To the Editor:
Chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection has only recently been recognized as the leading cause of mixed cryoglobulinemia.1,2 Rheumatoid factor B cells are part of the normal repertoire and significant titers of rheumatoid factors (RF) are induced during normal antiviral or antibacterial immune responses. Under the pressure of chronic antigen stimulation, RF repertoire is remodeled, and progressively includes monospecific, somatically mutated RF similar to those observed in chronic autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA).3 HCV-related proteins, genomic HCV sequences, and ongoing viral replication have been identified in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and lymph node cells from patients with type II mixed cryoglobulinemia and neoplastic lymphoproliferation.4,5 The emergence of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma has been associated to chronic HCV infection,6 7an observation that remains controversial. Here we examine whether RF activity and HCV genotype may be related to cryoglobulin clonality.
Among 965 patient sera positive for anti-HCV antibodies (Cobas Core anti-HCV EIA; Roche Diagnostic System, Basel, Switzerland), RF activity was >100 IU/mL in 60 (6.3%) (HCV group 1). As assessed by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2D-PAGE),8 cryoglobulins (>0.04 g/L) were present in 36 patients from group 1 (median protein concentration 0.12 g/L) and in 8 of 59 randomly selected patients with RF activity <100 IU/mL (HCV group 2, median protein concentration 0.06 g/L, group 1 vgroup 2 P < .0001). HCV reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) (Amplicor-HCV; Roche Molecular Systems, Branchburg, NJ) was positive in 56 patients (93.3%) from group 1, and in 46 (78%) from group 2. These results indicated that RF activity >100 IU/mL closely correlated with positive RT-PCR and was a good indicator of the probability to isolate a cryoglobulin. However, there was no strict correlation between absolute RF activity and the amount of cryoglobulin isolated from individual samples.
Among 82 patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection (Cobas Core EIA; Roche Diagnostic System), RF activity was >100 IU/mL in 11 (13.4%). Cryoglobulins were found positive in only two of these sera (18.2%), a strikingly lower proportion than in HCV patients from group 1 (60%, P = .019). This did not reflect a lower RF activity in HBV patients because median RF activity was 165 IU/mL versus 161 IU/mL in HCV group 1. The association of a cryoglobulin with HCV rather than with HBV infection was thus clearly confirmed9 and suggested that HCV itself and/or the immune response to HCV may play a critical role in the generation of cryoglobulins.
According to Brouet’s classification (modified as described8), among 36 cryoglobulins from HCV sera group 1 (RF activity > 100 IU/mL), 4 belonged to type II (monoclonal), 10 to type II-III (oligoclonal), and 22 to type III (polyclonal) (Table1 and Fig 1). There was no significant difference in median protein concentration between cryoglobulins type II/II-III and type III (0.15 g/Lv 0.11 g/L, P = .28). Cryoprecipitates (<0.04 g/L) isolated from cryoglobulin-negative HCV sera were all type III. In contrast to cryoglobulins isolated from patients with chronic HBV infection or with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with RF activity >100 IU/mL, or from HCV group 2 patients (RF activity <100 IU/mL), analysis of cryoglobulins from group 1 HCV patients indicated a strong trend toward cryoglobulins with monoclonal (type II) or oligoclonal (type II-III) IgM component (HCV sera RF > 100 vRF < 100: Fisher’s exact test, two-sided Pvalue = .0022).
Cryoglobulin Characterization
| Sera . | Cryoglobulin Type . | No Cryoglobulin . | Total . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II . | II-III-150 . | III . | |||
| HCV | |||||
| RF > 100 | 4 | 10 | 22 | 24 | 60 |
| RF < 100 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 51 | 59 |
| HBV | |||||
| RF > 100 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 11 |
| RA | |||||
| RF > 100 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 5 | 17 |
| Sera . | Cryoglobulin Type . | No Cryoglobulin . | Total . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II . | II-III-150 . | III . | |||
| HCV | |||||
| RF > 100 | 4 | 10 | 22 | 24 | 60 |
| RF < 100 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 51 | 59 |
| HBV | |||||
| RF > 100 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 11 |
| RA | |||||
| RF > 100 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 5 | 17 |
Abbreviations: RA, rhumatoid arthritis; RF, rheumatoid factor activity (IU/mL).
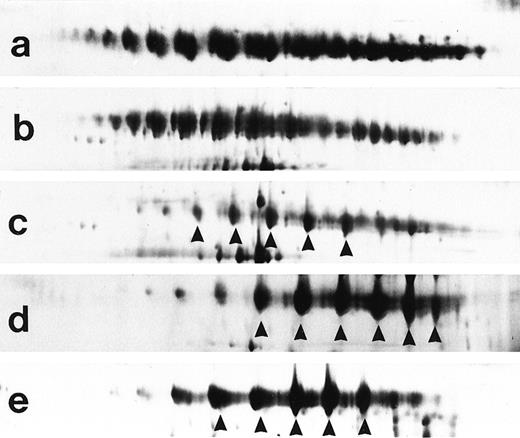
Type II-III is characterized by the presence of an IgM oligoclonal pattern associated with polyclonal Ig. This type of cryoglobulin can be considered as a transition between cryoglobulins type II and III.
Representative examples of type III (a and b), type II-III (c), and type II cryoglobulins (d and e). Type II and II-III cryoglobulins are characterized by a dominant clonal IgM component (arrows).
Representative examples of type III (a and b), type II-III (c), and type II cryoglobulins (d and e). Type II and II-III cryoglobulins are characterized by a dominant clonal IgM component (arrows).
HCV genotypes (Inno-LiPA HCV II; Innogenetics, Zwijndrecht, Belgium) were determined in sera with cryoglobulins from group 1 and compared with HCV genotype of cryoglobulin negative sera. Genotype 1b (15 of 36 cases, 41.7%) predominated in sera with cryoglobulins and was present in only 6 of 24 cryoglobulin-negative sera (25%), although without reaching significance (Table 2). Conversely, genotype 3a was predominant in cryoglobulin-negative sera (41.2%). There was no selection bias because global HCV genotype distribution in group 1 compared with that of an unselected group of patients from the same area (n = 263) was similar (genotype 1b: 35%v 29.7%, genotype 2a: 33% v34%10). Moreover, whereas type III cryoglobulins were associated with genotype 3a, genotype 1b was significantly more frequently found in cryoglobulins with a monoclonal or oligoclonal IgM component (type II or II-III) (Fisher’s exact test, two-sidedP value = .02).
HCV Genotypes in Sera From HCV Patient Group 1 (RF activity >100 IU/mL) With and Without Cryoglobulins
| . | HCV Genotype . | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n . | 1a . | 1b . | 2a . | 3a . | 4 . | Undetermined . | |
| Cryoglobulin type* | |||||||
| II | 4 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| II-III | 10 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| III | 22 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 9 | 2 | 3 |
| Total | 36 | 1 (2.8%) | 15 (42%) | 3 (8.4%) | 11 (30.1%) | 2 (5.6%) | 4 (11.1%) |
| No cryoglobulin | 24 | 1 (4.2%) | 6 (25%) | 3 (12.5%) | 10 (41.2%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (16.7%) |
| . | HCV Genotype . | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n . | 1a . | 1b . | 2a . | 3a . | 4 . | Undetermined . | |
| Cryoglobulin type* | |||||||
| II | 4 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| II-III | 10 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| III | 22 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 9 | 2 | 3 |
| Total | 36 | 1 (2.8%) | 15 (42%) | 3 (8.4%) | 11 (30.1%) | 2 (5.6%) | 4 (11.1%) |
| No cryoglobulin | 24 | 1 (4.2%) | 6 (25%) | 3 (12.5%) | 10 (41.2%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (16.7%) |
*As analyzed by 2D-PAGE.
Taken together, we here confirm the strong association between cryoglobulins and chronic HCV infection.1 Furthermore, our results support an association between high RF activity, HCV viral replication, and selection of monoclonal or oligoclonal RF secreting B cells, observations that may be representative of enhanced and/or long duration immune pressure in response to chronic HCV infection with subsequent selection of RF secreting B cells.3 Prospective studies with longitudinal cryoglobulin analysis will be necessary to ensure this hypothesis. Genotype 1b was overrepresented in HCV group 1 cryoglobulins. This did not result from a selection bias because the overall distribution of HCV genotypes in group 1 patients was very close to the prevalence of HCV genotypes in an unselected and contemporary group of patients with HCV infection from the same area.10 Furthermore, HCV genotype 1b was associated with monoclonal or oligoclonal cryoglobulin types (P = .02), whereas genotype 3a (the most frequent genotype in cryoglobulin negative sera from group 1) was associated with type III cryoglobulins. Our findings are not in agreement with those of a study in which an association between cryoglobulins and genotype 2a/III was found,11 nor with those of another study in which an association between cryoglobulins, type of cryoglobulins, and HCV genotype was lacking.12These discrepancies may be related to a geographical heterogeneity possibly related to genetic and environmental cofactors. However, in an unselected series of HCV patients, genotype 1 (1a and 1b) was shown to predominate (75%) in sera associated with blood transmitted HCV infection and a longer duration of infection.13 In our patients there was no particular selection bias in favor of blood-transmitted infection, which may explain the predominance of type 1b HCV in cryoglobulins. In contrast, the association of type 1 HCV with long duration of infection may be a factor favoring immune selection of oligoclonal or monoclonal RF.3 The respective role of immune response and HCV itself in their potential link to non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma will have to be further analyzed.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal