Abstract
Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia (CAMT) is a rare disease presenting with isolated thrombocytopenia in infancy and developing into a pancytopenia in later childhood. Thrombopoietin (TPO) is the main regulator of thrombocytopoiesis and has also been demonstrated to be an important factor in early hematopoiesis. We analyzed 9 patients with CAMT for defects in TPO production and reactivity. We found high levels of TPO in the sera of all patients. However, platelets and hematopoietic progenitor cells of patients with CAMT did not show any reactivity to TPO, as measured by testing TPO-synergism to adenosine diphosphate in platelet activation or by megakaryocyte colony assays. Flow cytometric analysis revealed absent surface expression of the TPO receptor c-Mpl in 3 of 3 patients. Sequence analysis of the c-mpl gene revealed point mutations in 8 of 8 patients: We found frameshift or nonsense mutations that are predicted to result in a complete loss of c-Mpl function in 5 patients. Heterozygous or homozygous missense mutations predicted to lead to amino acid exchanges in the extracellular domain of the receptor were found in 3 other patients. The type of mutations correlated with the clinical course of the disease. We propose a defective c-Mpl expression due to c-mpl mutations as the cause for thrombocytopenia and progression into pancytopenia seen in patients with CAMT.
Introduction
Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia (CAMT) is a rare disease characterized by a severe hypomegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia during the first years of life that develops into a pancytopenia in later childhood, suggesting a general defect in hematopoiesis.1 Bone marrow transplantation is the only curative therapy for CAMT so far.2
The pathophysiology of CAMT is not well understood. Experiments of Freedman and Estrov3 demonstrated that the cause of CAMT seems to be an intrinsic stem cell defect rather than an abnormality of the bone marrow microenvironment or an inhibitory factor in the patients' plasma. Serum levels of thrombopoietin (TPO), the pivotal regulator of megakaryopoiesis but also an important factor for early multipotential hematopoietic progenitors, are highly elevated in patients affected from CAMT.4 5
Recently, Muraoka and coworkers6 described a patient with CAMT who had a defective response to TPO in megakaryocyte colony formation, decreased numbers of erythroid and myeloid progenitors, and elevated TPO serum levels. Ihara and coworkers7 detected 2 heterozygous point mutations in the c-mpl gene of this patient that were predicted to result in a complete absence of functional c-Mpl protein.
In this report we describe a defective TPO reactivity of hematopoietic progenitor cells and platelets from 9 patients with CAMT. A lack of c-Mpl expression on the platelet surface could be demonstrated in 3 patients. Molecular sequencing of the c-mpl gene of 8 patients with CAMT revealed point mutations in all patients: We found frameshift or nonsense mutations in 5 patients belonging to a patient group with a very severe course of the disease, heterozygous or homozygous missense mutations were found in 3 other patients with a slower progression of the disease. We propose, that c-mplmutations are the cause for the amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia and the development of a pancytopenia in patients with CAMT. The type of mutations could be predictive for the course of the disease.
Patients, materials, and methods
Patients
Platelets and/or bone marrow mononuclear cells from 9 patients with CAMT were examined at different time points. All patients were found to be thrombocytopenic during the first year of life, had normal radii, and showed no or severely reduced numbers of megakaryocytes in bone marrow smears. Four of the patients are from Kurdish origin and have consanguineous parents. (Approval was obtained from the institutional review board for these studies. Informed consent was provided according to the Declaration of Helsinki.) Retrospective comparison of the clinical data from 18 patients with CAMT from different German clinics resulted in a division into 2 different groups of patients with a different time course of thrombocytopenia: About 60% of the patients presented with a more severe form of CAMT with an early development from isolated thrombocytopenia into pancytopenia (group I). A second group of patients demonstrated a transient increase of platelet counts during the first year of life and a later development of pancytopenia (group II). The patients' characteristics with the division into the 2 patient groups are described in Table1.
Patients' characteristics
| Patient identification . | Sex . | Age (y) . | BMT (age) (y) . | Patient group* . | Consanguineous parents . | WBC (nL−1) . | Hgb (g∗dL−1) . | Plt (nL−1) . | Tests performed† . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAMT-1 | F | 0.6 | I | + | 7 | ||||
| 0.3 | 7.8 | 5.6 | 20 | 2, 6 | |||||
| CAMT-6 | F | 0.8 | I | − | 7 | ||||
| 0.7 | 10.3 | 11.5 | 6 | 1, 4 | |||||
| 0.8 | 8.6 | 6.6 | PT‡ | 6 | |||||
| CAMT-7 (died after BMT) | M | 7.0 | II | − | 7 | ||||
| 1.4 | 6.8 | 11.1 | 26 | 6 | |||||
| 3.4 | 5.1 | 10.7 | 10 | 1, 2, 3, 4 | |||||
| 4.2 | 4.8 | 11.9 | 5 | 3, 4 | |||||
| 5.6 | 3.9 | 11.0 | 5 | 6 | |||||
| 6.5 | 3.6 | 9.0 | 1 | 1, 3, 4 | |||||
| CAMT-8 | M | 2.8 | II | − | |||||
| 2.2 | 12.4 | 11.1 | 14 | 1, 2, 4 | |||||
| CAMT-9 | F | 4.2 | I | + | 7 | ||||
| 2.3 | 12.4 | 11.1 | 7 | 2, 4 | |||||
| 3.0 | 8.1 | 10.1 | 8 | 1, 4, 6 | |||||
| CAMT-11 | F | — | II | − | 7 | ||||
| 7.8 | 6.5 | 13.0 | 29 | 1, 2, 4, 5 | |||||
| 9.3 | 4.6 | 12.6 | 25 | 3, 4, 5 | |||||
| CAMT-12 | M | 4.1 | II | − | 7 | ||||
| 3.7 | 8.3 | 11.7 | 7 | 1, 3, 4 | |||||
| CAMT-13 | F | 3.8 | I | + | 7 | ||||
| 1.5 | 7.0 | 9.1 | 35 | 1, 2, 4 | |||||
| CAMT-17 | F | 1.9 | I | + | 7 | ||||
| 0.8 | 8.6 | 9.8 | 13 | 6 | |||||
| 1.8 | na | na | na | 1, 2 |
| Patient identification . | Sex . | Age (y) . | BMT (age) (y) . | Patient group* . | Consanguineous parents . | WBC (nL−1) . | Hgb (g∗dL−1) . | Plt (nL−1) . | Tests performed† . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAMT-1 | F | 0.6 | I | + | 7 | ||||
| 0.3 | 7.8 | 5.6 | 20 | 2, 6 | |||||
| CAMT-6 | F | 0.8 | I | − | 7 | ||||
| 0.7 | 10.3 | 11.5 | 6 | 1, 4 | |||||
| 0.8 | 8.6 | 6.6 | PT‡ | 6 | |||||
| CAMT-7 (died after BMT) | M | 7.0 | II | − | 7 | ||||
| 1.4 | 6.8 | 11.1 | 26 | 6 | |||||
| 3.4 | 5.1 | 10.7 | 10 | 1, 2, 3, 4 | |||||
| 4.2 | 4.8 | 11.9 | 5 | 3, 4 | |||||
| 5.6 | 3.9 | 11.0 | 5 | 6 | |||||
| 6.5 | 3.6 | 9.0 | 1 | 1, 3, 4 | |||||
| CAMT-8 | M | 2.8 | II | − | |||||
| 2.2 | 12.4 | 11.1 | 14 | 1, 2, 4 | |||||
| CAMT-9 | F | 4.2 | I | + | 7 | ||||
| 2.3 | 12.4 | 11.1 | 7 | 2, 4 | |||||
| 3.0 | 8.1 | 10.1 | 8 | 1, 4, 6 | |||||
| CAMT-11 | F | — | II | − | 7 | ||||
| 7.8 | 6.5 | 13.0 | 29 | 1, 2, 4, 5 | |||||
| 9.3 | 4.6 | 12.6 | 25 | 3, 4, 5 | |||||
| CAMT-12 | M | 4.1 | II | − | 7 | ||||
| 3.7 | 8.3 | 11.7 | 7 | 1, 3, 4 | |||||
| CAMT-13 | F | 3.8 | I | + | 7 | ||||
| 1.5 | 7.0 | 9.1 | 35 | 1, 2, 4 | |||||
| CAMT-17 | F | 1.9 | I | + | 7 | ||||
| 0.8 | 8.6 | 9.8 | 13 | 6 | |||||
| 1.8 | na | na | na | 1, 2 |
BMT = bone marrow transplantation; WBC = white blood cells; Plt = platelets.
See “Patient, materials, and methods.”
Tests performed: 1. Thrombopoietin (TPO) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); 2. TPO bioassay; 3. c-Mpl expression (flow cytometry); 4. TPO reactivity (flow cytometry); 5. tyrosine phosphorylation in platelets; 6. colony assay from bone marrow mononuclear cells (BM-MNCs); 7. sequencing of c-mpl gene.
Platelet transfusion.
na: data not available.
Materials
Recombinant human (rh) TPO and the polyclonal rabbit antibody against human c-Mpl were kindly provided by Dr A. Shimosaka, Kirin Brewery (Tokyo, Japan). Amgen (Thousand Oaks, CA) provided rh granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) and rh stem cell factor (SCF). The rh granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and rh interleukin-3 (IL-3) were gifts from Behringwerke (Marburg, Germany); rh erythropoietin (EPO) was obtained from Boehringer Mannheim (Mannheim, Germany). Adenosine diphosphate, bovine pancreatic insulin, transferrin, prostaglandin E1, acetylic salicylic acid, apyrase (type VII), and bovine serum albumin were purchased from Sigma (Deisenhofen, Germany). Monoclonal antibodies against CD62P (clone CLB-Thromb/6) and CD41 (clone P2) as well as the IgG1 isotype control were purchased from Coulter-Immunotech (Hamburg, Germany), the recombinant, peroxidase-conjugated, antiphosphotyrosine antibody (RC20) was from Transduction Laboratories (Lexington, KY), the polyclonal antibody against Jak2 was from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). Cell culture media and fetal calf serum were purchased from Life Technologies (Eggenstein, Germany). Collagen solution was obtained from StemCell Technologies (Vancouver, British Columbia) and methyl cellulose (Methocel A4C) from WAK-Chemie (Bad Homburg, Germany).
Assays for colony-forming units
For detection of colony-forming unit (CFU)-GM and CFU/burst-forming unit, erythrocytes (BFU-E) we used a methyl-cellulose–based culture system. The 105 bone marrow mononuclear cells (BM-MNCs) were cultured in 1 mL of a semisolid medium containing 0.7% methyl cellulose, 30% fetal bovine serum, and 0.5 × 10−9 M 2-mercaptoethanol in Iscove's modified Dulbecco's medium (IMDM) with the hematopoietic growth factors rhG-CSF, rhGM-CSF, rhIL-3, rhSCF (all 10 ng/mL), and rhEPO (1 U/mL). The cultures were incubated at 37°C in an atmosphere of 5% CO2 and 100% humidity for 14 days. After this time, colonies consisting of more than 50 cells were classified according to their morphology and counted.
For detection of CFU-megakaryocytes (CFU-Mks), we used a serum-free,8 collagen-based culture system. The 105 BM-MNCs were cultured in a semisolid medium containing bovine serum albumin (10 mg/mL), bovine pancreatic insulin (10 μg/mL), human transferrin (iron-saturated, 200 μg/mL), 2-mercaptoethanol (0.5 × 10-9 M), collagen (1.1 mg/mL) in IMDM. Two different growth factor combinations were used: (1) rhTPO alone (50 ng/mL) and (2) rhTPO (50 ng/mL), rhIL-3 (10 ng/mL), and rhIL-6 (10 ng/mL). After 10 to 12 days of culture (37°C, 5% CO2, 100% humidity), collagen gels were dehydrated on slides and immunocytochemically stained with a primary monoclonal antibody against CD41 (clone P2) and an APAAP (alkaline phosphatase monoclonal antialkaline phosphatase) detection system. Colonies consisting of 5 or more CD41 positive cells were counted as CFU-Mk.
Thrombopoietin serum levels
Patients' sera were collected and stored at −80°C until analysis. The measurement of TPO was performed with either a commercially available capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) system (R&D systems, Abingdon, UK) or an ELISA system recently developed by Folman et al.9 Some of the samples were additionally tested in a TPO bioassay using the human c-mpl–transfected cell line 32D clone2310 as recently described.11
Flow cytometric analysis of in vitro platelet activation
TPO reactivity of platelets was tested as already described.11 In brief, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) was preincubated for 1 minute with or without rhTPO (50 ng/mL) before the platelet activator ADP (5 μM) was added. The stimulation was stopped by adding 1 mL of a formaldehyde solution (1% in phosphate-buffered saline [PBS]). Unstimulated platelets serving as a negative control were fixed immediately after preparation of PRP. After fixation for 30 minutes on ice, the samples were washed and stained for flow cytometric analysis. FITC-conjugated mAb anti-P-selectin (CD62P) as an activation-dependent marker and phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated anti-gpIIb/IIIa (CD41) as a pan-platelet marker were used for measuring platelet activation. FITC- and PE-labeled isotype control antibodies were used as controls. After staining, the platelets were analyzed in a FACScan flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, Heidelberg, Germany).
Flow cytometric analysis of c-Mpl expression on platelets
We used a polyclonal rabbit antiserum against human c-Mpl for flow cytometric detection of c-Mpl on the platelet surface. Incubation of unfixed platelets with the primary antibodies was followed by the staining with the FITC-conjugated goat-antirabbit Ig (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) and analysis on a FACScan flow cytometer.
Western blot detection of tyrosine phosphorylation in platelets
PRP was preincubated with acetyl salicylic acid (2 mM) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Prostaglandin E1 (1 μM) was added immediately before centrifugation of the platelets. The pellet was washed in a modified HEPES-Tyrode's buffer12 containing apyrase (2 U/mL). For stimulation with rhTPO (2.7 μg/mL), platelets were resuspended in a concentration of 4 to 5 × 108/μL in the same buffer supplemented with 1 mM CaCl2. The stimulation of platelets was terminated by adding one volume of 2 × concentrated sample buffer (10% glycerol, 1% SDS, 5% 2-mercaptoethanol, 50 mM Tris, pH 6.8, 10 mM EGTA, and 1 mM Na3VO4 and 0.002% bromophenol blue). After SDS-gel electrophoresis proteins were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (0.45 μm). Tyrosine phosphorylated proteins were detected with the horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated recombinant antibody RC20 using the enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) system (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Freiburg, Germany) according to the manufacturer's instructions. For immunoprecipitation, platelet stimulation was terminated by adding an equal amount of lysis buffer (15 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM EGTA, 1 mM Na3VO4, 2% Triton X-100, 1 μg/mL of each leupeptin, pepstatin A, and aprotinin, and 1 mM PMSF). The samples were incubated on ice for 30 minutes, and afterward, the debris was pelleted at 13 000g for 10 minutes at 4°C. The supernatant was precleared with protein A-agarose beads before adding the polyclonal antibody against Jak2. The antigen-antibody complex was captured by addition of protein A-agarose beads and analyzed with SDS-gel electrophoresis and Western blotting. After detection of tyrosine phosphorylation the membrane was stripped and incubated with an anti-Jak2 antibody. The following detection used a HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (swine antirabbit) and the ECL system.
DNA sequencing and mutation analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood using standard procedures. Exons 1 to 4 of c-mpl gene were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using 100 ng of template DNA, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 100 μM dNTP, and 10 pmol of each primer (exons 1-2: 5′CTGAAGGGAGGATGGGC, 5′AGGGACAGATACATGGG, exon 3: 5′GCATGGTGGCTGTGTAGG, 5′GTCTGATTCCGGGAGCTGG, exon 4: 5′GACTGTGGTACTCAGAG, 5′ GGCAAGATTGAAGGTAGG) in PCR buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, 500 mM KCl, pH 8.3). Exons 5 to 8, 11, and 12 were amplified in 1 × PCR buffer using 100 ng template DNA, 2 mM MgCl2, 0.1% Triton, 100 μM dNTP, and 10 pmol of each primer (exons 5-6: 5′TAGATTGTGAAGCTGGG, 5′CTCCCATGACACAAACC, exons 7-8: 5′GGGATTAGTCTCTGAGG, 5′CCCTGCGTAGTGAGGTC, exons 11-12: 5′CCTCCCTGCCAATCCAC, 5′GGTAGGGTAGGGAAGTT) in PCR buffer. Exons 9 and 10 were amplified by PCR using 100 ng template DNA, 3 mM MgCl2, 0.1% Triton-X 100, 20 μM dNTP, and 25 pmol of each primer (exon 9: 5′TCTTTGTGGGAATCTCCGAC, 5′AGGCGCTGTGCGGCTTTGGT, exon 10: 5′AGTAGGGGCTGGCTGGATGA, 5′GAGATCTGGGGTCACAGA) in PCR buffer. All PCRs included 1 unit Taq DNA polymerase (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) and Pfu DNA polymerase (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) in a total reaction volume of 25 μL. The PCRs were performed at 95°C for 5 minutes, followed by 35 cycles at 95°C for 1 minute, 58°C (exons 1-8, 11, 12) or 60°C (exons 9 and 10) for 1 minute, and 72°C for 1 minute, with a final extension at 72°C for 10 minutes. Direct sequencing of the purified PCR fragments was performed on a semiautomatic sequencer (LI-COR, MWG-Biotech, Ebersberg, Germany) using the Thermo Sequenase cycle sequencing kit with 7-deaza-dGTP (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Freiburg, Germany) and fluorescent c-mpl primers.
Results
Thrombopoietin serum levels
TPO serum levels were highly elevated in all patients (Table2). No correlation between serum levels and platelet counts in the patients could be observed. Sera of 7 patients were tested for TPO bioactivity, all of them supported the growth of the factor-dependent, c-mpl–transfected cell line 32D clonel 2310 (Table 2), excluding a not biologically active TPO as the cause for the thrombocytopenia.
Thrombopoietin serum levels in patients with congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia
| Patient identification . | Age (y) . | TPO serum level (pg/mL) . | TPO bioactivity . |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAMT-1 | 0.3 | nt | + |
| CAMT-6 | 0.7 | 1606* | nt |
| CAMT-7 | 3.4 | 2653† | + |
| 6.5 | 3290* | nt | |
| CAMT-8 | 2.2 | 2436* | + |
| CAMT-9 | 2.3 | nt | + |
| 3.0 | 2083* | nt | |
| CAMT-11 | 7.8 | 3226* | + |
| CAMT-12 | 3.7 | 1022* | nt |
| CAMT-13 | 1.5 | 2674† | + |
| CAMT-17 | 1.8 | 1092† | + |
| Healthy donors (mean ± SD, n = 40) | 120 ± 76 | − |
| Patient identification . | Age (y) . | TPO serum level (pg/mL) . | TPO bioactivity . |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAMT-1 | 0.3 | nt | + |
| CAMT-6 | 0.7 | 1606* | nt |
| CAMT-7 | 3.4 | 2653† | + |
| 6.5 | 3290* | nt | |
| CAMT-8 | 2.2 | 2436* | + |
| CAMT-9 | 2.3 | nt | + |
| 3.0 | 2083* | nt | |
| CAMT-11 | 7.8 | 3226* | + |
| CAMT-12 | 3.7 | 1022* | nt |
| CAMT-13 | 1.5 | 2674† | + |
| CAMT-17 | 1.8 | 1092† | + |
| Healthy donors (mean ± SD, n = 40) | 120 ± 76 | − |
nt = not tested.
Measured with R&D systems enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Measured with an ELISA system developed by Folman et al.9
Thrombopoietin reactivity of platelets
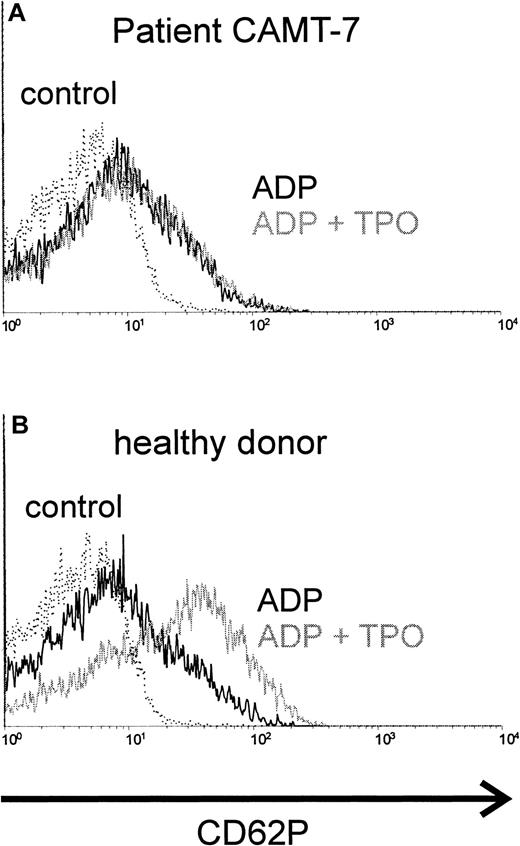
TPO synergizes with ADP in platelet activation. Preincubation with TPO enhanced the activating effect of ADP in platelets from healthy donors (Figure 1B) or from patients affected from immunologic thrombocytopenias (data not shown). In contrast, we were not able to detect any synergism between TPO and ADP (Figure 1A) in platelets from all patients with CAMT tested (10 samples from 7 patients, described in Table 1). The activation obtained with ADP alone in platelets from patients with CAMT was similar to that in healthy donors.
Costimulation of platelets with rhTPO, CAMT versus healthy control.
Platelets of patient CAMT-7 (A) and of a healthy control donor (B) were stimulated with ADP (5 μM) after preincubation with or without rhTPO (50 ng/mL). Flow cytometric analysis of platelet activation was performed using a monoclonal antibody against CD62P. CD62P expression of unstimulated platelets is shown in each histogram.
Costimulation of platelets with rhTPO, CAMT versus healthy control.
Platelets of patient CAMT-7 (A) and of a healthy control donor (B) were stimulated with ADP (5 μM) after preincubation with or without rhTPO (50 ng/mL). Flow cytometric analysis of platelet activation was performed using a monoclonal antibody against CD62P. CD62P expression of unstimulated platelets is shown in each histogram.
c-Mpl signaling in platelets of a patient with CAMT
c-Mpl is a member of the cytokine receptor superfamily and leads to tyrosine phosphorylation of cellular proteins after stimulation. We could demonstrate that stimulation of platelets from healthy donors with TPO led to phosphorylation of several proteins, the most prominent band appearing at about 95 kd (Figure2A). We were able to investigate c-Mpl signaling in platelets from patient CAMT-11, which did not show any difference in the tyrosine phosphorylation pattern before and after stimulation with TPO (Figure 2A). The protein pattern of constitutively tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins between the healthy donor and the patient was similar, with the exception of a 60 kd protein band only detectable in the patient's platelets, independent of the state of stimulation. This is most likely a consequence of a higher amount of contaminating plasma proteins in platelet preparations from thrombocytopenic patients. Subsequent analysis of TPO-dependent phosphorylation of Jak2 in platelets of patient CAMT-11 did not reveal any activation of this molecule in contrast to platelets of healthy donors, although Jak2 expression could be detected in this patient (Figure 2B).
Tyrosine phosphorylation in platelets after TPO stimulation.
Platelets of patient CAMT-11 and of a healthy donor were preincubated with 2.7 μg/mL rhTPO before lysis and Western blot analysis of tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins (A). Phosphorylation of Jak2 was proved after immunoprecipitation with anti-Jak2 and Western blot detection of tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins and Jak2 (B).
Tyrosine phosphorylation in platelets after TPO stimulation.
Platelets of patient CAMT-11 and of a healthy donor were preincubated with 2.7 μg/mL rhTPO before lysis and Western blot analysis of tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins (A). Phosphorylation of Jak2 was proved after immunoprecipitation with anti-Jak2 and Western blot detection of tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins and Jak2 (B).
Expression of c-Mpl in platelets
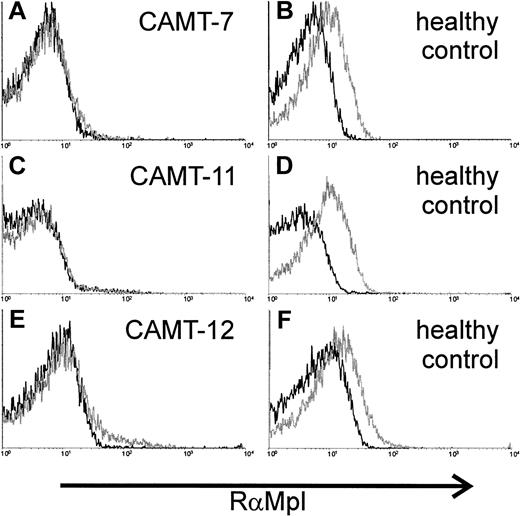
c-Mpl expression on the surface of platelets was analyzed in 3 patients. We used a polyclonal rabbit antiserum against c-Mpl. Specificity of the serum was tested with the c-mpl–transfected cell line 32D clone 23 (data not shown). The antibodies demonstrated a weak, but distinct reactivity with platelets from healthy donors (Figure3B,D,F). In contrast, we could not detect any binding of the antibody to platelets from patients with CAMT (CAMT-7, -11, -12, Figure 3A,C,E).
Expression of c-Mpl on platelets of 2 patients affected from CAMT.
Flow cytometric detection of c-Mpl expression on the surface of platelets from patients CAMT-7 (A), CAMT-11 (C), and CAMT-12 (E) using a polyclonal antiserum against human c-Mpl. Because the flow cytometric measurements were made in different laboratories under slightly different conditions, individual controls from healthy donors are shown for each patient (B,D,F).
Expression of c-Mpl on platelets of 2 patients affected from CAMT.
Flow cytometric detection of c-Mpl expression on the surface of platelets from patients CAMT-7 (A), CAMT-11 (C), and CAMT-12 (E) using a polyclonal antiserum against human c-Mpl. Because the flow cytometric measurements were made in different laboratories under slightly different conditions, individual controls from healthy donors are shown for each patient (B,D,F).
Colony-forming unit assays
Colony-forming assays were performed with bone marrow mononuclear cells of 5 patients, one of them at 2 different time points (Table3). The growth of megakaryocytic and also of myeloid and erythroid colonies was impaired in all samples.
Colony-forming unit assay
| Patient identification . | Age (y) . | CFU-GM . | CFU-E . | CFU-Mk 1* . | CFU-Mk 2† . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAMT-1 | 0.3 | 93 | 51 | 0 | 15 |
| CAMT-6 | 0.8 | 52 | 26 | 0 | 4 |
| CAMT-7 | 1.4 | 149 | 29 | 2 | 15 |
| 5.6 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| CAMT-9 | 3.0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| CAMT-17 | 0.8 | 52 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| Controls (mean ± SD, n = 5) | 168 ± 40 | 139 ± 66 | 42 ± 13 | 69 ± 23 |
| Patient identification . | Age (y) . | CFU-GM . | CFU-E . | CFU-Mk 1* . | CFU-Mk 2† . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAMT-1 | 0.3 | 93 | 51 | 0 | 15 |
| CAMT-6 | 0.8 | 52 | 26 | 0 | 4 |
| CAMT-7 | 1.4 | 149 | 29 | 2 | 15 |
| 5.6 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| CAMT-9 | 3.0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| CAMT-17 | 0.8 | 52 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| Controls (mean ± SD, n = 5) | 168 ± 40 | 139 ± 66 | 42 ± 13 | 69 ± 23 |
CFU-GM = colony-forming unit-granulocyte-macrophage; CFU-E = colony-forming unit-erythrocyte; CFU-Mk 1 = colony-forming unit-megakaryocyte 1; CFU-Mk 2 = CFU-Mk 2.
Colonies per 105 BM-MNCs; 1 with TPO alone; 2 with IL-3, IL-6, TPO.
No growth of megakaryocytic colonies with TPO as a single growth factor could be observed, with the exception of one assay in which only 2 CFU-Mks grew. In contrast, TPO induced the growth of 42 ± 23 CFU-Mks per 105 BM-MNCs from healthy controls. We observed the growth of some megakaryocytic colonies after stimulation with IL-3, IL-6, and TPO only in samples from the younger patients with CAMT (less than 2 years). There was no growth of megakaryocytic colonies from samples of 2 patients older than 3 years.
In the younger patients, we found a strongly decreased growth of erythroid and a modestly decreased growth of myeloid colonies, whereas in patients older than 3 years, an almost complete lack of nonmegakaryocytic colony growth was observed. There was no obvious difference in the colony sizes of nonmegakaryocytic colonies between healthy donors and patients with CAMT.
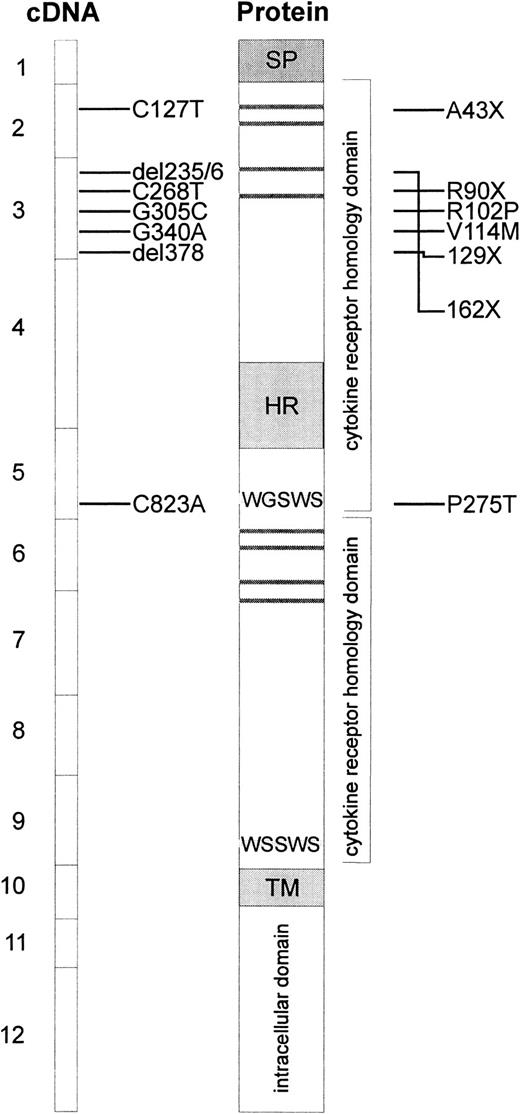
Mutation analysis
Because of the absence of TPO reactivity in cells from patients with CAMT, c-mpl was considered to be one of the candidate genes for this disorder. Therefore, sequence analysis of the entire coding region and all exon/intron boundaries in the c-mplgene was performed on genomic DNA isolated from peripheral blood cells of 8 patients with CAMT. Our studies revealed 7 different mutations in the c-mpl gene of these patients (Table4, Figure4). Five of these mutations are located in exon 3, one mutation is located in exon 5 and one in exon 2 of the c-mpl gene. The nucleotide positions refer to c-mpl-P complementary DNA (cDNA).13 In all cases in which family studies were possible, we could demonstrate that the mutations found in the patients with CAMT were inherited from their heterozygous parents (Table 4).
The c-mpl gene sequence analysis in patients with congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia
| Patient identification . | Mutation4-150 . | Exon no. . | Homozygous/heterozygous . | Predicted aa sequence4-151 . | Inherited from . | Patient group . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAMT-1 | C127T | 2 | Homo- | A43X | Not tested | I |
| CAMT-6 | C268T | 3 | Homo- | R90X | Father/mother | I |
| G340A | 3 | Homo- | V114M | Father/mother | ||
| CAMT-9 | del378 | 3 | Homo- | Frameshift: 126L WTVX | Father/mother | I |
| CAMT-13 | del235/36 | 3 | Homo- | Frameshift: change in aa 79-161, stop after 161 aa | Not tested | I |
| CAMT-17 | C127T | 2 | Homo- | A43X | Not tested | I |
| CAMT-7 | G305C | 3 | Homo- | R102P | Father/mother | II |
| CAMT-11 | C823A | 5 | Hetero- | P275T | Father | II |
| G305C | 3 | Hetero- | R102P | Mother | ||
| CAMT-12 | G305C | 3 | Homo- | R102P | Father/mother | II |
| Patient identification . | Mutation4-150 . | Exon no. . | Homozygous/heterozygous . | Predicted aa sequence4-151 . | Inherited from . | Patient group . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAMT-1 | C127T | 2 | Homo- | A43X | Not tested | I |
| CAMT-6 | C268T | 3 | Homo- | R90X | Father/mother | I |
| G340A | 3 | Homo- | V114M | Father/mother | ||
| CAMT-9 | del378 | 3 | Homo- | Frameshift: 126L WTVX | Father/mother | I |
| CAMT-13 | del235/36 | 3 | Homo- | Frameshift: change in aa 79-161, stop after 161 aa | Not tested | I |
| CAMT-17 | C127T | 2 | Homo- | A43X | Not tested | I |
| CAMT-7 | G305C | 3 | Homo- | R102P | Father/mother | II |
| CAMT-11 | C823A | 5 | Hetero- | P275T | Father | II |
| G305C | 3 | Hetero- | R102P | Mother | ||
| CAMT-12 | G305C | 3 | Homo- | R102P | Father/mother | II |
Schematic presentation of reported c-mplmutations and predicted alterations in the c-Mpl protein.
The boxes at the left side represent the exons of the coding sequence of c-mpl, mutations found in patients with CAMT are indicated with horizontal bars. The resulting alterations in the c-Mpl protein are shown at the right side. Horizontal gray bars represent the consensus pairs of cysteine residues in cytokine receptors. The signal peptide (SP), the hydrophilic insert in the first cytokine receptor domain (HR), and the transmembrane region (TM) are indicated by gray boxes.
Schematic presentation of reported c-mplmutations and predicted alterations in the c-Mpl protein.
The boxes at the left side represent the exons of the coding sequence of c-mpl, mutations found in patients with CAMT are indicated with horizontal bars. The resulting alterations in the c-Mpl protein are shown at the right side. Horizontal gray bars represent the consensus pairs of cysteine residues in cytokine receptors. The signal peptide (SP), the hydrophilic insert in the first cytokine receptor domain (HR), and the transmembrane region (TM) are indicated by gray boxes.
Patients CAMT-1 and CAMT-17 presented with a homozygous nonsense mutation in exon 2 of c-mpl gene (C127T leading to A43X). CAMT-6 is characterized by one homozygous missense mutation (G340A leading to V114M) and one homozygous nonsense mutation (C268T leading to R90X) in exon 3. Family studies revealed that this patient inherited both mutations from his father and mother who are heterozygous for both mutations. The sister of this patient displayed none of these mutations (data not shown). The homozygous deletion of thymine at cDNA nucleotide position 378 in exon 3 of c-mpl gene in patient CAMT-9 creates a frameshift and leads to a premature stop codon at amino acid position 129. The c-mpl gene of patient CAMT-13 is characterized by the homozygous delCT at nucleotide positions 235/236 of c-mpl cDNA leading to an altered amino acid sequence from position 79 until a stop after amino acid 161. The mutations found in patients CAMT-1, -6, -9, -13, and -17 are predicted to lead to a complete loss of a functional TPO receptor c-Mpl. All patients belong to the group I of patients with CAMT with a very severe form of CAMT with an early progression into pancytopenia.
Patients CAMT-7 and CAMT-12 demonstrated a homozygous G to C transversion in exon 3 of the c-mpl gene (G305C) that was inherited from their unrelated heterozygous parents and resulted in the substitution of the amino acid arginine by a proline at amino acid position 102. In patient CAMT-11, we found 2 heterozygous point mutations (C823A, G305C), both leading to amino acid exchanges (R102P, P275T) in the extracellular domain of c-Mpl. All patients with missense mutations belong to group II of patients with CAMT.
Discussion
In this study, we describe a lack of TPO reactivity of platelets and hematopoietic progenitors from patients with CAMT. This lack is due to point mutations in the c-mpl gene in all patients with CAMT tested.
Platelets of patients with CAMT did not respond to rhTPO as demonstrated by an absent synergism with the platelet-activator ADP in platelet activation. We used this experimental system for an initial screening because of the limited availability of bone marrow samples from patients. Platelets are easily available and normally express a functional TPO receptor. Measuring the effect of TPO on platelet activation has already been used as a diagnostic tool for the detection of defects in TPO reactivity.11,14,15 Because signal transduction pathways of the TPO receptor c-Mpl are essentially similar in platelets and their progenitors in the bone marrow, we assume a general defect of all c-Mpl–bearing cells in the hematopoietic system. The TPO reactivity of hematopoietic progenitors was tested in bone marrow samples from 5 patients. We were not able to detect growth of megakaryocytic colonies after stimulation with TPO as a single hematopoietic growth factor, with the exception of a very weak growth of CFU-Mks in a bone marrow sample from patient CAMT-7 at the age of 1.4 years. Examination of a later bone marrow sample from this patient (age: 5.6 years) revealed no reactivity to TPO anymore. A defective response to TPO in megakaryocyte-colony formation was described in one patient with CAMT by Muraoka et al.6
The defective response of platelets and hematopoietic progenitors to TPO was confirmed by studies on the signal transduction of c-Mpl in platelets, which are assumed to be representative for c-Mpl signal transduction in megakaryocytes and their progenitors: We observed no induction of intracellular tyrosine phosphorylations in total platelet lysates or in Jak-2 immunoprecipitates, respectively, after stimulation with TPO in patient CAMT-11.
So far, these results very much resembled those obtained with platelets from patients suffering from thrombocytopenia with absent radii (TAR) in a previous study.11 However, we could demonstrate that c-Mpl expression on TAR patients' platelets was normal,11 and others found no alterations in the c-mpl gene of TAR patients.16 These results led us to the hypothesis that a defect in c-Mpl–dependent signaling pathways is the cause for thrombocytopenia in TAR syndrome.
To analyze the TPO receptor expression in patients with CAMT, we investigated the c-Mpl protein and the genomic sequence of the c-mpl gene. We could not detect c-Mpl on the surface of the platelets from 2 patients affected from CAMT. Sequence analysis revealed point mutations in 8 of 8 patients. Homozygous deletions (CAMT-9 and -13) or nonsense mutations (CAMT-1, -6, and -17) were found in 5 patients, all of them predicted to result, if translated, in a premature terminated c-Mpl protein, which lacks a transmembrane and intracellular domain. These patients should have a complete loss of c-Mpl function. Interestingly, all these patients belong to the group I of patients with CAMT who have a more severe thrombocytopenia and reveal a more rapid progression into pancytopenia. In contrast, patients CAMT-7 and CAMT-12 who demonstrated a homozygous missense mutation, and CAMT-11 with 2 heterozygous missense mutations in the c-mpl gene belong to group II. This might correspond to a residual function of c-Mpl in these patients.
The homozygous point mutation in exon 3 of c-mpl found in patients CAMT-7 and -12 leads to an exchange of arginine 102 to proline. This substitution, which is located close to the highly conserved cysteine residues, may have an important influence on protein folding and therefore on the binding of TPO. The receptor could not be detected on platelets of patients CAMT-7 and CAMT-12 by flow cytometry using a polyclonal antiserum against the extracellular domain of the protein. However, there might be a residual signal transduction activity of c-Mpl in these patients as could be deduced from the weak reactivity to TPO in a colony assay (CAMT-7) and from the fact that these patients were clinically stable over several years before the deteriorating hematopoiesis necessitated a bone marrow transplantation.
In patient CAMT-11, we detected 2 heterozygous missense mutation in the c-mpl gene that are inherited from her heterozygous parents. This patient presented with a less severe form of CAMT, she is the only one of the patients in this report who did not show a tendency for a pancytopenia to develop so far. CAMT-11 is heterozygous for the mutation G305C, which causes a more severe course of the disease if homozygously expressed (CAMT-7, -12). We conclude that the exchange of proline to tyrosine at amino acid position 275, caused by the other heterozygous mutation found in this patient (C823A), seems to have less effect on c-Mpl function.
Mutations in the c-mpl gene in patients with CAMT have been reported by others: Ihara and coworkers7 detected 2 heterozygous point mutations in the c-mpl gene that were predicted to result in a complete lack of functional c-Mpl protein in this patient. Van den Oudenrijn et al17 reported c-mpl mutations in 4 of 5 patients with CAMT, 3 of them with 2 heterozygous mutations, one with a homozygous splice defect. In contrast to the previous reported mutations in the c-mplgene of patients with CAMT, which are evenly distributed over the c-mpl gene, we found a strong accumulation of mutations in exon 3, all mutations are located in the first cytokine receptor homology domain. The high frequency of homozygous mutations in our patients is partly due to the consanguinity in their parents (patients CAMT-9, -13, and -17). The mutation found in patients CAMT-7, -11, and -12 was reported for another patient by van den Oudenrijn et al.17 Because all these patients are unrelated and their parents are not consanguineous, this mutation seems to occur more frequently, at least in Europe.
There are some striking similarities in the phenotypes observed in patients affected from CAMT with c-Mpl–deficient mice generated by gene targeting. Disruption of the c-mpl gene in mice resulted in a specific loss of both megakaryocytes and platelets with an approximately 85% decrease in peripheral platelet counts. The remaining platelets were functionally normal.18 These observations correspond well to those made in patients with CAMT: We found very low platelet counts, as low as 5 × 109/L, and these platelets had a normal reactivity to the platelet agonists TRAP or ADP. High TPO serum levels were demonstrated in c-mpl−/− mice.18 Because TPO knock-out mice demonstrate a very similar phenotype to the c-mpl−/−,19,20 a TPO production defect could also be postulated as a cause of CAMT. However, TPO serum levels have been shown to be generally high in these patients.4,5,21 In all patients tested so far, serum TPO revealed full biologic activity.5
In addition to the lineage specific effects on megakaryocytopoiesis, there are deficiencies in other nonmegakaryocytic lineages of hematopoiesis in patients with CAMT,1,3,6 which also seem to be quite similar in c-mpl−/−mice.19,22,23 The role of TPO in early hematopoiesis has been elucidated by several investigators during the last few years. In vitro studies demonstrated that TPO supports the survival of multilineage progenitors or synergizes with other hematopoietic growth factors in expansion of these cells.24-27 Solar et al28 found a significantly better engraftment of CD34+CD38− c-Mpl+ human hematopoietic progenitor cells compared with CD34+CD38−c-Mpl− cells in transplanting SCID mice.
Although no decline in peripheral blood counts in c-mpl−/− mice has been described, the impairment of nonmegakaryocytic progenitors in c-mpl−/− mice seems to deteriorate during ontogeny: Alexander et al22 demonstrated normal growth of hematopoietic progenitors of all lineages from the fetal liver of c-mpl−/− mice (day 12 of gestation), whereas growth of myeloid and erythroid progenitors as well as that of early bipotential or multipotential progenitors from hematopoietic tissues from neonate mice was already markedly reduced. In analogy, Freedman and Estrov3 demonstrated a decline in the growth of nonmegakaryocytic progenitors and earlier multipotential progenitors during the development from isolated thrombocytopenia into aplastic anemia in serial analyses of one patients with CAMT. In accordance with these observations, we found an age-dependent decline in the growth of nonmegakaryocytic progenitors with an earlier drop in the erythroid colonies. The decline in the growth of nonmegakaryocytic progenitors precedes the drop of the corresponding mature cells in the peripheral blood and may reflect an exhaustion of early multipotential progenitors due to the lack of TPO reactivity. Interestingly, we found growth of megakaryocyte colonies from BM-MNCs from 2 younger patients with CAMT using TPO, IL-3, and IL-6, but not using TPO as a single growth factor. This observation also supports the hypothesis that only the response to TPO is affected in CAMT. Several attempts have been made to treat patients with CAMT with hematopoietic growth factors: In a clinical study with rhIL-3 in 5 patients with CAMT, Guinan and coworkers29 could demonstrate at least a short-term improvement in platelet counts, bleeding diatheses, or transfusion requirement. A subsequent study with the GM-CSF/IL-3 fusion protein PIXY321 revealed a platelet count elevation only for those patients who demonstrated a modest impairment of hematopoiesis, suggesting that the early multilineage pool, which seems to be affected from the c-mpl defect, was not yet completely exhausted in these patients.30 Two of our patients (CAMT-7 and CAMT-9) were treated with rhIL-11 (NEUMEGA). After a short decrease of bleeding symptoms, platelet counts dropped under the baseline values from before therapy, which was stopped on day 10, and more than 6 weeks were needed for a complete platelet recovery. We conclude that rhIL-11 treatment led to a transient exhaustion of the megakaryocytic progenitor cell pool as an effect of faster maturation of megakaryocytes, which is followed by a decreased platelet counts for some weeks (G. Strauss, unpublished results).
In conclusion, we propose a defective c-Mpl expression leading to a defect in the reactivity to TPO as the cause for CAMT in the majority of patients. CAMT could be considered as a model for investigating the in vivo role of TPO in human hematopoiesis. From our observations, we may offer 2 hypotheses. The first one is that TPO and c-Mpl seem to be essential for growth and maintenance of multipotential hematopoietic progenitor cells. A lack or misfunction of c-Mpl leads to an exhaustion of the early progenitor cell pool over the first years of life. The second hypothesis is that mechanisms independent of c-Mpl are responsible for the formation of multipotential progenitors in early ontogeny. The understanding of these mechanisms might provide closer insights into hematopoietic regulation and a therapeutic approach in the treatment of CAMT.
Acknowledgment
We are indebted to the patients and families who participated in this study and the referring physicians for their cooperation. We would especially like to thank the following physicians for providing us with samples from their patients: Dr Kremens (Essen), Dr Sieverts (Heidelberg), Dr Rossi (Berlin), Dr Brackmann (Detmold), Dr Spaar (Bremen), Dr Pekrun (Göttingen), Prof Dr Zintl (Jena), Dr Lassay (Aachen), and Prof Dr Rister (Koblenz).
Supported by grant We 942/5-2 from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG).
M.B. and M.G. contributed equally to this work.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Matthias Ballmaier, Abt. Pädiatrische Hämatologie und Onkologie, Medizinische Hochschule Hannover, D-30625 Hannover, Germany; e-mail: Ballmaier.Matthias@MH-Hannover.de.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal