (this study). (B) Platelet-size polyP (60-100mers) acts most potently at 2 points in the clotting cascade, indicated in red: b, accelerates FV activation21 ; and d, accelerates FXI activation by thrombin (this study).
In addition to activated platelets, various injured tissues may release polyP, because mammalian tissues have been reported to contain polyP in sizes ranging from 50mers to 800mers, with brain containing primarily very long-chain polyP (∼ 800mers).39 Interestingly, a recent study described a significant reduction in the incidence of ischemic stroke in patients with severe FXI deficiency,40 whereas another found that homozygous FXI knockout mice are protected against ischemic brain injury in an experimental stroke model.41 Our demonstration that polyP is a potent cofactor for FXI activation by thrombin offers a potentially important piece of the puzzle regarding the role of FXI in hemostasis and thrombosis.
An Inside Blood analysis of this article appears at the front of this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Florian Freimoser (ETH, Zurich, Switzerland) for providing the plasmid DNA for EcPPXc and Dr Rebecca Davis-Harrison for assistance with SPR. They also thank Dr Roberto Docampo (University of Georgia, Athens, GA) for providing rPPX1. This work was supported by grants R01 HL047014 (J.H.M.) and F30HL107089 (S.H.C.) from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health.
National Institutes of Health
Authorship
Contribution: S.H.C. and S.A.S. performed experiments and contributed figures; and S.H.C., S.A.S., and J.H.M. designed the research, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J.H.M., S.A.S., and S.H.C. are coinventors on patent applications covering potential medical uses of polyP.
Correspondence: James H. Morrissey, Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 417 Medical Sciences Bldg MC-714, 506 S. Mathews Ave, Urbana, IL 61801; e-mail: jhmorris@illinois.edu.