Abstract
A retrospective analysis on chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients ≤55 years observed at a single institution was performed with the purpose of characterizing the clinical features and outcome of young CLL and of identifying patients with different prognostic features. Over the period from 1984 to 1994, 1,011 CLL patients (204 [20%] ≤55 years of age and 807 [80%] >55 years of age) were observed. At diagnosis, younger and older patients displayed a similar distribution of clinical features, except for a significantly higher male/female ratio in younger patients (2.85 v 1.29;P < .0001). Both groups showed an elevated rate of second primary cancers (8.3% v 10.7%), whereas the occurrence of Richter’s syndrome was significantly higher in younger patients (5.9% v 1.2%; P < .00001). Younger and older patients showed a similar overall median survival probability (10 years) but were characterized by a different distribution of causes of deaths: CLL unrelated deaths and second primary malignancies predominated in the older age group, whereas the direct effects of leukemia were prevalent in the younger age group. Although younger and older patients displayed a similar survival, the evaluation of the relative survival rates showed that the disease had a greater adverse effect on the expected survival probability of the younger population. Multivariate analysis showed that for young CLL patients only dynamic parameters, such as lymphocyte doubling time and other signs of active disease, were the independent factors that significantly influenced survival probability (P = .00001). A prolonged clinico-hematologic follow-up allowed us to identify two subsets of young CLL patients with a different prognostic outcome: a group of patients (40%) with long-lasting stable disease without treatment and an actuarial survival probability of 94% at 12 years from diagnosis and another group (60%) with progressive disease and a median survival probability of 5 years after therapy. For the latter patients, the therapeutic effect of innovative therapies with curative intents needs to be investigated in prospective, comparative clinical trials.
CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC leukemia (CLL) is the most common leukemia of the elderly people in the western world, with only 10% to 15% of patients diagnosed while less than 50 years of age.1,2 In the last decade, retrospective studies, mainly multicentric, have focused on patients who are 50 years old or less.2-6 Montserrat et al2 demonstrated that the clinical features of these young patients do not differ significantly from those of elderly patients and that traditional clinical factors, such as stage, blood lymphocyte count, lymphocyte doubling time (LDT), and bone marrow histology, bear the same known predictive effect on survival. However, at present, there is only limited information about the outcome of young patients after therapy. Dhodapkar et al4 reported in 39 treated young patients an overall actuarial median survival of 67 months; in patients refractory to alkylating drugs, this rate decreased to only 19 months. More recently, Seymour et al7 reported that the survival of 91 poor prognosis CLL patients ≤55 years old unresponsive to fludarabine or relapsing after fludarabine-induced remission was very low.
Although for elderly patients a traditional conservative management is a realistic and reasonable strategy, for younger patients this approach may prove unsatisfactory. Thus, there is a general agreement that young patients should deserve curative therapeutic efforts. Although purine analogues, in particular fludarabine, have proven capable of inducing a consistent proportion of complete responses (CR),8-10residual disease is generally still present even in apparent complete responders, suggesting that in most, if not all, cases the leukemic clone is not eradicated. An increasing number of autologous and allogeneic cell transplants has been attempted in younger patients with poor prognosis CLL.11-16 The limited data available appear promising, because both autologous and allogeneic transplants can effectively induce long-term disease-free survival and in some cases the molecular disappearance of the leukemic clone.16 Thus, the question that becomes relevant is which subset of young CLL patients may benefit from intensive therapeutic programs?
We report here a retrospective study performed on a series of 204 young CLL patients ≤55 years of age observed at a single institution from 1984 onwards. The upper cut-off age for the definition of young CLL patients was extended to 55 years, because this is the normally adopted limit for the inclusion of patients into intensive chemotherapeutic programs. The objective of this study was to characterize the clinical features and the outcome of young (≤55 years) CLL patients and to identify patients for whom the outcome was so poor to justify the potential toxicity of more intensive therapeutic programs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients.
Over the period from 1984 to 1994, 204 CLL patients 55 year of age or younger were observed at the Dipartimento di Biotecnologie Cellulari ed Ematologia of the University “La Sapienza” of Rome (Rome, Italy). During the same period, 807 CLL patients greater than 55 years of age were also observed, leading to an overall total of 1,011 cases included in this series. The cytomorphological and immunological diagnostic criteria recommended by the National Cancer Institute (NCI; Bethesda, MD)17 were applied to all patients included in this study. Bone marrow biopsy was performed in the majority of younger patients (170/204), and the pattern of marrow infiltration was evaluated according to the criteria suggested by Rozman et al.18 The clinical stage was defined according to Rai19 and Binet.20 The clinical and hematological features of smouldering CLL described by Montserrat et al21 were considered for stage A patients. LDT was evaluated according to the criteria proposed by Montserrat et al.22
A group of patients did not double their lymphocyte count within 12 months from diagnosis, but showed during this period other signs of active disease (AD) as defined by the NCI17 (marrow failure, high and progressive lymphocyte counts, and massive increase of nodal and/or spleen size) that required therapy. For the purpose of this study, we identified these patients as patients with AD. We evaluated the clinical and prognostic characteristics of such patients, as well as of those with an LDT of ≤12 months and >12 months.
Patients were treated in the presence of advanced stage or progressive disease according to the NCI recommendations for therapy17and independently of age. Patients with advanced stages were treated at the time of diagnosis, whereas earlier stage patients were treated only at the time of disease progression. Response to therapy was assessed according to the NCI criteria.17 One hundred twenty-three young patients and 399 old patients required treatment. The majority of young (67%) and old patients (90%) received chlorambucil associated with prednisone as first-line therapy, whereas fludarabine associated with prednisone was administered to 26% of younger patients and to 7% of older patients; different therapy schedules (CHOP, CVP, and CTX) were used in the remaining cases. A second-line therapy was administered to 52% of the younger patients and to 35% of the older patients. Fludarabine was used as second-line therapy in a similar proportion of younger (14%) and older (16%) patients.
With regard to mortality, active leukemia, associated infections, Richter’s syndrome, marrow failure, and second primary cancers were considered as CLL-related causes of death. The clinical characteristics and survival probability of the 204 younger patients were compared with those of the 807 older patients of our series.
Statistical analysis.
The corrected χ2 test was applied to compare groups. Survival curves were calculated according to Kaplan and Meier23 and compared with the log-rank test.24To evaluate the relative significance of some prognostic factors, the multiple regression model of Cox was applied.25 The set variables analyzed were as follows: age (≤55 v >55 years), sex (male v female), stage according to Rai’s classification (0 v I+II v III+IV), signs of disease progression (LDT >12 v ≤12 months v AD), bone marrow histology (nondiffuse v diffuse), and lymphocyte count (<50 × 109/L v ≤50 × 109/L).
The expected survival probability of the age- and sex-matched Italian population was calculated on the basis of the life expectancy obtained from the Italian 1986 lifetables and the relative survival rates were calculated according to the method of Ederer et al.26
RESULTS
Patients’ characteristics.
The overall proportion of young CLL patients ≤55 years of age in our series of 1,011 cases was 20% (204 patients). Eleven percent (108 patients) were ≤50 years of age and 9% (96 patients) were between 50 and 55 years of age; 93 patients (9%) were between 40 and 50 years of age, whereas 15 (1.5%) were less than 40 years of age. During the period from 1984 to 1994, a median of 20% young patients per year has been observed. The clinical features of both younger and older CLL patients are reported in Table 1. When the male (M) and female (F) distribution among younger and older patients was compared, a significantly higher M/F ratio was noted in the former group: 2.85 compared with 1.29 for older patients (P < .0001). Within young CLL patients, 74% (151/204) were males, whereas in the group greater than 55 years of age, the percentage of males decreased to 56% (454/807). An inverse correlation between M/F ratio and age was observed. Younger and older patients showed similar median values of peripheral blood lymphocytes, a similar proportion of patients with clinical signs of progressive disease (LDT and AD), and no difference in the distribution of clinical stages and bone marrow patterns of lymphocyte infiltration. Furthermore, the same proportion of smouldering CLL was observed among younger (34%) and older (33%) patients (Table 1). No differences in the above-noted parameters were recorded between patients less than 50 years of age and patients between 50 and 55 years of age.
Clinical Features of Younger and Older CLL Patients
| . | CLL ≤55 yrs . | CLL >55 yrs . | P Value . |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients | 204 | 807 | — |
| Median age in yrs (range) | 48.7 (31-55) | 66.7 (56-91) | — |
| Male/female ratio | 2.85 | 1.29 | <.0001 |
| Median no. of lymphocytes (109/L) | 29.7 | 27.6 | NS |
| Rai’s stages | |||
| 0 | 39% | 43% | |
| I-II | 52% | 45% | NS |
| III-IV | 9% | 12% | |
| Binet’s stages | |||
| A | 75% | 80% | |
| B | 17% | 11% | NS |
| C | 8% | 9% | |
| Smouldering disease | 34% | 33% | NS |
| BM histology | |||
| Nondiffuse | 74% | 72% | NS |
| Diffuse | 26% | 28% | |
| LDT | |||
| >12 mo | 54% | 59% | |
| ≤12 mo | 16% | 16% | NS |
| AD | |||
| ≤12 mo | 30% | 25% |
| . | CLL ≤55 yrs . | CLL >55 yrs . | P Value . |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients | 204 | 807 | — |
| Median age in yrs (range) | 48.7 (31-55) | 66.7 (56-91) | — |
| Male/female ratio | 2.85 | 1.29 | <.0001 |
| Median no. of lymphocytes (109/L) | 29.7 | 27.6 | NS |
| Rai’s stages | |||
| 0 | 39% | 43% | |
| I-II | 52% | 45% | NS |
| III-IV | 9% | 12% | |
| Binet’s stages | |||
| A | 75% | 80% | |
| B | 17% | 11% | NS |
| C | 8% | 9% | |
| Smouldering disease | 34% | 33% | NS |
| BM histology | |||
| Nondiffuse | 74% | 72% | NS |
| Diffuse | 26% | 28% | |
| LDT | |||
| >12 mo | 54% | 59% | |
| ≤12 mo | 16% | 16% | NS |
| AD | |||
| ≤12 mo | 30% | 25% |
Abbreviation: NS, not significant.
Treatment.
Forty percent of young patients (81) have so far not required treatment, whereas 60% of patients (123) have been treated. All advanced-stage patients were treated at diagnosis, whereas 48% (74/154) of stage A patients were treated at the time of disease progression after a median time of 23 months from diagnosis. Only 24% of young patients with smouldering features of CLL progressed and were subsequently treated. The overall response rate (complete and partial responses) to first- and to second-line therapy was 86% and 32%, respectively. Forty-nine percent of the older patients (399) required treatment. The proportion of stage A (40%) and of smouldering CLL (18%) patients that progressed and required treatment, as well as the overall response rate to first-line therapy (87%) and to second-line therapy (36%), was similar to those of the younger age group.
Second primary cancers and Richter’s syndromes.
The rate of second primary cancers within the overall series of 1,011 CLL patients was 10.2% (104): 8.3% (17) for younger patients and 10.7% (87) for older patients (P = not significant [NS]). Skin cancers were observed only in the older age group, in which they represented the most frequent type of tumor (2.1%). Other tumors recorded only among elderly patients were prostate, larynx, pancreas, and brain malignancies. Excluding the latter, the neoplasias most frequently encountered in both groups of patients were gastrointestinal, lung, kidney, bladder, and mammary cancers. Three cases of acute myeloid leukemia were observed, 2 in young patients previously treated with fludarabine and 1 in an old patient previously treated with chlorambucil. A similar overall rate of second cancers was documented among treated and untreated patients (50/522 [9.5%]v 54/489 [11%]; P = NS). Twenty-two patients (2.2%) developed Richter’s syndrome, in the form of a large-cell lymphoma in 18 cases (1.8%) and in the form of a Hodgkin’s disease in 4 (0.4%). Younger patients showed a significantly higher rate of Richter’s syndrome than did older patients (5.9% v 1.2%; P < .00001).
Survival analysis.
At the time of this analysis, 21% of patients (208) of the whole series have died: 26% within the younger patients group and 19% within the older patients group. As expected, CLL-unrelated deaths were significantly greater in older than in younger patients (P < .0001). With regard to the CLL-related causes of deaths, an overall rate of 98% for young patients and of 72% for old patients was observed (P < .0001). The distribution of the different CLL-related causes of deaths varied significantly according to age. The rate of deaths due to neoplasia was 4% in young patients and 14% in the older patients (P < .05). Conversely, the proportion of deaths considered as directly due to progressive CLL was significantly greater in younger than in older patients (85% v 49%;P < .0001; Table 2).
Causes of Death by Age
| . | Total . | ≤55 yrs . | >55 yrs . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 208/1,011 (21%) | 54/204 (26%) | 154/807 (19%) | ||
| CLL-related deaths | 164 (79%) | 53 (98%) | 111 (72%) | <.0001 |
| CLL ± infections | 122 (59%) | 46 (85%) | 76 (49%) | <.0001 |
| Infections | 19 (9%) | 5 (9%) | 14 (9%) | NS |
| Second cancers | 23 (11%) | 2 (4%) | 21 (14%) | <.05 |
| CLL-unrelated deaths | 44 (21%) | 1 (2%) | 43 (28%) | <.0001 |
| . | Total . | ≤55 yrs . | >55 yrs . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 208/1,011 (21%) | 54/204 (26%) | 154/807 (19%) | ||
| CLL-related deaths | 164 (79%) | 53 (98%) | 111 (72%) | <.0001 |
| CLL ± infections | 122 (59%) | 46 (85%) | 76 (49%) | <.0001 |
| Infections | 19 (9%) | 5 (9%) | 14 (9%) | NS |
| Second cancers | 23 (11%) | 2 (4%) | 21 (14%) | <.05 |
| CLL-unrelated deaths | 44 (21%) | 1 (2%) | 43 (28%) | <.0001 |
Abbreviation: NS, not significant.
The overall actuarial median survival from diagnosis for both groups of patients was similar (10 years). Patients less than 50 years of age and between 50 and 55 years of age displayed a similar survival trend.
Both young and old CLL patients showed a 10-year survival rate significantly lower compared with the expected survival probability of the age- and sex-matched Italian population: ≤55 years of age: controls 96.2% versus CLL 45.3%; greater than 55 years of age: controls 81.7% versus CLL 54.8%. When the relative survival rates were calculated, younger patients showed a lower relative survival rate compared with older patients (47% v 67%).
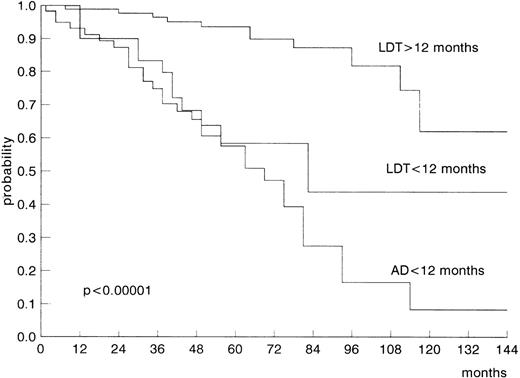
Stage according to Rai’s classification and Binet’s classification, bone marrow histology, lymphocyte count, LDT value, or the presence of AD (Fig 1) showed a significant prognostic effect on survival by univariate analysis (Table 3). Male and female young patients showed a similar survival probability. The multiple regression analysis of Cox was applied to evaluate the relative prognostic significance on survival of clinical stage (Rai’s classification), bone marrow histology, lymphocyte count, and signs of disease progression (LDT and AD). In the group of older patients, two variables emerged as independent prognostic parameters of statistical significance: stage (P < .01) and signs of disease progression (LDT and AD;P = .0001; Table 3). The same analysis performed in the group of younger patients showed that only signs of disease progression (LDT and AD) entered the modal at a highly significant level (P = .00001; Table 3). This means that, in the subset of young patients, only dynamic parameters indicative of disease progression showed a significant and independent value in predicting survival.
Significance of Prognostic Variables in Younger and Older CLL Patients
| Prognostic Variables . | P Value at Univariate (U) and Multivariate (M) Analysis . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Younger CLL Patients . | Older CLL Patients . | |||
| U . | M . | U . | M . | |
| Rai’s stage 0 v I + II v III + IV | <.00001 | NS | <.00001 | <.01 |
| BM histology: diffuse v nondiffuse | <.05 | NS | .01 | NS |
| Lymphocytes <50 v≥50 × 109/L | <.00001 | NS | <.001 | NS |
| LDT >12 mo v LDT ≤12 mo v AD ≤12 mo | <.00001 | .00001 | <.00001 | .0001 |
| Prognostic Variables . | P Value at Univariate (U) and Multivariate (M) Analysis . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Younger CLL Patients . | Older CLL Patients . | |||
| U . | M . | U . | M . | |
| Rai’s stage 0 v I + II v III + IV | <.00001 | NS | <.00001 | <.01 |
| BM histology: diffuse v nondiffuse | <.05 | NS | .01 | NS |
| Lymphocytes <50 v≥50 × 109/L | <.00001 | NS | <.001 | NS |
| LDT >12 mo v LDT ≤12 mo v AD ≤12 mo | <.00001 | .00001 | <.00001 | .0001 |
Abbreviation: NS, not significant.
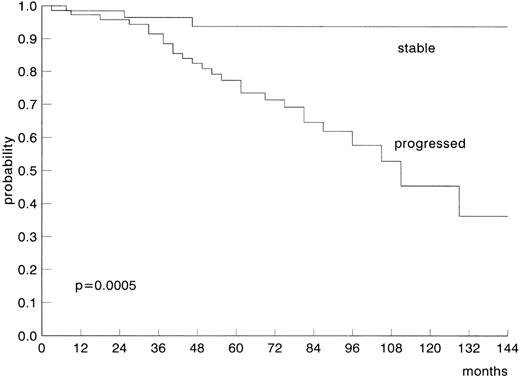
The overall median survival probability from the start of therapy for the 123 treated younger patients was lower, although not significantly, than that of the 399 treated older patients (5 v 7 years;P = .14). No significant differences were observed when all non–CLL-related causes of death were removed. The median survival probability of young patients from the start of a second-line therapy was 28 months. The projected survival probability of stable and untreated stage A patients was 94% at 12 years (Fig 2).
Projected survival probability of young stage A CLL patients according to disease status.
Projected survival probability of young stage A CLL patients according to disease status.
DISCUSSION
This study has been performed with the objective of better defining in a large series of CLL followed at a single institution the incidence of young CLL patients as well as their clinical and prognostic features. Our main purpose was to identify young CLL patients with a poor prognostic outcome who could be eligible for more aggressive therapeutic strategies. Within our overall series of 1,011 CLL, the proportion of patients ≤55 years of age was 20%. During the period from 1984 to 1994, we have observed a progressively increasing number of newly diagnosed CLL matched by a constant rate of about 20% young patients per year. As previously described,2-6 younger and older patients showed at diagnosis a similar distribution of clinical features: stage, lymphocyte count, bone marrow histology, LDT, and AD. The only unexplained difference between the two age groups was a significantly higher male/female ratio in the younger group that could be accounted for by a hypothetical protective endocrine effect in young female subjects.
The association of a second primary malignancy with CLL is well known. A recent epidemiological study performed on approximately 10,000 CLL patients reported to tumor registries participating in the NCI Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) Program27reported a significantly increased risk of developing second cancers in CLL patients, with an overall incidence of 8.7% that is similar to the one observed in the present series. Second primary cancers occurred at a not statistically different rate in both age group patients and did not appear to be influenced by the effect of previous therapy. This finding suggests that the disease-related immunodeficiency state of CLL that most likely predisposes to the development of second malignancies is independent of treatment and of age. The simultaneous occurrence of a leukemia of the elderly and of a second cancer before 55 years of age strongly suggests that some patients may have an increased risk of developing early a tumor due to individual predisposing factors. The rate of Richter’s syndrome (2.2%) recorded in our series is comparable to that reported by Robertson et al.28 Younger patients showed a Richter’s syndrome rate fivefold higher than older patients. It should be recalled that the rate of lymphomas in the old age group is possibly underestimated, because very old patients with advanced and unresponsive disease are not always submitted, for ethical reasons, to surgical biopsies.
The overall median survival probability of young patients was 10 years, which is in line with the range of median survival values for young patients included in other series.2-4,29,30 Stage, peripheral blood lymphocytes, marrow histology, LDT, and AD correlated significantly with survival in univariate analysis. However, in multivariate analysis, LDT and AD (parameters indicative of early disease progression) represented the only independent factors capable of significantly predicting survival for young CLL patients. As previously reported by us and by others,31 32 bone marrow histology lost its prognostic value when tested in multivariate analysis. Paradoxically, young age did not represent a survival advantage, because both younger and older patients showed a similar survival probability. However, causes of deaths directly related to CLL progression predominated significantly in the younger age group, and the evaluation of the relative survival rates showed a greater impact of the disease on survival in the younger than in the older age group. These findings indicate that a diagnosis of CLL implies a more adverse effect on survival in younger people than in older people.
Sixty percent of younger patients required treatment, and the majority of them have obtained a clinical response to first-line therapy. The median survival probability of younger patients from the start of first line therapy was 5 years, which is lower, although not significantly, compared with that of 7 years for the older patients. On the other hand, a substantial group of young patients (40%) with an extremely good prognostic likelihood could be identified within stage A patients with stable disease: 94% of them are projected long-term survivors at 12 years from diagnosis without treatment. Such a different outcome for patients with an apparently identical disease clearly indicates that age is not a priori a sufficient reason to treat every young CLL patient early after diagnosis. This finding suggests that, for both younger and older patients, the same therapeutic policy should be recommended: stage A patients should be treated only at the time of disease progression, whereas advanced-stage patients require treatment earlier. This is in agreement with the lack of survival advantage in the early treatment of all stage A CLL patients reported in the past33 and recently confirmed in a large randomized study.34 Cytogenetic markers, molecular abnormalities, and serologic molecules (soluble CD23 and interleukin-2 [IL-2] receptor, β2-microglobulin, etc) within large prospective studies could provide helpful prognostic information for a better identification at diagnosis of patients with stable or progressive disease.
Whereas young CLL patients with early stage disease should not be treated, young CLL patients with progressive disease have to be considered for more effective treatment programs, because the achievement of a better quality response may translate into a longer relapse-free survival duration.35-37 Despite the high activity of fludarabine, no significant advantage of this drug compared with other regimens on the long-term survival and cure of CLL has so far been recorded.36,38 However, the possibility of obtaining complete responses with little residual disease allows the design of postinduction therapies, such as stem cells autologous transplantation, monoclonal antibodies, or other biologic agents. Since the first reports of Rabinowe et al11 and Khouri et al,13 an increasing number of patients have undergone allogeneic or autologous bone marrow transplants and have been referred to the transplant registries.15,39 At the present time, there are insufficient data to establish whether transplant procedures may improve the survival of CLL patients. However, the finding of cases with long-lasting undetectable disease at the molecular level, both after allogeneic and autologous transplant, is promising.16Moreover, recent experiences indicate the feasibility of intensive therapies followed by transplant procedures also in patients greater than 50 years of age and the possibility of using autologous peripheral stem cells in young CLL patients responsive to nucleoside analogues.40 41 The poor prognosis of the younger CLL patients who require therapy should encourage to investigate the benefit of such potentially eradicative programs.
Taken together, the results of the present study indicate that, although the two age groups show similar CLL features at diagnosis and overall survival, the disease itself appears to have a more adverse effect on the expected survival of younger individuals. Two different prognostic subsets of young CLL patients could be clearly identified: a group of 40% of patients with long-lasting stable disease without treatment and a group of 60% of patients with progressive disease and low survival probability after therapy. For the latter patients, the therapeutic effect of innovative treatment modalities with curative intents needs to be investigated in prospective, comparative clinical trials.
Supported by ROMAIL (Italian Association Against Leukemia-Section of Rome) and by Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Italy-USA project on “Therapy of Tumors,” Rome, Italy.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
REFERENCES
Author notes
Address reprint requests to Francesca R. Mauro, MD, Dipartimento di Biotecnologie Cellulari ed Ematologia, University “La Sapienza,” Via Benevento, 6, 00161 Rome, Italy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal